Summary
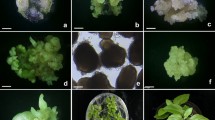
A solid feeder layer technique was developed to improve callus formation of Black Mexican Sweet maize (Zea mays L.) suspension culture protoplasts. Protoplasts were plated in 0.2 ml liquid media onto a cellulose nitrate filter on top of agarose-solidified media in which Black Mexican Sweet suspension feeder cells were embedded. Callus colony formation frequencies exceeding 10% of the plated protoplasts were obtained for densities of 103–105 protoplasts/ 0.2 ml, which was 100- to 1,000-fold higher than colony formation frequencies obtained for conventional protoplast plating methods such as liquid culture or embedding in agarose media. Compared with conventional methods, the feeder layer method gave higher colony formation frequencies for three independently maintained Black Mexican Sweet suspension lines. Differences among the three lines indicated that colony formation frequencies might also be influenced by the suspension culture maintenance regime and length of time on different 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid concentrations. The callus colony formation frequency reported is an essential prerequesite for recovering rare mutants or genetically transformed maize protoplasts.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Chourey PS, Zurawski DB (1981) Callus formation from protoplasts of a maize cell culture. Theor Appl Genet 59: 341–344
Dellaporta SL, Fraley RT (1981) Delivery of liposome-encapsulated nucleic acids into plant protoplasts. PMB Newslett 2:59–66
Green CE (1977) Prospects for crop improvement in the field of cell culture. HortSci 12:131–134
Harms CT (1982) Maize and cereal protoplasts — facts and perspectives. In: Sheridan WF (ed) Maize for biological research. University of North Dakota Press, Grand Forks, pp 373–384
Hooykaas-Van Slogteren GMS, Hooykaas PJJ, Schilperoort RA (1984) Expression of Ti plasmid genes in monocotyledonous plants infected with Agrobacterium tumefaciens. Nature 311:763–764
Kao KN, Michayluk MR (1975) Nutritional requirements for growth of Vicia hajastana cells and protoplasts at very low population density in liquid media. Planta 126: 105–110
Kuang VD, Shamina ZB, Butenko RG (1983) Use of nurse tissue culture to obtain clones from cultured cells and protoplasts of corn. Fiziol Rast 30:803–812
Murashige T, Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol Plant 15:473–497
Nagata T, Takebe I (1970) Cell wall regeneration and cell division in isolated tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Planta 92:301–308
Paszkowski J, Shillito RD, Saul S, Mandak V, Hohn T, Hohn B, Potrykus I (1984) Direct gene transfer to plants. EMBO J 3:2717–2722
Potrykus I, Harms CT, Lorz H, Thomas E (1977) Callus formation from stem protoplasts of corn (Zea mays L.). Mol Gen Genet 156:347–350
Potrykus I, Harms CT, Lorz H (1979) Callus formation from cell culture protoplasts of corn (Zea mays L.). Theor Appl Genet 54:209–214
Shneyour Y, Zelcer A, Izhar S, Beckman JS (1984) A simple feeder-layer technique for the plating of plant cells and protoplasts at low density. Plant Sci Lett 33:293–302
Smith JA, Green CE, Gengenbach BG (1984) Feeder layer support of low density populations of Zea mays L. suspension cells. Plant Sci Lett 36:67–72
Widholm JM (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain Technol 47:189
Zambryski P, Herrera-Estrella L, De Block M, Van Montagu M, Schell J (1984) The use of the Ti plasmid of Agrobacterium to study the transfer and expression of foreign DNA in plant cells: new vectors and methods. In: Setlow JK, Hollaender A (eds) Genetic engineering, vol VI. Plenum, New York, pp 253–278
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by D. von Wettstein
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ludwig, S.R., Somers, D.A., Petersen, W.L. et al. High frequency callus formation from maize protoplasts. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 71, 344–350 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252078
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00252078