Abstract
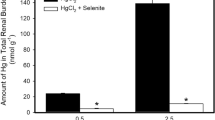
Twenty-four h after the subcutaneous administration of 0.5 μmoles selenite labelled with 75Se to rats of 200 g body weight, the retention of selenium at the injection site was significantly increased by the presence of equimolar amounts of methylmercury in the injection solution. The retention of Me203HgCl was not affected by the presence of selenite. The most significant shift caused by interaction was a decrease in the blood content and an increase in the brain content of 203Hg. The brain content of 75Se was also increased to a lesser extent. The shift in the distribution — which was the same whether the two metals were injected at the same site or separately — continuously decreased from 6–48 h. The same interaction pattern was observed when methylmercury and selenite were administered by gastric gavage and differences in distribution increased when the dose was increased from 1.25 μmoles/kg to 2.5 μmoles/kg. The increase in the brain content of mercury caused by selenite was not restricted to simultaneous administration and occurred when selenite was given 2–7 days after methylmercury.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Burk, R. F., Foster, K. A., Greenfield, R. M., Kiker, K. W.: Binding of simultaneously administered inorganic selenium and mercury to a rat plasma protein. Proc. Soc. exp. Biol. (N.Y.) 145, 782–785 (1974)
Fang, S. C., Chen, R. W., Fallin, E.: Influence of dietary selenite on the binding characteristics of rat serum proteins to mercurial compounds. Chem. Biol. Interact. 15, 51–57 (1976)
Ganther, H. E., Goudie, C., Sunde, M. L., Kopecky, M. J., Wagner, P., Sang-Hwan Oh, Hoekstra, W. G.: Selenium: relation to decreased toxicity of methylmercury added to diets containing tuna. Science 175, 1122–1124 (1972)
Gasiewitz, T. A., Smith, J. C.: Interactions of cadmium and selenium in rat plasma in vivo and in vitro. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 428, 113–122 (1976)
Iwata, H., Okamoto, H., Ohsawa, Y.: Effect of selenium on methylmercury poisoning. Res. Comm. Chem. Path. Pharmacol. 5, 673–680 (1973)
Magos, L., Webb, M.: Differences in distribution and excretion of selenium and cadmium or mercury after their simultaneous administration in equimolar doses. Arch. Toxicol. 36, 63–69 (1976a)
Magos, L., Webb, M.: The interaction between cadmium, mercury and zinc — administered subcutaneously in a single injection. Arch. Toxicol. 36, 53–61 (1976b)
Magos, L., Webb, M., Butler, W. H.: The effect of cadmium pretreatment on the nephrotoxic action and kidney uptake of mercury in male and female rats. Brit. J. exp. Path. 55, 589–594 (1974)
Ohi, G., Nishigaki, S., Seki, H., Tamura, Y., Maki, T., Maeda, H., Ochiai, S., Yamada, H., Shimamura, Y., Yagyu, H.: Interaction of dietary methylmercury and selenium on accumulation and retention of these substances in rat organs. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 32, 527–533 (1975)
Ohi, G., Nishigaki, S., Seki, H., Tamura, Y., Maki, T., Konno, H., Ochiai, S., Yamada, H., Shimamura, Y., Mizoguchi, I., Yagyu, H.: Efficacy of selenium in tuna and selenite in modifying methylmercury and mercuric mercury in the rat. J. Nutr. 104, 638–647 (1974)
Stillings, B. R., Lagally, H., Bauersfeld, P., Soares, J.: Effect of cystine, selenium and fish protein on the toxicity and metabolism of methylmercury in rats. Toxicol. appl. Pharmacol. 30, 243–254 (1974)
Stoeswand, G. S., Bache, C. A., Lisk, D. J.: Dietary selenium protection of methylmercury intoxication of Japanese quail. Bull. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 11, 152–156 (1974)
Wannag, A.: The importance of organ blood mercury when comparing foetal and maternal rat organ distribution of mercury after methylmercury exposure. Acta pharmacol. (Kbh.) 38, 289–298 (1976)
Webb, M., Magos, L.: Cadmium-thionein and the protection by cadmium against the nephrotoxicity of mercury. Chem. Biol. Interact. 14, 357–369 (1976)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported partly by International Atomic Energy Agency Grant Number 1530/RB
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Magos, L., Webb, M. The effect of selenium on the brain uptake of methylmercury. Arch. Toxicol. 38, 201–207 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293654
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00293654