Summary
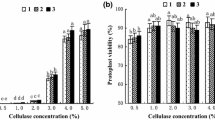
Methods were developed for transient gene expression in protoplasts of black spruce (Picea mariana) and jack pine (Pinus banksiana). Protoplasts were isolated from embryogenic suspension cultures of black spruce and from non-embryogenic suspensions of jack pine. Using electroporation, transient expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase (CAT) gene was assayed and shown to be affected by the cell line used, by voltage, temperature, and by the plasmid concentration and conformation. Increasing the plasmid DNA concentration (0–150μg ml−1) resulted in higher levels of transient CAT expression. In jack pine, linearized plasmid gave 2.5 times higher levels of CAT enzyme activity than circular. Optimal voltage varied for each cell line of the two species within the range 200–350 V cm−1 (960 μF). A heat shock treatment of protoplasts for 5 min at 45 °C resulted in enhanced CAT gene expression for both species.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1986) Information reports digest. Can For Serv 7:21–24
Attree SM, Dunstan DI, Fowke LC (1989) Picea glauca (Moench) (white spruce) and Picea mariana (Mill) (black spruce). In: Bajaj YPS (ed) Plant protoplasts and genetic engineering I. (Biotechnology agriculture 8). Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York (in press)
Ballas N, Zakai N, Friedberg D, Loyter A (1988) Linear forms of plasmid DNA are superior to supercoiled structures as active templates for gene expression in plant protoplasts. Plant Mol Biol 11:517–527
Bates GW, Piastuch W, Riggs CD, Rabussay D (1988) Electroporation for DNA delivery to plant protoplasts. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 12:213–218
Bekkaoui F, Saxena PK, Attree SM, Fowke LC, Dunstan DI (1987) The isolation and culture of protoplasts from an embryogenic cell suspension culture of Picea glauca (Moench) Voss. Plant Cell Rep 6:476–479
Bekkaoui F, Pilon M, Lainé E, Raju DSS, Crosby WL, Dunstan DI (1988) Transient gene expression in electroporated Picea glauca protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep 7:481–484
Boston RS, Becwar MR, Ryan RD, Goldsbrough PB, Larkins BA, Hodges TK (1987) Expression from heterologous promoters in electroporated carrot protoplasts. Plant Physiol 83:742–746
Dunstan DI (1988) Prospects and progress in conifer biotechnology. Can J For Res 18:1497–1506
Ebert PR, Ha SB, An G (1987) Identification of an essential upstream element in the nopaline synthase promoter by stable and transient assay. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:5745–5749
Fromm M, Taylor LP, Walbot V (1985) Expression of genes transferred into monocot and dicot plant cells by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:5824–5828
Fromm ME, Taylor LP, Walbot V (1986) Stable transformation of maize after gene transfer by electroporation. Nature 319:791–793
Gorman CM, Moffat LF, Howard BH (1982) Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cel Biol 2:1044–1051
Gupta PK, Dandekar AM, Durzan DJ (1988) Somatic proembryo formation and transient expression of a luciferase gene in Douglas fir and loblolly pine protoplasts. Plant Sci 58: 85–92
Hakman I, Fowke LC (1987) Somatic embryogenesis in Picea glauca (white spruce) and Picea mariana (black spruce). Can J Bot 65:656–659
Key JL, Lin CY, Chen YM (1981) Heat shock proteins of higher plants. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 78:3526–3530
Langridge WHR, Li BJ, Szalay AA (1985) Electric field mediated stable transformation of carrot protoplasts with naked DNA. Plant Cell Rep 4:355–359
Litvay JD, Johnson MA, Verma D, Einspahr D, Weyrauch K (1981) Conifer suspension culture medium development using analytical data from developing seeds. Institute Paper Chemistry Technical Paper Series No. 115, Appleton/WI
Morikawa H, Iida A, Yamada Y (1988) Electric gene transfer into plant protoplasts and cells. In: Mizrahi A (ed) Biotechnology in agriculture. Alan Liss, New York, pp 175–202
Okada K, Takebe I, Nagata T (1986) Expression and integration of genes introduced into highly synchronized plant protoplasts. Mol Gen Genet 205:398–403
Potter H, Weir L, Leder P (1984) Enhancer-dependent expression of human k immunoglobulin genes introduced into mouse pre-B lymphocytes by electroporation. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81:7161–7165
Seguin A, Lalonde M (1988) Gene transfer by electroporation in betulaceae protoplasts: Alnus incana. Plant Cell Rep 7:367–370
Shigekawa K, Dower WJ (1988) Electroporation of eukaryotes and prokaryotes: a general approach to the introduction of macromolecules into cells. Biotechniques 6:742–751
Shillito RD, Saul MW, Paszkowski J, Muller M, Potrykus I (1985) High efficiency direct gene transfer to plants. Bio Technol 3:1099–1103
Stopper H, Jones H, Zimmermann U (1987) Large scale transfection of mouse L-cells by electropermeabilization. Biochim Biophys Acta 900:38–44
Thompson JA, Abdullah R, Chen WH, Gartland KMA (1987) Enhanced protoplast division in rice (Oryza sativa L.) following heat shock treatment. J Plant Physiol 127:367–370
Thorpe TA, Biondi S (1984) Conifers. In: Sharp WR, Evans DA, Ammirato PV, Yamada Y (eds) Handbook of plant cell culture, vol 2. Macmillan, New York, pp 435–470
Werr W, Lörz H (1986) Transient gene expression in a Gramineae cell line. A rapid procedure for studying plant promoters. Mol Gen Genet 202:471–475
Widholm JM (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol 47:189–194
Wilson SM, Thorpe TA, Moloney MM (1989) PEG-mediated expression of GUS and CAT genes in protoplasts from embryogenic suspension cultures of Picea glauca. Plant Cell Rep 7:704–707
Zhang W, Wu R (1988) Efficient regeneration of transgenic plants from rice protoplasts and correctly regulated expression of the foreign gene in the plants. Theor Appl Genet 76:835–840
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by J. W. Snape
NRCC No. 30491
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tautorus, T.E., Bekkaoui, F., Pilon, M. et al. Factors affecting transient gene expression in electroporated black spruce (Picea mariana) and jack pine (Pinus banksiana) protoplasts. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 78, 531–536 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290838
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00290838