Summary
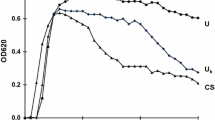
The influence of various factors on aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals in vitro was determined. Aggregation was assessed by filtering the crystal suspension and measuring the flow rate through a filter. 10% urine completely inhibited aggregation. Orthophosphate and magnesium at concentrations occurring in urine had no effect. Citrate had no effect at 10-4 M, but did inhibit at 10-3 M. The latter effect is probably due to calcium binding. Pyrophosphate and disodium dichloromethylene diphosphonate (Cl2MDP) inhibited strongly at 10-4 M, disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP) at 10-5 M, whereas pentanemonophosphonate had no effect. Uromucoid also did not show any inhibitory activity. Studies by means of heat inactivation, ultrafiltration and fractionation on DEAE-cellulose and gel-filtration indicated that the inhibitory activity was heterogenous and that the major part was larger than 10000 daltons.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann, J. M., Ganz, U., Bisaz, S., Fleisch, H., Rutishauser, G.: Verabreichung eines Diphosphonats zur Steinprophylaxe. Helvetica chirurgica Acta 41, 421 (1974)
Bichler, K.-H., Haupt, H., Uhlemann, G., Schwick, H. G.: Human uromucoid. I. Quantitative immunoassay. Urological Research 1, 50 (1973)
Boyce, W. H., King, J. S.: Crystal-matrix interrelation in calculi. Journal of Urology 81, 351 (1959)
Fleisch, H., Neuman, W. F.: Mechanisms of calcification: role of collagen, polyphosphates, and phosphatase. American Journal of Physiology 200, 1296 (1961)
Fleisch, H., Bisaz, S.: Isolation from urine of pyrophosphate, a calcification inhibitor. American Journal of Physiology 203, 671 (1962)
Fleisch, H., Bisaz, S., Care, A. D.: Effect of orthophosphate on urinary pyrophosphate excretion and the prevention of urolithiasis. Lancet 1964 I, 1965
Fleisch, H., Bisaz, S.: The inhibitory effect of pyrophosphate on calcium oxalate precipitation and its relation to urolithiasis. Experientia 20, 276 (1964)
Fleisch, H., Russell, R. G. G., Bisaz, S., Mühlbauer, R. C., Williams, D. A.: The inhibitory effect of phosphonates on the formation of calcium phosphate crystals in vitro and on aortic and kidney calcification in vivo. European Journal of Clinical Investigation 1, 12 (1970)
Fleisch, H., Monod, A.: A new technique for measuring aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals in vitro: effect of urine, magnesium, pyrophosphate and diphosphonates. Urinary calculi. International Symposium on Renal Stone Research Madrid, pp. 53. Basel: Karger 1973
Francis, M. D., Russell, R. G. G., Fleisch, H.: Diphosphonates inhibit formation of calcium phosphate crystals in vitro and pathological calcification in vivo. Science 165, 1264 (1969)
Fraser, D., Russell, R. G. G., Pohler, O., Robertson, W. G. and Fleisch, H.: The influence of disodium ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP) on the development of experimentally induced urinary stones in rats. Clinical Science 42, 197 (1972)
Hall, R. J.: An improved method for the microdetermination of inorganic phosphate in small volume of biological fluids. Journal of Medical Laboratory Technology 20, 97 (1963)
Howard, J. E., Thomas, W. C.: Some observations on rachitic rat cartilage of probably significance in the etiology of renal calculi. Transactions of the American Clinical Chemical Association 70, 94 (1958)
Ohata, M., Pak, C. Y. C.: Preliminary study of the treatment of nephrolithiasis (calcium stones) with diphosphonate. Metabolism 23, 1167 (1974)
Robertson, W. G., Peacock, M., Nordin, B. E. C.: Activity products in stone-forming and non-stone-forming urine. Clinical Science 34, 579 (1968)
Robertson, W. G., Peacock, M., Nordin, B. E. C.: Calcium crystalluria in recurrent renal-stone formers. Lancet 1969 II, 21
Robertson, W. G., Peacock, M.: Calcium oxalate crystalluria and inhibitors of crystallization in recurrent renal-stone formers. Clinical Science 43, 499 (1972)
Robertson, W. G., Peacock, M., Nordin, B. E. C.: Inhibitors of the growth and aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals in vitro. Clinica Chimica Acta 43, 31 (1973)
Robertson, W. G., Peacock, M., Marshall, R. W., Knowles, K.: The effect of ethane-1-hydroxy-1, 1-diphosphonate (EHDP) on calcium oxalate crystalluria in recurrent renal stone-formers. Clinical Science and Molecular Medicine 47, 13 (1974)
Smith, L. H., Meyer, J. L., McCall, J. T.: Chemical nature of crystal inhibitors isolated from human urine. Urinary calculi. International Symposium on Renal Stone Research Madrid, p 318, Basel: Karger 1973
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Felix, R., Monod, A., Broge, L. et al. Aggregation of calcium oxalate crystals: Effect of urine and various inhibitors. Urol. Res. 5, 21–28 (1977). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257112
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00257112