Abstract
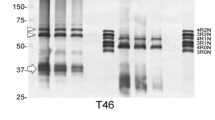
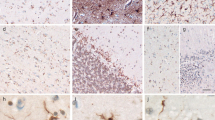
A 74-year-old woman with corticobasal degeneration (CBD) had a 9-year history of progressive loss of strength and rigidity of her right hand and then arm, followed by speech difficulties, dyskinesia, rigidity, spasticity and weakness of the ipsilateral lower limb, ultimately also involving the apposite side. She later developed supranuclear gaze palsy. Her memory remained intact during most of the duration of her disease. Laboratory tests and anti-Parkinsonian medications were not helpful. At autopsy, frontal lobe atrophy, discoloration of putamen (Pt) and pallor of substantia nigra (Sn) were observed. Neuronal loss and gliosis were extensive in motor cortex and milder in frontal cortex, abruptly ending at the central sulcus and junction of cingulate gyrus. “Achromatic” neurons were present. Neuronal loss and gliosis were seen in Pt and Sn and corticobasal inclusions in Sn. Numerous Gallyas/tau-positive, Bielschowsky/ubiquitin-negative coil, sickle, or coma-shaped tangles and thread-like processes were found in affected cortex, Pt and Sn. Some of the tangles were in neurons, but most occurred in astroglia, and their processes. The presence of Gallyas/tau-positive glia in CBD may have the same diagnostic significance as in progressive supranuclear palsy, analogous to the argyrophilic ubiquinated inclusions in oligodendroglia in multisystem atrophy. We suggest that in CBD: (1) cytoskeletal protein metabolism in neurons and glia can simultaneously be perturbed in certain neurodegenerative diseases, and (2) the astrocytosis in CBD may not be simply a reactive process but an integral part of the disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akashi T, Arima K, Maruyama N, Ando S, Inose T (1989) Severe cerebral atrophy in progressive supranuclear palsy: a case report. Clin Neuropathol 8: 195–199
Bancher C, Lassmann H, Budka H, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Wiche G, Seitelberger F, Wisniewski HM (1989) Neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy: antigenic similarities and differences. Microtubule-associated protein tau antigenicity is prominent in all types of tangles. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 74: 39–46
Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital (1985) Case 38-1985. N Engl J Med 318: 739–748
Costa C, Duyckaerts C, Cervera P, Hauw JJ (1992) Les inclusions oligodendrogliales, un marqueur des atrophies multisystematisées. Rev Neurol (Paris) 148: 274–280
Dickson DW, Ksiezak-Reding H, Liu WK, Davies P, Crowe A, Yen SH (1992) Immunocytochemistry of neurofibrillary tangles with antibodies to subregions of tau protein: identification of hidden and cleaved tau epitopes and a new phosphorylation site. Acta Neuropathol 84: 596–605
Duvoisin RC (1992) Clinical diagnosis. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progresive supranuclear palsy: clinical and research approaches. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 15–33
Feigin I, Naoumenko J (1976) Some chemical principles applicable to some silver and gold staining methods for neuropathological studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 35: 495–507
Gallyas F (1971) Silver staining of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary changes by means of physical development. Acta Morphol Acad Sci Hung 19: 1–8
Gibb WRG, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD (1989) Corticobasal degeneration. Brain 112: 1171–1192
Gibb WRG, Luthert PJ, Marsden CD (1990) Clinical and pathological features of corticobasal degeneration. Parkinson's disease: anatomy, pathology and therapy. Adv Neurol 53: 51–54
Hauw JJ, Verny M, Delaere P, Cervera P, He Y, Duyckaerts C (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Basic differences with Alzheimer's disease and aging. Neurosci Lett 119: 182–186
Hof PR, Delacourte A, Bouras C (1992) Distribution of cortical neurofibrillary tangles in progressive supranuclear palsy: a quantitative analysis of six cases. Acta Neuropathol 84: 45–51
Hirano A, Malamud N, Kurland LT (1961) Parkinsonism-dementia complex, an endemic disease on the island of Guam. II. Pathological features. Brain 84: 662–679
Horoupian DS (1992) Oligodendroglial and neuronal cytoplasmic inclusions in multisystem atrophy. Progr Brain Res 94: 423–428
Horoupian DS, Dickson DW (1991) Striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and “atypical Pick's disease”. Acta Neuropathol 81: 287–295
Horoupian DS, Thal L, Katzman R, Terry RD, Davies P, Hirano A, DeTeresa R, Fuld PA, Petito C, Blass J, Ellis JM (1984) Dementia and motor neuron disease: morphometric, biochemical and Golgi studies. Ann Neurol 16: 305–313
Ishino H, Otsuki S (1976) Frequency of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles in cerebral cortex in progressive supranuclear palsy (subcortical argyrophilic dystrophy). J Neurol Sci 28: 309–316
Jellinger KA, Bancher C (1992) Neuropathology. In: Litvan I, Agid Y (eds) Progressive supranuclear palsy, clinical and research approaches. Oxford University Press, New York, pp 44–88
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinicopathological and biochemical studies. J Neurol Transm [Suppl] 16: 111–128
Lippa CF, Smith TW, Fontneau N (1990) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. A clinicopathologic study of two cases. J Neurol Sci 98: 301–310
Mitsuyama Y (1984) Presenile dementia with motor neuron disease in Japan: clinico-pathological review of 26 cases. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47: 953–959
Miyazono M, Iwaki T, Kitamoto T, Shin RW, Fukui M, Tateishi J (1993) Widespread distribution of tau in the astrocytic elements of glial tumors. Acta Neuropathol 86: 236–241
Nishimura M, Namba Y, Ikeda K, Oda M (1992) Glial fibrillary tangles with straight tubules in the brains of patients with progressive supranuclear palsy. Neurosci Lett 143: 35–38
Noteworthy Brains (1992) Alzheimer's disease with relative hippocampal sparing. In: Clark A (ed) A newsletter from CERAD Neuropathology task force, vol 2
Nukina N, Quan Y, Nakano I, Otomo E (1992) Widespread tau abnormality in a case of corticobasal degeneration. Clin Neurol 32: 1093–1101
Papp MI, Kahn JE, Lantos PL (1989) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome). J Neurol Sci 94: 79–100
Paulus W, Selim M (1990) Corticonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia and basal neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol 81: 89–94
Probst A, Langui D, Lautenschlager C, Ulrich J, Brion JP, Anderton DH (1988) Progressive supranuclear palsy: extensive neuropil threads in addition to neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol 77: 61–68
Rebeiz JJ, Kolodny EH, Richardson EP (1968) Corticodentatonigral degeneration with neuronal achromasia. Arch Neurol 18: 20–33
Thompson PD, Marsden CD (1992) Corticobasal degeneration. Baillieres Clin Neurol 1: 677–686
Vacca LL (1985) Laboratory manual of histochemistry. Raven Press, New York, pp 385–387
Watts RL, Williams RS, Growdon JD, Young RR, Haley EC, Beal MF (1985) Corticobasal ganglionic degeneration. Neurology 35 [Suppl 1]: 178
Yamada T, McGreer PL, McGreer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, tau positive glia in patients with progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissue. Neurosci Lett 135: 99–102
Yamada T, Calne DB, Akiyama H, McGreer EG, McGreer PL (1993) Further observations on tau-positive glia in the brains with progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 85: 308–315
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horoupian, D.S., Chu, P.L. Unusual case of corticobasal degeneration with tau/Gallyas-positive neuronal and glial tangles. Acta Neuropathol 88, 592–598 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296499
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00296499