Summary
-
1.
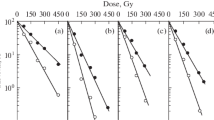
The X-ray-induced frequency of mutation, mitotic recombination and gene conversion was determined in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.
-
2.
X-rays induced only few mutations compared with alkylating nitrosamides but were highly efficient in the induction of mitotic recombination and gene conversion. Therefore, X-rays in spite of their low mutagenicity turned out genetically to be a very harmful agent for diploid yeast cells.
-
3.
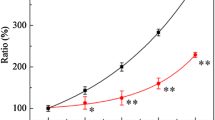
A protection against X-ray induced recombination and conversion could be achieved by the well known protecting agent cysteine. The protection factor is about 2. A similar effect could be observed with yeast extract-peptone medium but not with the amino acid serine.
-
4.
Furthermore, the protective effect of cysteine and yeast-extract peptone medium was studied at various concentrations and preincubation times.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bacq Zénon, M.: Chemical protection against ionising radiation. Springfield, Ill.: Ch. C. Thomas Publ. 1965.
Gichner, T., and J. Veleminsky: The mutagenic activity of 1-alkyl-1-nitrosoureas and 1-alkyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidines. Mutation Res. 4, 207–212 (1967).
Greve, E.: Über den Einfluß verschiedener Kohlenhydratquellen und der osmotischen Verhältnisse auf die Strahlenempfindlichkeit der Zellen von Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Z. Naturforsch. 16b, 589–594 (1961).
Haefner, K.: Zum Mechanismus der Entstehung auxotropher Zellen in heterozygoten Saccharomyces-Stämmen nach UV-und Röntgen-Bestrahlung. Z. Vererbungsl. 98, 82–90 (1966).
Kølmark, C.: Chemical protection against radiation effects in Neurospora crassa. Radiat. Res. 11, 450 (1959).
Loprieno, N.: Cysteine protection against reversion to methionine independence induced by N-nitroso-N-methylurethane in Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Mutation Res. 1, 469–472 (1964).
Manney, T. R., and R. K. Mortimer: Allelic mapping in yeast by X-ray-induced mitotic reversion. Science 143, 581–583 (1964).
Marquardt, H.: Genetische Strahlenschädigung somatischer Zellen durch Mutation, Rekombination und Genkonversion. Libro de Resúmenes, I Congr. Asoc. Europea Radiología, Barcelona 1967, p. 389.
—, U. v. Laer u. F. K. Zimmermann: Das spontane nitrosamid-und nitritinduzierte Mutationsmuster von 6 Adenin-Genloci der Hefe. Z. Vererbungsl. 98, 1–9 (1966).
Melching, H.-J., u. C. Streffer: Zur Beeinflussung der Strahlenempfindlichkeit von Säugetieren durch chemische Substanzen. In: Fortschritte der Arzneimittelforschung, Bd. 10. Basel: Birkhäuser 1966.
Rüger, W., u. R. W. Kaplan: Mutationsauslösung durch Röntgenstrahlen bei Bestrahlung des freien Bakteriophagen Kappa unter verschiedenen Bedingungen. Z. allg. Mikrobiol. 6, 253–269 (1966).
Schaedel, U., E. R. Lochmann, and W. Laskowski: Cysteine incorporation and radioprotection in Saccharomyces. Nature (Lond.) 211, 431–432 (1966).
Schoental, R.: Interaction of the carcinogenic N-methyl-nitrosourethane with sulphydryl groups. Nature (Lond.) 192, 670 (1961).
—, and D.-J. Rive: Interaction of N-Alkyl-N-nitroso-urethane with Thiols. Biochem. J. 97, 466–474 (1965).
Surdin, Y., W. Sly, J. Sire, A. M. Bordes et H. de Robichon-Szulmajster: Propriétés et contrôle génétique du système d'accumulation des acides aminés chez Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Biochim. biophys. Acta (Amst.) 107, 546–566 (1965).
Zimmermann, F. K.: Nicht reziproke mitotische Rekombination. Ber. dtsch. bot. Ges. 80, 492–496 (1967).
—, Enzyme studies on the products of mitotic gene conversion in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molec. Gen. Genetics, 101, 171–184 (1968).
—, and R. Schwaier: A genetic of symmetric dimethyl-hydrazine: induction of mitotic recombination. Naturwissenschaften 54, 251 (1967).
——: Induction of mitotic gene conversion with nitrous acid, 1-Methyl-3-nitro-1-nitrosoguanidine and other alkylating agents in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Molec. Gen. Genetics 100, 63–76 (1967).
——, and U. v. Laer: Mitotic recombination induced in Saccharomyces cerevisiae with nitrous acid, diethylsulfate and carcinogenic, alkylating nitrosamides. Z. Vererbungsl. 98, 230–246 (1966).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schwaier, R. X-ray-induced mitotic recombination, gene conversion and mutation in Saccharomyces and the radioprotective effect of cysteine. Molec. Gen. Genet. 101, 203–211 (1968). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271622
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00271622