Summary
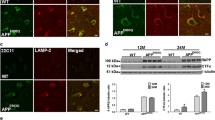
To verify our hypothesis of defective protease inhibitor domains that are encoded by abnormal processing of amyloid precursor protein (APP) in brains of patients with neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses (NCL), immunohistochemical and cytochemical studies were performed with monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) directed against various domains of APP. For the studies, 22 autopsy brains were used: 12 with different forms of NCL, and 10 control brains. The staining procedure for the avidin-biotin complex (ABC) technique and the postembedding gold-labelled procedure for electron microscopy (EM) were employed. Of all mAbs used for the study, only mAbs generated against amyloid B-protein bound to neural tissue were affected with NCL. The strongest immunostaining of neurons and of some reactive glial cells was found in brains with the juvenile form of NCL. Only in the infantile form of the disease were some neurons overloaded with storage material weakly immunoreactive. In brains of patients with the adult form of NCL, immunoreactivity was found in affected neurons and in extracellularly deposited material of senile plaques. The results of EM study showed that the immunoreactivity was restricted to lysosomal cytosomes in neural tissue with any form of NCL selectively localized on the curvilinear and fingerprint proteinaceous component of ceroid lipofuscin. Studies performed on control aging brains and Alzheimer's disease (AD) brains confirmed previous observations of immunoreactivity being found diffusely in the protein component of some neurons containing lipopigment. The defective processing of APP in brains with NCL and AD and in ageing brains is discussed. Our present results support the notion of heterogeneity of ceroid lipofuscin storage material in various forms of NCL and underline the hypothesis that abnormalities found in the protease inhibitors or APP in the proteinaceous composition of storage lipopigment could be a key to the unknown etiology of NCL.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong D, Koppang N (1981) Ceroid lipofuscinosis, a model of aging. In: Sohal RS (ed) Age pigments. Elsevier/North Holland Amsterdam, pp 355–382
Bancher C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, Kim KS, Wisniewski HM (1989) Immunoreactivity of neuronal lipofuscin with monoclonal antibodies to the amyloid B-protein. Neurobiol Aging 10:125–135
Castano EM, Frangione B (1988) Human amyloidosis, Alzheimer disease and related disorders. Lab Invest 58:122–132
Dyrks T, Weidemann A, Multhaup G, Salbaum JM, Lemaire H-G, Kang J, Muller-Hill B, Masters CL, Beyreuther K, (1988) Identification, transmembrane orientation and biogenesis of the amyloid A4 precursor of Alzheimer's disease. EMBO J 7:949–957
Glenner GG, Wong CW (1984) Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrosvascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 120:885–890
Goebel HH, Zeman W, Pilz H (1975) Significance of muscle biopsies in neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry, 38:985–993
Goebel HH, Zeman W, Damaske E (1977) An ultrastructural study of the retina in the Jansky-Bielschowsky type of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Am J Ophthalmol 83:70–79
Goebel HH, Braak H, Seidel D, Doshi R, Marsden CD, Gullotta F (1982) Morphologic studies on adult neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis (NCL). Clin Neuropathol 1:151–162
Goldgaber D, Lerman MI, McBride OW, Saffiotti U, Gajdusek DC (1987) Characterization and chromosomal localization of a cDNA encoding brain amyloid of Alzheimer's disease. Science 235:877–880
Grundke-Iqbal I, Iqbal K, George L, Tung Y-C, Kim KS, Wisniewski HM (1989) Amyloid protein and neurofibrillary tangles coexist in the same neuron in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:2853–2857
Hsu S-M, Raine L, Fanger H (1981) Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem 29:577–580
Ivy GO, Schottler F, Wenzel J, Baudry M, Lynch G (1984) Inhibitors of lysosomal enzymes: Accumulation of lipofuscinlike dense bodies in the brain. Science 226:985–987
Kang J, Lemaire H-G, Unterbeck A, Salbaum JM, Masters CL, Grzeschik K-H, Multhaup G, Beyreuther K, Muller-Hill B (1987) The precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid A4 protein resembles a cell-surface receptor. Nature 325:733–736
Kim KS, Miller DL, Sapienza VJ, Chen C-J, Bai C, Grundke-Iqbal I, Currie JR, Wisniewski HM (1988) Production and characterization of monoclonal antibodies reactive to synthetic cerebrovascular amyloid peptide. Neurosci Res Commun 2: 121–130
