Summary
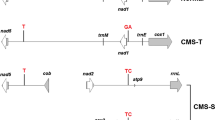
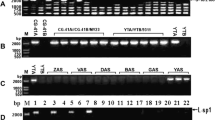
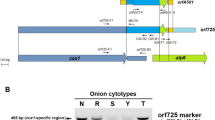
Cytoplasmic reversion to fertility in cms-S maize has been previously correlated with changes in mitochondrial genome organization, specifically with loss of the autonomously replicating linear plasmid-like DNAs, S1 and S2, and with accompanying alterations in the high molecular weight mtDNA (main genome) that specifically involved S1 and S2 sequences. These studies, however, dealt with cytoplasmic revertants occurring in the cms-VG M825 inbred line and in the cms-VG M825/Oh07 F1 hybrid. This paper deals principally with patterns of mitochondrial DNA reorganization accompanying cytoplasmic reversion to fertility in the WF9 inbred line nuclear background. Here the free S1 and S2 plasmid-like DNAs are retained in the revertants. Mitochondrial DNA analysis by Southern hybridization using cloned fragments of S1 and S2 shows altered organization around S-homologous regions in the main mitochondrial genome of revertants as compared with that of the male-sterile parental controls, but the pattern of main genome changes involving these regions differs from that of the cytoplasmic revertants that occurred in M825 and M825/Oh07 backgrounds. Similar experiments using a clone of the cytochrome oxidase I (COX I) gene of maize as a probe indicate that reorganization in this region is also involved in the changes in mtDNA that accompany cytoplasmic reversion to male fertility in cms-S WF9. The heterogeneity in patterns of reorganization of the main mtDNA genome that accompany cytoplasmic reversion in the same and different nuclear backgrounds are discussed in relation to cytoplasmic male sterility (CMS).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Benson SA (1984) A rapid procedure for isolation of DNA fragments from agarose gels. Biotechniques 2:66–68
Carlson JE, Gabay-Laughnan S, Laughnan JR (1982) Nucleocytoplasmic interactions in cms-S of maize. In: Sheridan WF (ed) Maize for biological research. Plant Mol Biol Assn, pp 243–245
Dawson AJ, Jones VP, Leaver CJ (1984) The apocytochrome b gene in maize mitochondria does not contain introns and is preceded by a potential ribosome binding site. EMBO J 3:2107–2113
Escote LJ, Gabay-Laughnan S, Laughnan JR (1985) Cytoplasmic reversion to fertility in cms-S maize need not involve loss of linear mitochondrial plasmids. Plasmid 14:264–267
Fox TD, Leaver CJ (1981) The Zea mays mitochondrial gene coding cytochrome oxidase subunit II has an intervening sequence and does not contain TGA codons. Cell 26:215–232
Gabay-Laughnan S, Laughnan JR (1983) Characteristics of low-frequency male-fertile revenants in S malesterile inbred lines of maize. Maydica 28:251–263
Isaac PG, Jones VP, Leaver CJ (1985) The maize cytochrome c oxidase subunit I gene: sequence, expression and rearrangement in cytoplasmic male-sterile plants. EMBO J 4:1617–1623
Ishige T, Storey KK, Gengenbach BG (1985) Cytoplasmic fertile revertants possessing S1 and S2 DNAs in S male-sterile maize. Jpn J Breed 35:285–291
Kemble RJ, Mans RJ (1983) Examination of the mitochondrial genome of revertant progeny from S-cms maize with cloned S-1 and S-2 hybridization probes. J Mol Appl Genet 2:161–171
Kemble RJ, Thompson RD (1982) S1 and S2, the linear mitochondrial DNAs present in a male-sterile line of maize, possess terminally attached proteins. Nucleic Acids Res 10:8181–8190
Kemble RJ, Gunn RE, Flavell RB (1980) Classification of normal and male sterile cytoplasms in maize. II. Electrophoretic analysis of DNA species in mitochondria. Genetics 95:451–458
Kim BD, Mans RJ, Conde MF, Pring PR, Levings CS III (1982) Physical mapping of homologous segments of mitochondrial episomes from S male-sterile maize. Plasmid 7:1–14
Laughnan JR, Gabay SJ (1975) An episomal basis for instability of S male sterility in maize and some implications for plant breeding. In: Birky CW Jr, Perlman PS, Byers TJ (eds) Genetics and biogenesis of cell organelles. Ohio State University Press, Columbus, pp 330–349
Laughnan JR, Gabay-Laughnan SJ (1978) Nuclear and cytoplasmic mutations to fertility in S male-sterile maize. In: Waiden DB (ed) Maize breeding and genetics. Wiley, New York, pp 427–447
Laughnan JR, Gabay-Laughnan S, Carlson JE (1981) Characteristics of cms-S reversion to male fertility in maize. Stadler Genet Symp 13:93–114
Levings CS III, Sederoff RR (1983) Nucleotide sequence of the S-2 mitochondrial DNA from the S-cytoplasm of maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:4055–4059
Levings CS III, Kim BD, Pring DR, Conde MF, Mans RJ, Laughnan JR, Gabay-Laughnan SJ (1980) Cytoplasmic reversion of cms-S in maize: association with a transpositional event. Science 209:1021–1023
Lonsdale DM, Thompson RD, Hodge TP (1981) The integrated forms of the S-1 and S-2 DNA elements of maize sterile mitochondrial DNA are flanked by the large repeated sequence. Nucleic Acids Res 9:3657–3669
Lonsdale DM, Schardl CL, Pring DR (1984) The mitochondrial genome of the S-male sterile cytoplasm of maize: organization and rearrangements associated with fertility reversion. In: Randall DD, Blevins DG, Larson RL, Rapp BJ (eds) Current topics in plant biochemistry and physiology. University of Missouri, Columbia, pp 133–140
Maniatis T, Fritsch EF, Sambrook JC (1982) Molecular Cloning, A Laboratory Manual. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, pp 88–94
Paillard M, Sederoff RR, Levings CS III (1985) Nucleotide sequence of the S-1 mitochondrial DNA from the S cytoplasm of maize. EMBO J 4:1125–1128
Pring DR, Levings CS III, Hu WWL, Timothy DH (1977) Unique DNA associated with mitochondria in the S-type cytoplasm of male-sterile maize. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:2904–2908
Schardl CL, Lonsdale DM, Pring DR, Rose KR (1984) Linearization of maize mitochondrial chromosomes by recombination with linear episomes. Nature 310:292–296
Schardl CL, Pring DR, Lonsdale DM (1985) Mitochondrial DNA rearrangement associated with fertile revenants of S-type male-sterile maize. Cell 43:361–368
Shapiro JA (1983) Mobile genetic elements. Academic Press, New York
Southern EM (1975) Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol 98:503–517
Thompson RD, Kemble RJ, Flavell RB (1980) Variations in mitochondrial DNA organization between normal and male-sterile cytoplasms of maize. Nucleic Acids Res 8:1999–2008
Weissinger AK, Timothy DH, Levings CS III, Hu WWL, Goodman MM (1982) Unique plasmid-like mitochondrial DNAs from indigenous maize races of Latin America. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 79:1–5
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by R. Hagemann
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Escote-Carlson, L.J., Gabay-Laughnan, S. & Laughnan, J.R. Reorganization of mitochondrial genomes of cytoplasmic revertants in cms-S inbred line WF9 in maize. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 75, 659–667 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289135
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00289135