Abstract
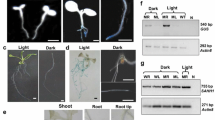
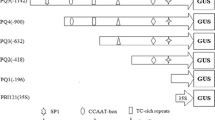
The activity of the Arabidopsis thalana A1 EF-1α gene promoter was analyzed in transgenic Arabidopsis plants. The 5′ upstream sequence of the A1 gene and several promoter deletions were fused to the β-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region. Promoter activity was monitored by quantitative and histochemical assays of GUS activity. The results show that the A1 promoter exhibits a modular organization. Sequences both upstream and downstream relative to the transcription initiation site are involved in quantitative and tissue-specific expression during vegetative growth. One upstream element may be involved in the activation of expression in meristematic tissues; the downstream region, corresponding to an intron within the 5′ non-coding region (5′IVS), is important for expression in roots; both upstream and downstream sequences are required for expression in leaves, suggesting combinatorial properties of EF-1α cis-regulatory elements. This notion of specific combinatorial regulation is reinforced by the results of transient expression experiments in transfected Arabidopsis protoplasts. The deletion of the 5′IVS has much more effect on expression when the promoter activity is under the control of A1 EF-1α upstream sequences than when these upstream sequences were replaced by the 35S enhancer. Similarly, a synthetic oligonucleotide corresponding to an A1 EF-1α upstream cis-acting element (the TEF1 box), is able to restore partially the original activity when fused to a TEF1-less EF1-α promoter but has no significant effect when fused to an enhancer-less 35S promoter.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Atanassova R, Chaubet N, Gigot C (1992) A 126 bp fragment of a plant historic gene promoter confers preferential expression in meristems of transgenic Arabidopsis. Plant J 2:291–300
Axelos M, Bardet C, Liboz T, Le Van Thai A, Curie C, Lescure B (1989) The gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha: molecular cloning, characterization and expression. Mol Gen Genet 219:106–112
Axelos M, Curie C, Mazzolini L, Bardet C, Lescure B (1992) A protocol for transient expression in Arabidopsis thaliana protoplasts isolated from cell suspension cultures. Plant Physiol Biochem 30:123–128
Benfey PN, Chua N-H (1990) The cauliflower mosaic virus 35S promoter: combinatorial regulation of transcription in plants. Science 250:959–966
Benfey PN, Ren L, Chua N-H (1989) The CaMV 35S enhancer contains at least two domains which can confer different developmental and tissue expression patterns. EMBO J 8:2195–2202
Bouchez D, Tokuhisa JG, Llewellyn DJ, Dennis ES, Ellis JG (1989) The ocs-element is a component of the promoters of several T-DNA and plant viral genes. EMBO J 8:4197–4204
Bradford MM (1976) Rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Bruhat A, Tourmente S, Chapel S, Sobrier ML, Couderc JL, Dastugue B (1990) Regulatory elements in the first intron contribute to transcriptional regulation of beta 3 tubulin gene by 20-hydroxyecdysone in Drosophila Kc cells. Nucleic Acids Res 18:2861–2867
Brujidou C, Marty I, Chartier Y, Meyer Y (1993) The Nicotiana tabacum genome endodes thioredoxin genes which are differentialy expressed. Mol Gen Genet (in press)
Buchman AR, Kimmerly WJ, Rine J, Kornberg RD (1988) Two DNA-binding factors recognize specific sequences at silencers, upstream activating sequences, autonomously replicating sequences, and telomeres in S. cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol 8:210–225
Chung S, Perry RP (1989) Importance of introns for expression of mouse ribosomal protein gene rpL32. Mol Cell Biol 9:2075–2082
Curie C, Liboz T, Bardet C, Gander E, Médale C, Axelos M, Lescure B (1991) Cis and trans-acting elements involved in the activation of Arabidopsis thaliana A1 gene encoding the translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha. Nucleic Acids Res 19:1305–1310
Curie C, Liboz T, Montané M-H, Rouan D, Axelos M, Lescure B (1992) The activation process of Arabidopsis thaliana A1 gene encoding the translation elongation factor EF-1 alpha is conserved among angiosperms. Plant Mol Biol 18:1083–1089
De Lange T (1992) Human telomeres are attached to the nuclear matrix. EMBO J 11:717–724
Dobres MS, Thompson WF (1989) A developmentally regulated, bud-specific transcript in pea has sequences similarity to seed lectins. Plant Physiol 89:833–838
Dynan WS (1989) Modularity in promoters and enhancers. Cell 58:1–4
Ellis JG, Llewellyn DJ, Walker JC, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (1987) The ocs element: a 16 base pair palindrome essential for activity of the octopine synthase enhancer. EMBO J 6:3203–3208
Evans MJ, Scrapulla RC (1988) Both upstream and intron sequence elements are required for elevated expression of the rat somatic cytochrome c gene in COS-1 cells. Mol Cell Biol 8:35–41
