Abstract
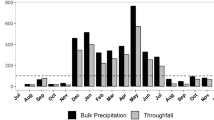
Atmospheric dry deposition in two forest edges was studied by means of monitoring canopy throughfall in Douglas Fir stands. Throughfall fluxes in the first 50 to 100 m of forest edges were found to be substantially higher than fluxes in the interior of forest stands. Sodium and chloride showed the steepest throughfall flux gradients. Ions important for soil acidification and eutrophication showed relatively less steep but still significant gradients. The mean increase of the throughfall flux at 10 m, with respect to the flux at 200 m from the forest edge amounted to 150% for Na+, 119% for Cl−, 54% for S04 2−, 38% for NO3 − , and 39% for NH4 + The enhancement of dry deposition in forest edges strongly depends on wind velocity and wind direction during dry deposition. Particularly trees in forest edges exposed to prevailing wind directions receive relatively large amounts of dry deposition.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adema, E. H.: 1986,On the Dry Deposition ofNH,, S02 and N02 on Wet Surfaces in a Small Scale Windtunnel, 7th World Clean Air Congress, Sydney, 25–29 September, 1986.
Bredemeier, M.: 1987,Forest Canopy Transformation of Atmospheric Deposition, presented at the IIASA/IMGW Task Force Meeting on Atmospheric Computation to Assess Acidification in Europe, Warsaw, April 1987.
Breemen, N. van, Burrough, P. A., Velthorst, E. J., Dobben, H. F. van, Wit, F. de, Ridder, T. B., and Reijnders, H. F. R.: 1982,Nature 299, 548.
Draaijers, G. P. J., Ivens, W. P. M. F., and Bleuten, W.: 1987a,The Interaction of NH 3 and SO2 in the Process of Dry Deposition on Plant Surfaces, Proceedings Int. Syrup. on Ammonia and Acidification (EUROSAP), Bilthoven, 13–15 April, 1987.
Draaijers, G. P. J., Ivens, W. P. M. F., and Bleuten, W.: 1987b,Measurements on the Temporal Variability of the Atmospheric Deposition in Forests by Sampling Through/all on an Event Basis, Proceedings Int. Acid Rain Conference, Lisbon, 1–3 September, 1987.
Erisman, J. W., Leeuw, F. A. A. M. de, and Aalst, R. M.: 1987,Deposition of the Most Important Acidifying Components in The Netherlands in 1980–1986, RIVM report 228473001.
Garten, C. T., Bondietti, E. A., and Lomax, R. D.: 1988,Atmospheric Environment 22, 1425.
Harmsel, A. ter, Klein Tank, A., Draaijers, G. P. J., Ivens, W. P. M. F., Bos, M. M., and Bleuten, W.: 1988,Atmospheric Dry Deposition in a Forest Edge Measured by Means of Inert Surfaces (in prep.).
Hasselrot, B. and Grenffelt, P.: 1987,Water, Air, and Soil Pollut. 34, 135.
Ivens, W. P. M. F.: 1988,Atmospheric Deposition of Sulphur and Base Cations to European Forests, IIASA, Laxenburg, Austria (in press).
Johansson, C., Richter, A., and Granat, L.: 1983, ‘Dry Deposition on Coniferous Forest of SO2 at ppb Levels’, in H. R. Pruppacker (ed.),Precipitation Scavenging, Dry Deposition and Resuspension.
Pinksterboer, E. F., Erisman, J. W., Maas, J. F. M., Asman, W. A. H., Waijers Ypelaan, A., and Slanina, J.: 1987,Horizontal Gradients of Ammonia: Comparison of Model Results with Measurements, IMOU report 87–11. Verstraten, J. M., Duijsings, J. J. H. M., Bouten, W., Wijk, A. J. van, and Bruijnzeel, L. A.: 1983,Effect van de vegetatie (eiken/beuken/fjnspar) op de depositie van zuurvormende bestanddelen op de bodem, Proceedings Symp. Zuren Regen: oorzaken, effecten en belcid, Den Bosch, 17–18 November, 1983.
Wiman, B. L. B.: 1985, ‘Aerosol Dynamics in Coniferous Forests’,Thesis, Dept. of Plant Ecology, University of Lund, Sweden.
Wiman, B. L. B. and Agren, G. I.: 1985,Atmospheric Environment 2, 335.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Draaijers, G.P.J., Ivens, W.P.M.F. & Bleuten, W. Atmospheric deposition in forest edges measured by monitoring canopy throughfall. Water Air Soil Pollut 42, 129–136 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282396
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00282396