Abstract
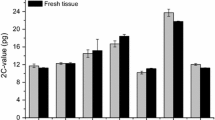
Cellular DNA content (2 C-value) was measured by fluorescence flow cytometry of chromomycin-A3 stained spleen cells in 2 subgenera, 5 species, and 21 subspecies of pocket gophers (genus Thomomys). The data indicate that, in Thomomys: (1) interspecific variation is extensive but, while some congeneric species differ by as much as 230%, others are identical in C-value; (2) intraspecific differentiation can be extensive with C-values differing by as much as 35%; and (3) populations of the same subspecies with apparently similar karyotypes can differ significantly in C-value. The implications of these results for hypotheses of the “adaptive” significance of C-value variation and genome evolution are discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bachmann, K., Goin, O.B., Goin, C.J.: Nuclear DNA amounts in vertebrates. In: Evolution of genetic systems (H.H. Smith, ed.). New York: Gordon and Breach, 1972
Bennett, M.D.: Nuclear DNA content and minimum mitotic time in herbaceous plants. Proc. roy. Soc. Lond. Ser. B. 181, 109–135 (1972)
Bennett, M.D., Smith, J.B.: Nuclear DNA amounts in angiosperms. Phil. Trans. roy. Soc. Lond. Ser. B 2274, 227 (1976)
Bostock, C.J., Gosden, J.R., Mitchell, A.R.: Localization of a male-specific DNA fragment to a sub-region of the human Y chromosome. Nature (Lond.) 272, 324–328 (1978)
Callis, J., Hoehn, H.: Flow-fluorometric diagnosis of euploid and aneuploid human lymphocytes. Am. J. Human Genet. 28, 577–584 (1976)
Cavalier-Smith, T.: Nuclear volume control by nucleoskeleton DNA, selection for cell volume and cell growth rate, and solution of the C-value paradox. J. Cell Sci. 34, 247–278 (1978)
Comings, D.E., Avelino, E.: DNA loss during Robertsonian fusion studies of the tobacco mouse. Nature (Lond.) New Biol. 237, 199 (1972)
Crissman, H.A., Tobey, R.A.: Cell cycle analysis in 20 minutes. Science 184, 1297–1298 (1974)
Crissman, H.A., Oka, M.S., Steinkamp, J.A.: Rapid staining methods for analysis of deoxyribonucleis acid and protein in mammalian cells. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 24, 64–71 (1976)
Crissman, H.A., Stevenson, A.P., Kissane, R.J., Tobey, R.A.: Techniques for quantitative staining of cellular DNA for flor cytometric analysis. In: Flow sytometry and sorting (M.R. Melamed et al., eds.) New York: John Wiley and Sons, Inc. (1979)
Dean, P., Jett, J.H.: Mathematical analysis of DNA distributions derived from flow microfluorometry. J. Cell Biol. 60 523–532 (1974)
Deaven, L.L., Vidal-Rioja, L., Jett, J.H., Hsu, T.C.: Chromosomes of Peromyscus (Rodentia, Cricetidae). VI. Genomic size. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 19, 241–249 (1977)
Doolittle, W.F., Sapienza, C.: Selfish genes, the phenotype paradigm and genome evolution. Nature (Lond.) 284, 601–603 (1980)
Dover, G.: Ignorant DNA? Nature (Lond.) 285, 618–619 (1981)
Goin, O.B., Goin, C.J., Bachmann, K.: DNA and amphibian life history. Copeia 1968
Gosden, J.R., Lowrie, S.S., Cooke, H.J.: 1981. A cloned repeated DNA sequence in human chromosome heteromorphisms. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29, 32–39 (1981)
Hatch, F.T., Bodner, A.J., Mazrimas, J.A.: Satellite DNA and cytogenetic evolution. Chromosoma (Berl.) 58, 155–168 (1976)
Hinegardner, P.: Evolution of genome size. In: Molecular evolution (F.J. Ayala, ed.). Sunderland (Mass.): Sinauer Press (1976)
Hutchinson, J., Narayan, R.K.J., Rees, H.: Constraints on the composition of supplementary DNA. Chromosoma (Berl.) 78, 137–145 (1980)
Jensen, R.H.: Chromomycin A3 as a fluorescent probe for flor cytometry of human gynecological samples. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 25, 573–579 (1977)
Keyl, H.G.: A demonstrable local and geometric increase in the chromosomal DNA of Chironomus. Experientia (Basel) 21, 191–193 (1965)
Kurnitt, D.M.: Satellite DNA and heterochromatin variants: the case for unequal mitotic crossover. Human Genet. 47, 169–186 (1979)
Lewin, B.: Gene expression 2. Eukaryotic chromosomes. New York: John Wiley and Sons Inc. 1980
Manfredi-Romanini, M.G.M., Minazza, E., Capanna, E.: DNA nuclear content in lymphocytes from Mus musculus L. and Mus poschiavinus (Fatio). Boll. Zool. 38, 321–326 (1971)
Mayr, E.: Animal Species and Evolution. Cambridge (Mass.): Belknap Press, 1963
Mendelsohn, M.L.: The attributes and applications of flow cytometry. Flow cytometry 4, 15–27 (1980)
Mizuno, S., Macgregor, H.C.: Chromosomes, DNA sequences and evolution in salamanders of the genus Plethodon. Chromosoma (Berl.) 48, 239–296 (1974)