Kitaguchi N, Takahashi Y, Tokushima Y, Shiojiri S, Ito H (1988) Novel precursor of Alzheimer's disease amyloid protein shows protease inhibitory activity. Nature 331:530–532
Kitaguchi T, Wisniewski KE, Maslinski S, Maslinska D (1989) Electron microscopic and biochemical characteristic of immunoreactivity of the amyloid B-protein in storage materials from neuronal ceroid lipofuscinosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:328 (abstr)
Kitamoto T, Ogomori K, Tateishi J, Prusiner SB (1987) Formic acid pretreatment enhances immunostaining of cerebral and systemic amyloids. Lab Invest 57:230–236
Maslinska D, Wisniewski KE, Goebel HH, Kim KS (1989) Amyloid B-protein epitopes in brains with different forms of neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 48:332 (abstr)
Masters CL, Multhaup G, Simms G, Pottgiesser J, Martins RN, Beyreuther K (1985) Neuronal origin of a cerebral amyloid: neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer's disease contain the same protein as the amyloid of plaque cores and blood vessels. EMBO J 4:2757–2763
Masters CL, Simms G, Weinman NA, Multhaup G, McDonald BL, Beyreuther K (1985) Amyloid plaque core protein in Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:4245–4249
Palmer DN, Martinus RD, Cooper SM, Midwinter GG, Reid JC, Jolly RD (1989) Ovine ceroid lipofuscinosis. The major lipopigment protein and the lipid binding subunit of mitochondrial ATP synthase have the same NH2-terminal sequence. J Biol Chem 264:5736–5740
Ponte P, Gonzalez-DeWhitt P, Schilling J, Miller J, Hsu D, Greenberg B, Davis K, Wallace W, Lieberburg I, Fuller F, Cordell B (1988) A new A4 amyloid mRNA contains a domain homologous to serine proteinase inhibitors. Nature 331:525–527
Robakis NK, Wisniewski HM, Jenkins EC, Devine-Gage EA, Houck GE, Yao XL, Ramakrishna N, Wolfe G, Silverman WP, Brown WT (1987) Chromosome 21q21 sublocalization of gene encoding B-amyloid peptide in cerebral vessels and neuritic (senile) plaques of people with Alzheimer disease and Down syndrome. Lancet I:384–385
Roth I, Bendayan M, Carlemalm E, Villiger W, Garavito M (1981) Enhancement of structural preservation and immunocytochemical staining in low temperature embedded pancreatic tissue. J Histochem Cytochem 29:663–671
Roth J, Bendayan M, Orci L (1978) Ultrastructural localization of intracellular antigens by the use of protein A-gold complex. J Histochem Cytochem 26:1074–1081
Schubert D, Schroeder R, LaCorbiere M, Saitoh T, Cole G (1988) Amyloid B protein precursor is possibly a heparan sulfate proteoglycan core protein. Science 241:223–226
Siegismund G, Goebel HH, Loblich HJ (1982) Ultrastructure and visceral distribution of lipopigments in infantile neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinosis. Pathol Res Pract 175:335–347
Sohal RS, Wolfe LS (1986) Lipofuscin: characteristics and significance. In: Swaab DF, Fliers E, Mirmiran M, Van Gool WA (eds), Aging of the brain and Alzheimer's disease. Prog Brain Res 70:171–183
Tanzi RE, Gusella JF, Watkins PC, Bruns GAP, StGeorge-Hyslop P, Van Keuren ML, Patterson D, Pagan S, Kurnit DM, Neve RL (1987) Amyloid B-protein gene: cDNA, mRNA distribution, and genetic linkage near the Alzheimer locus. Science 235:880–884
Tanzi RE, McClatchey AI, Lamberti ED, Villa-Komaroff L, Gusella JF, Neve RL (1988) Protease inhibitor domain encoded by an amyloid protein precursor mRNA associated with Alzheimer's disease. Nature 331:528–530
Wisniewski KE, Maslinska D (1989) Immunoreactivity of ceroid lipofuscin storage pigment in Batten disease with monoclonal antibodies to the amyloid B-protein (Letter to the Editor). N Engl J Med 320:256–257
Wisniewski KE, Madrid RE, Dambska M, Rapin I, Pullarkat R, Sklower S (1988) Spino-cerebellar degeneration with polyneuropathy associated with ceroid lipofuscinosis in one family. J Child Neurol 3:33–41
Wisniewski KE, Rapin I, Heaney-Kieras J (1988) Clinico-pathological variability in the childhood neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses and new observations on glycoprotein abnormalities. Am J Med Genet [Suppl] 5:27–46
Zeman W (1976) The neuronal ceroid-lipofuscinoses. Prog Neuropathol 3:203–223
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by NIH grant NS23717
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wisniewski, K.E., Maslinska, D., Kitaguchi, T. et al. Topographic heterogeneity of amyloid B-protein epitopes in brains with various forms of neuronal ceroid lipofuscinoses suggesting defective processing of amyloid precursor protein. Acta Neuropathol 80, 26–34 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294218
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00294218