Franklin GC, Donovan M, Adam GIR, Holmgren L, Pfeifer-Ohlsson F, Ohlsson R (1991) Expression of the human PDGF-B gene is regulated by both positively and negatively acting cell type-specific regulatory elements located in the first intron. EMBO J 10:1365–1373
Fromm H, Katagiri F, Chua N-H (1989) An octopine synthase enhancer element element directs tissue-specific expression and binds ASF-1, a factor from tobacco nuclear extracts. Plant Cell 1:977–984
Hemerly A, Bergounioux C, Van Montagu M, Inze D, Ferreira P (1992) Genes regulating the plant cell cycle: Isolation of a mitotic-like cyclin from Arabidopsis thaliana. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:3295–3299
Hofmann JFX, Laroche T, Brand AH, Gasser SM (1989) RAP-1 factor is necessary for DNA loop formation in vitro at the silent mating type locus HML. Cell 57:725–737
Hovemann B, Richter S, Walldorf U, Cziepluch C (1988) Two genes encode related cytoplasmic elongation factor (EF-1 alpha) in Drosophila melanogaster with continuous and stage-specific expression. Nucleic Acids Res 16:3175–3194
Huet J, Cottrelle P, Cool M, Vignais ML, Thiele D, Mark C, Buhler JM, Sentenac A, Fromageot P (1985) A general upstream binding factor for genes of the yeast translational apparatus. EMBO J 4:3539–3547
Jefferson RA (1987) Assaying chimeric genes in plants: The GUS gene fusion system. Plant Mol Biol Rep 5:387–405
Jefferson RA, Kavanagh TA, Bevan MW (1987) GUS fusions: beta-Glucuronidase as a sensitive and versatile gene fusion marker in higher plants. EMBO J 6:3901–3907
Koning AJ, Tanimoto EY, Kiehne K, Rost T, Comai L (1991) Cell-specific expression of plant historic H2A genes. Plant Cell 3:657–665
Lam E, Benfey PN, Gilmartin PM, Rong-Xiang F, Chua N-H (1989) Site-specific mutations alter in vitro factor binding and change promoter expression pattern in transgenic plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:7890–7894
Leer RJ, Van Raamsdonk-Duin MC, Mager WH, Planta RJ (1985) Conserved sequences upstream of yeast ribosomal protein genes. Curr Genet 9:273–277
Lendstra JA, Van Vliet A, Arnberg AC, Van Hemert FJ, Möller W (1986) Genes coding for the elongation factor EF-1 alpha in Artemia. Eur J Biochem 155:475–483
Lepetit M, Ehling M, Chaubet N, Gigot C (1992) A plant histone gene promoter can direct both replication-dependent and independent gene expression in transgenic plants. Mol Gen Genet 231:276–285
Liboz T, Bardet C, Le Van Thai A, Axelos M, Lescure B (1990) The four members of the gene family encoding the Arabidopsis thaliana translation factor EF-1 alpha are actively transcribed. Plant Mol Biol 14:107–110
Luehrson KR, Walbot V (1991) Intron enhancement of gene expression and the splicing efficiency of introns in maize cells. Mol Gen Genet 225:81–93
Maas C, Laufs J, Grant S, Korfhage C, Werr W (1991) The combination of a novel stimulatory element in the first exon of the maize Shrunken-1 gene with the following intron 1 enhances reporter gene expression up to 1000-fold. Plant Mol Biol 16:199–207
Medford JI, Elmer JS, Klee HJ (1991) Molecular cloning and characterization of genes expressed in shoot apical meristems. Plant Cell 3:359–370
Pri-Hadash A, Hareven D, Lifschitz E (1992) A meristem-related gene from tomato encodes a dUTPase: Analysis of expression in vegetative and floral meristems. Plant Cell 4:149–159
Richards EJ, Ausubel FM (1988) Isolation of a higher eukaryotic telomere from Arabidopsis thaliana. Cell 53:127–136
Riis B, Rattan SIS, Clark BFC, Merrick WC (1990) Eukaryotic protein elongation factors. Trends Biochem Sci 15:420–424
Ripe RA, Lorenzen SI, Brenner DA, Breindl M (1989) Regulatory elements in 5′ flanking region and the first intron contribute to transcriptional control of the mouse alpha 1 type collagen gene. Mol Cell Biol 9:2224–2227
Shewmaker CK, Ridge NP, Pokalsky AR, Rose RE, Hiatt WR (1990) Nucleotide sequence of an EF-1 alpha genomic clone from tomato. Nucleic Acids Res 18:4276
Sussex IM (1989) Developmental programming of the shoot meristem. Cell 56:225–229
Tokuhisa JG, Singh K, Dennis ES, Peacock WJ (1990) A DNA-binding protein factor recognizes two binding domains within the octopine synthase enhancer element. Plant Cell 2:215–224
Uetsuki T, Naito A, Nagata S, Kaziro Y (1989) Isolation and characterization of the human chromosomal gene for polypeptide chain elongation factor EF-1 alpha. J Biol Chem 264:5791–5798
Ursin VM, Irvine JM, Hiatt WR, Shewmaker CK (1991) Developmental analysis of elongation factor-1 alpha expression in transgenic tobacco. Plant Cell 3:583–591
Valvekens D, Van Montagu M, Van Lijsebettens M (1988) Agrobacterium tumefaciens-mediated transformation of Arabidopsis thaliana root explants by using kanamycin selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 85:5536–5540
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C.A.J.J. van den Houndel
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Curie, C., Axelos, M., Bardet, C. et al. Modular organization and developmental activity of an Arabidopsis thaliana EF-1α gene promoter. Molec. Gen. Genet. 238, 428–436 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292002
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00292002