Abstract
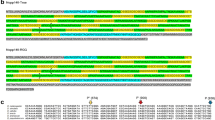
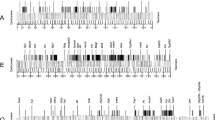
Ribosomal DNA nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila virilis DNA have been examined in some detail by restriction site analysis of cloned segments of rDNA, nucleic acid hybridizations involving unfractionated rDNA, and base composition estimates. The overall G+C content of the spacer is 27–28%; this compares with 39% for rDNA as a whole, 40% for main band DNA, and 26% for the D. virilis satellites. Much of the spacer is comprised of 0.25 kb repeats revealed by digestion with Msp I, Fnu DII or Rsd I, which terminate very near the beginning of the template for the ribosomal RNA precursor. The spacers are heterogeneous in length among rDNA repeats, and this is largely accounted for by variation among rDNA units in the number of 0.25 kb elements per spacer. Despite its high A+T content and the repetitive nature of much of the spacer, and the proximity of rDNA and heterochromatin in Drosophila, pyrimidine tract analysis gave no indication of relatedness between the spacer and satellite DNA sequences. Species of Drosophila closely related to D. virilis have rDNA spacers that are homologous with those in D. virilis to the extent that hybridization of a cloned spacer segment of D. virilis rDNA to various DNA is comparable with hybridization to homologous DNA, and distributions of restriction enzyme cleavage sites are very similar (but not identical) among spacers of the various species. There is spacer length heterogeneity in the rDNA of all species, and each species has a unique major rDNA spacer length. Judging from Southern blot hybridization, D. hydei rDNA spacers have 20–30% sequence homology with D. virilis rDNA spacers, and a repetitive component is similarly sensitive to Msp I and Fnu DII digestion, D. melanogaster rDNA spacers have little or no homology with counterparts in D. virilis rDNA, despite a similar content of 0.25 kb repetitive elements. In contrast, sequences in rDNA that encode 18S and 28S ribosomal RNA have been highly conserved during the divergence of Drosophila species; this is inferred from interspecific hybridizations involving ribosomal RNA and a comparison of distributions of restriction enzyme cleavage sites in rDNA.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barnett, T.R.: Ribosomal DNA sequences and gene interruptions in Drosophila. Ph. D. Thesis, Yale University, New Haven, Connecticut, 1978
Barnett, T., Rae, P.M.M.: A 9.6 kb intervening sequence in D. virilis rDNA, and sequence homology in rDNA interruptions of diverse species of Drosophila and other diptera. Cell 16, 763–775 (1979)
Berk, A.J., Sharp, P.A.: Sizing and mapping of early adenovirus mRNAs by gel electrophoresis of S1 endonuclease-digested hybrids. Cell 12, 721–732 (1977)
Brown, D.D., Wensink, P.C., Jordan, E.: A comparison of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri: the evolution of tandem genes. J. molec. Biol. 63, 57–73 (1972)
Cohen, E.H., Bowman, S.C.: Detection and location of three simple sequence DNAs in polytene chromosomes from virilis group species of Drosophila. Chromosoma (Berl.) 73, 327–355 (1979)
Dawid, I.B., Wellauer, P.K., Long, E.O.: Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster I. Isolation and characterization of cloned fragments. J. molec. Biol. 126, 749–768 (1978)
Forsheit, A.B., Davidson, N., Brown, D.D.: An electron microscopic heteroduplex study of the ribosomal DNAs of Xenopus laevis and Xenopus mulleri. J. molec. Biol. 90, 301–314 (1974)
Gall, J.G., Atherton, D.D.: Satellite DNA sequences in Drosophila virilis. J. molec. Biol. 85, 633–664 (1974)
Gall, J.G., Cohen, E.H., Polan, M.L.: Repetitive DNA sequences in Drosophila. Chromosoma (Berl.) 33, 319–344 (1971)
Glover, D.M., Hogness, D.S.: A novel arrangement of the 18S and 28S sequences in a repeating unit of Drosophila melanogaster rDNA. Cell 10, 167–176 (1977)
Ling, V.: Fractionation and sequences of the large pyrimidine oligonucleotides from bacteriophage fd DNA. J. molec. Biol. 64, 87–102 (1972)
Long, E.O., Dawid, I.B.: Restriction analysis of spacers in ribosomal DNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Nucleic Acids Res. 7, 205–215 (1979)
