Abstract
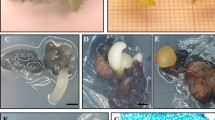
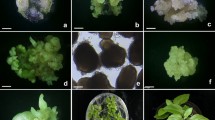
Procedures were developed for disinfestation of non-dormant basal plate tissue excised from field grown basal plate tissue of diploid Allium fistulosum × A. cepa F1 hybrid onions. Contamination levels varied with the season and vegetative development of plant material. Callus initiated from basal plate tissue and immature inflorescences of the F1 hybrids was maintained on a BDS-based medium containing 0.75 mg/l picloram and 2.0 mg/l BA. When this medium was supplemented with vitamins and glycine, and with proline at 2.5 gm/1, somatic embryos began to form. Their development continued on a BDS-based shoot promotion medium containing 0.03 mg/l picloram and 0.32 mg/l 2iP supplemented with vitamins, glycine and proline. Genotypes differed significantly in the numbers of structures regenerated. Plantlets from somatic embryos were rooted into BDS or half-strength BDS medium without growth substances and were successfully transferred to sterilized potting mix in plastic commercial corsage boxes.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BA:
-
benzyladenine
- 2,4-D:
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
- picloram:
-
4-amino-3,5,6-trichloropicolinic acid
- 2iP:
-
N6-(2-isopentenyl)adenine
- NAA:
-
1-naphthylacetic acid
- BDS:
-
Gamborg's B5 medium modified by Dunstan and Short (1977a)
References
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1977a) Physiol Plant 41:70–72
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1977b) Acta Hort 78:139–148
Dunstan DI, Short KC (1978) Scientia Hort 9:99–110
Emsweller SL, Jones HA (1938) Bot Gaz 99:729–773
Fridborg G. (1971) Physiol Plant 25:436–440
Lapitan NLV, Sears RG, Gill BS (1984) Theor Appl Genet 68:547–554
Novak, FJ (1980) Z Pflanzenzuchtg 84:250–260
Novak FJ, Havel L, Dolezel J (1986) In Evans, DA, Sharp, WR, Ammirato, PV (eds) Handbook of Plant Cell Culture: Techniques and Applications, vol 4, Macmillan, New York, pp. 419–456
Orton TJ, (1980) J Hered 71:280–282
Peffley, EB (1986) J Amer Soc Hort Sci 111:126–129
Phillips GC, Hubstenberger JF (1987) HortScience 22:124–125
Phillips GC, Luteyn KJ (1983) J Amer Soc Hort Sci 108:948–953
Shahin EA (1984) In: Vasil IK (ed) Cell Culture and Somatic Cell Genetics of Plants, vol I, Academic Press, New York, pp. 381–390
Shahin EA, Kaneko K (1986) HortScience 21:294–295
Stewart GR, Lee JA (1974) Planta (Berl) 120:279–289
Strom AR, LeRudelier D, Jakowec MW, Bunnell RC, Valentine RC (1983) Osmoregulatory (Osm) genes and osmoprotective compounds. In Kosuge K, Meredith CP, Hollaender A (eds) Genetic Engineering of Plants, an Agricultural Perspective, Plenum Press, New York, pp 39–59
van der Meer QP, van Bennekom JL (1978) Biul Warzywniczy 22:87–91
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by C. Quiros
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, CC., Currah, L. & Peffley, E.B. Somatic embryogenesis and plant regeneration in diploid Allium fistulosum × A. cepa F1 hybrid onions. Plant Cell Reports 7, 696–700 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272064
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00272064