Abstract
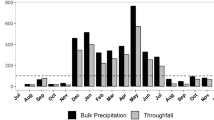
Solute fluxes to the ground in open plots and under the forest canopy of different species were investigated in a number of long-term ecosystem studies in West Germany. From the canopy flux balance, rates of interception deposition and canopy/deposition interactions were assessed. Chemically, both open precipitation and throughfall are dilute solutions of H2SO4 and HNO3 and their salts. For the sites investigated, mean pH in bulk precipitation ranged from 4.1 to 4.6, and in throughfall from 3.4 to 4.7. The increase in acidity after canopy passage at most sites indicates considerable interception deposition of strong acids to the forest stands, exceeding the rate of H+ buffering in the canopy.
Evidence for buffering processes can be directly deduced from the fact that on sites with high soil alkalinity and high foliage base status, throughfall pH is usually higher than precipitation pH. Furthermore, the same idea can be concluded from changes in solution composition after canopy passage: the H+/SO sup2−inf4 ratio is decreasing at most sites, while alkali earth cations from exchange processes occur in throughfall (Ca2+/SO sup2−inf4 ratio increases). Solution composition and element flux data are presented for each of the sites, and the regional, orographical and site specific (species composition, ecosystem state) differentiations are discussed.
A method for the assessment of total deposition and of canopy interactions such as H+-buffering and cation leaching is described, and results of calculations are shown. From these calculations it is concluded that forest ecosystems in Germany receive mean H+ loads of ca. 1 to 4 keq H+ · ha−1 · a−1 from atmospheric deposition. Acidity deposition rates seem to be related to a few key factors such as regional characteristics and ecosystem characteristics.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boynton, D.: 1954,Ann. Rev. Plant. Physiol. 5, 31.
Bredemeier, M.: 1987, ‘Stoflbilanzen, interne Protonenproduktion unc d Gesamtsäurebelastung des Bodens in verschiedenen Waldökosystemen Norddeutschlands’, Dissertation Univ. Göttingen.
Büttner,, G., Lamersdorf, N., Schultz, R., and Ulrich, B.: 1986,Deposition und Vertefung chemischer Elemente in küstennahen Waldstandorten, Ber. d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben, Univ. Göttingen, Reihe B Bd. 1.
Fassbender, H. W.: 1977,Ecologia plantarum 12, 263.
Garten, C. T.: 1986, ‘Sulfur Isotope Studies on Whole Trees’, in S. I. Auerbach (ed.),Annual Report of the Environmental Sciences Division 1986, ORNL, Oak Ridge, U.S.A.
Godt, J.: 1986,Untersuchung von Prozessen im Kronenraum van Waldökosystemen, Ber. d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben, Univ. Göttingen, Bd. 19, pp. 1–265.
Hauhs, M.: 1985,Wasser- und Stoffhaushalt im Einzugsgebiet der Langen Bramke (Harz), Ber. d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben, Univ. Göttingen, Bd. 17, pp. 1–206.
Höfken, K. D.: 1981, ‘Untersuchungen über die Deposition atmosphärischer Spurenstoffe an Buchen- und Fichtenwald’, Dissertation, Institut für Meteorologie und Geophysik der J. W. Goethe-Univ. Frankfurt.
Hofman, W. A., Lindberg, S. E., and Turner, R. R.: 1980,J. Env. Qual. 9, 95.
Lindberg, S. E., Lovett, G. M., Richter, D. D., and Johnson, D. W.: 1986,Science 231, 141.
Lovett, G. M. and Lindberg, S. E.: 1984,J. Appl. Ecol. 21, 1013.
Lutz, H. J.: 1987, ‘Einfluß von saurem Nebel auf die Ausbildung von Schadsymptomen bei jungen Fichten’, Dissertation Univ. Gießen, F.R.G., 128 p.
Matzner, E.: 1984,Deposition und Umsatz chemischer Elemente im Kronenraum von Waldbeständen, Ber. d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben, Univ. Göttingen, Bd. 2, pp. 61–87.
Matzner, E., Khanna, P. K., Meiwes, K. J., Gassens-Sasse, E., Bredemeier, M., und Ulrich, B.: 1984,Ergebnisse der Flüssemessungen in verschiedenen Waldökosystemen, Ber: d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben Univ. Göttingen, Bd. 2, pp. 29–49.
Matzner, E.: 1986, ‘Deposition/Canopy — Interactions in Two Forest Ecosystems of Northwest Germany’, in H. W. Georgii (ed.),Atmospheric Pollutants in Forest Areas, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, pp. 247–262.
Mayer, R. and Ulrich, B.: 1974,Oecol. Plant. 9, 157.
Meiwes, K. J.: 1979,Gött. Bdkdl. Ber. 60, 1.
Meiwes, K. J. und König, N.: 1986,H-Ionen-Deposition in Waldökosystemen in Norddeutschland, GSF München, BPT-Bericht 8/86, pp. 25–35.
Nodop, K.: 1987, ‘Nitrate and Sulfate Wet Deposition in Europe’, in G. Angeletti and G. Restelli (eds.),Physico-Chemical Behaviour of Atmospheric Pollutants, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, pp. 520–528.
Reiners, W. A. and Olson, R. K.: 1984,Oecologia 63, 320.
Roelofs, J. G. M., Kempers, A. J., Hondijk, A. L. F. M., and Jansen,J.: 1985,Plant and Sorl 84, 45.
Semb, A.: 1978,Atm. Env. 12, 455.
Streletzki, H. W.: 1986,Forst- und Holzwirt 41, 541.
Ulrich, B., Mayer, R., und Khanna, P. K.: 1979,Die Deposition von Luftverunreinigungen und ihre Auswirkungen in Waldökosystemen im Solling, Schriften aus der Forstl. Fak. d. Univ. Göttingen, Bd. 58, Sauerländer-Verlag.
Ulrich, B.: 1983a, ‘Interaction of Forest Canopies with Atmospheric Constituents: SO2, Alkali and Earth Alkali Cations and Chloride’, in B. Ulrich and J. Pankrath (eds.),Effects of Accumulation of Air Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, pp. 33–45.
Ulrich, B.: 1983b, ‘A Concept of Forest Ecosystem Stability and of Acid Deposition as Driving Force for Destabilization’, in B. Ulrich and J. Pankrath (eds.),Effects of Accumulation of Air Pollutants in Forest Ecosystems, D. Reidel Publ. Co., Dordrecht, Holland, pp. 1–29.
Ulrich, B. (ed.): 1986,Raten der Deposition, Akkumulation und des Austrags toxischer Luftverunreinigungen als Maß der Belastung und Belastbarkeit von Waldökosystemen, Ber. d. Fz. Waldökosys./Waldsterben, Univ. Göttingen, Reihe B, Bd. 2, pp. 1–210.
Wilmers, F. and Ellenberg, H.: 1986, in H. Ellenberg, R. Mayer, and J. Schauermann (eds.),Ökosystemforschung — Ergebnisse des Solling-Projekts, Ulmer, Stuttgart, pp. 61–76.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bredemeier, M. Forest canopy transformation of atmospheric deposition. Water Air Soil Pollut 40, 121–138 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279460
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00279460