Morescalchi, A.: Phylogenetic aspects of karyological evidence. In: Major patterns in vertebrate evolution (M.K. Hecht, P.C. Goody, and B.M. Hecht, eds.). New York: Plenum Press 1977
Nagl, W., Ehrendorfer, F.: DNA content, heterochromatin, mitotic index and growth in perennial and annual Anthemedia (Asteraceae). Plant Syst. Evol. 123, 35–54 (1974)
Ohno, S.: So much “junk” DNA in our genome. Brookhaven Symp. Biol. 23, 366–370 (1972)
Olmo, E., Morescalchi, A.: Evolution of the genome and cell sizes in salamanders. Experientia (Basel) 31, 804–806 (1975)
Patton, J.L.: Karyotypic variation following an elevational gradient in the pocket gopher, Thomomys bottae grahamensis Goldman. Chromosoma (Berl.) 31, 41–50 (1970)
Patton, J.L.: Patterns of geographic variation in karyotype in the pocket gopher, Thomomys bottae (Eydoux and Gervais). Evolution (Lawrence, Kansas) 26, 574–586 (1972)
Patton, J.L.: An analysis of natural hybridization between the pocket gophers, Thomomys bottae and Thomomys umbrinus, in Arizona. J. Mammal. 54, 561–584 (1973)
Patton, J.L.: Chromosomal and genic divergence, population structure, and speciation potential in Thomomys bottae pocket gophers. In: Ecologia y genetica de la especiacion animal (O.A. Reig, ed.), pp. 255–295. Caracas, Venezuela: Esquinoccio 1981
Patton, J.L., Feder, J.H.: Genetic divergence between populations of the pocket gopher, Thomomys umbrinus (Richardson). Z. Säugetier 43, 12–30 (1978)
Patton, J.L., Smith, M.F.: Molecular evolution in Thomomys pocket gophers: phyletic systematics, paraphyly, and rates of evolution. J. Mammal. 62, 493–500 (1981)
Patton, J.L., Sherwood, S.W.: Genome evolution in pocket gophers (genus Thomomys) I. Heterochromatin variation and speciational potential. Chromosoma (Berl.) (in press, 1982)
Patton, J.L., Yang, S.Y.: Genetic variation in Thomomys bottae pocket gophers: macrogeographic patterns. Evolution (Lawrence, Kansas) 31, 697–720 (1977)
Patton, J.L., Hafner, J.C., Hafner, M.S., Smith, M.F.: Hybrid zones in Thomomys bottae pocket gophers: genetic, phenetic, and ecologic concordance patterns. Evolution (Lawrence, Kansas) 33, 860–876 (1979)
Rabinovich, P.S., O'Brien, K., Simpson, M., Callis, J.B., Hoehn, H.: Flow cytogenetics II. High resolution ploidy measurements in human fibroblast cultures. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29, 65–76 (1981)
Rees, H.: DNA in higher plants. In: Evolution of genetic systems (H.H. Smith, ed.). New York: Gordon and Breach 1972
Rees, H., Jones, R.N.: The origin of wide species variation in nuclear DNA content. Int. Rev. Cytol. 32, 53–92 (1972)
Robertston, M.: Gene families, hopeful monsters and the selfish genetics of DNA. Nature (Lond.) 293, 333–334 (1981)
Sage, R.D.: Wild mice. In: The mouse in biomedical research, Vol. I (H.L. Foster, J.D. Small, and J.G. Fox, eds.). New York: Academic Press 1981
Sokal, R.R., Rohlf, F.J.: Biometry. San Francisco: W.H. Freeman and Co. 1969
Sparrow, A.H., Price, H.S., Underbrink, A.G.: A survey of DNA content per cell and per chromosome of prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms: some evolutionary considerations. In: Evolution of genetic systems (H.H. Smith, ed.). New York: Gordon and Breach 1972
Szarski, H.: Cell size and nuclear DNA content in vertebrates. Int. Rev. Cytol. 44, 93–111 (1974)
Szilkai, O., El-Lakany, M.H., DeVescovi, M.A.: On the clinical variability in nuclear characteristics of Douglas-fir, its possible causes and applications. Egypt. J. Genet. Cytol. 5, 146–152 (1975)
Tannenbaum, E., Cassidy, M., Alabaster, O., Herman, C.: Measurement of cellular DNA mass by flow microfluorometry with the use of a biological internal standard. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 26, 145–148 (1978)
Thaeler, C.S., Jr.: An analysis of three hybrid populations of pocket gophers (genus Thomomys). Evolution (Lawrence, Kansas) 22, 543–555 (1968)
Thaeler, C.S., Jr.: Chromosome numbers and systematic relations in the genus Thomomys (Rodentia, Geomyidae). J. Mammal. 61 414–422 (1980)
Van't Hoff, S., Sparrow, A.H.: A relationship between DNA content, nuclear volume, and minimum mitotic cycle time. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 49, 897–902 (1963)
Wentworth, F.A., Sutton, D.A.: Chromosomes of the Townsend pocket gopher, Thomomys townsendii. Southwestern Naturalist 14, 157–161 (1969)
White, M.J.D.: Animal Cytology and Evolution (3 edit.) and Cambridge: Cambridge University Press 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sherwood, S.W., Patton, J.L. Genome evolution in pocket gophers (genus Thomomys). Chromosoma 85, 163–179 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294963
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294963