Long, E.O., Rebbert, M.L., Dawid, I.B.: The nucleotide sequence of the initiation site for ribosomal RNA transcription in Drosophila melanogaster. Comparison of genes with and without insertions. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) (in press, 1981)
Maizels, N.: Dictyostelium 17S, 25S and 5S rDNAs lie within a 38,000 base pair repeated unit. Cell 9, 431–438 (1976)
Maniatis, T., Jeffrey, A., Kleid, D.C.: Nucleotide sequence of the rightward operator of phage λ Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 72, 1184–1188 (1975)
Maxam, A., Gilbert, W.: Sequencing DNA by labelling the end and breaking at bases: DNA segments, end-labels, cleavage reactions, polyacrylamide gels, and strategies. Methods in enzymology 65, 499–560 (1980)
Murray, K., Murray, N.: Phage lambda receptor chromosomes for DNA fragments made with restriction endonuclease III of Haemophilus influenzae and restriction endonuclease I of E. coli. J. molec. Biol. 98, 551–564 (1975)
Pellegrini, M., Manning, J., Davidson, N.: Sequence arrangement of the rDNA of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 10, 213–224 (1977)
Polisky, B., Greene, P., Garfin, D.E., McCarthy, B.J., Goodman, H.M., Boyer, H.W.: Specificity of substrate recognition by the Eco RI restriction endonuclease. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 72, 3310–3314 (1975)
Rae, P.M.M., Kohorn, B.D., Wade, R.P.: The 10 kb Drosophila virilis 28S rDNA intervening sequence is flanked by a direct repeat of 14 base pairs of coding sequence. Nucl. Acids Res. 8, 3491–3504 (1980)
Rae, P.M.M., Steele, R.E.: Absence of cytosine methylation at C-C-G-G and G-C-G-C sites in the rDNA coding regions and intervening sequences of Drosophila and the rDNA of other higher insects. Nucl. Acids Res. 6, 2987–2995 (1979)
Renkawitz-Pohl, R., Glätzer, K.H., Kuntz, W.: Characterization of cloned ribosomal DNA from Drosophila hydei. Nucl. Acids Res. 8, 4593–4611 (1980)
Sharp, P.A., Sugden, B., Sambrook, J.: Detection of two restriction endonuclease activities in haemophilus parainfluenzae using analytical agarose-ethidium bromide electrophoresis. Biochemistry 12, 3055–3063 (1973)
Smith, H.O., Birnstiel, M.L.: A simple method for DNA restriction site mapping. Nucleic Acids Res. 3, 2387–2398 (1976)
Smith, M., Leung, D.W., Gillam, S., Astell, C.R., Montgomery, D.L., Hall, B.D.: Sequence of the gene for iso-l-cytochrome c in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell 16, 753–761 (1979)
Southern, E.M.: Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J. molec. Biol. 98, 503–517 (1975)
Stone, W.S., Guest, W.C., Wilson, F.D.: The evolutionary implications of the cytological polymorphism and phylogeny of the virilis group of Drosophila. Proc. nat. Acad. Sci. (Wash.) 46, 350–361 (1960)
Sutcliffe, J.G.: pBR322 restriction map derived from the DNA sequence: accurate size markers up to 4361 nucleotide pairs long. Nucleic Acids Res. 5, 2721–2728 (1978)
Tartof, K.D.: Evolution of transcribed and spacer sequences in the ribosomal RNA genes of Drosophila. Cell 17, 607–614 (1979)
Thomas, M., Davis, R.W.: Studies on the cleavage of bacteriophage lambda DNA with Eco RI restriction endonuclease. J. molec. Biol. 91, 315–328 (1975)
Throckmorton, L.H.: The problem of phylogeny in the genus Drosophila. In Studies in Genetics II. Research reports on Drosophila genetics, taxonomy and evolution. Univ. of Texas Publi. 6205, 207–337 (1962)
Wellauer, P.K., Dawid, I.B.: The structural organization of ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 10, 193–212 (1977)
Wellauer, P.K., Dawid, I.B.: Ribosomal DNA in Drosophila melanogaster II. Heteroduplex mapping of cloned and uncloned rDNA. J. molec. Biol. 126, 769–782 (1978)
Wensink, P.C., Finnegan, D.J., Donelson, J.E., Hogness, D.A.: A system for mapping DNA sequences in the chromosomes of Drosophila melanogaster. Cell 3, 315–325 (1974)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Dedicated to Professor Wolfgang Beermann on the occasion of his sixtieth birthday
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rae, P.M.M., Barnett, T. & Murtif, V.L. Nontranscribed spacers in Drosophila ribosomal DNA. Chromosoma 82, 637–655 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285773
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00285773