Abstract
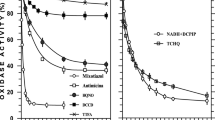
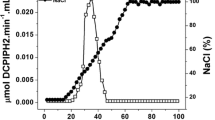
The interaction of the membrane-bound glucose dehydrogenase from the anaerobic but aerotolerant bacterium Zymomonas mobilis with components of the electron transport chain has been studied. Cytoplasmic membranes showed reduction of oxygen to water with the substrates glucose or NADH. The effects of the respiratory chain inhibitors piericidin, capsaicin, rotenone, antimycin, myxothiazol, HQNO, and stigmatellin on the oxygen comsumption rates in the presence of NADH or glucose as substrates indicated that a complete and in the most parts identical respiratory chain is participating in the glucose as well as in the NADH oxidation. Furthermore, the presence of coenzyme Q10 (ubiquinone 10) in Z. mobilis was demonstrated. Extraction from and reincorporation of the quinone into the membranes revealed that ubiquinone is essential for the respiratory activity with glucose and NADH. In addition, a membrane-associated tetramethyl-p-phenylene-diamine-oxidase activity could be detected in Z. mobilis.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ABTS:
-
2,2′-Azino-di-[3-ethyl-benzthiazolinesulfonate (6)]
- GDH:
-
glucose dehydrogenase
- HQNO:
-
2-heptyl-4-hydroxy-quinoline-N-oxide
- PQQ:
-
pyrroloquinoline quinone
- TMPD:
-
N,N,N′,N′-tetramethyl-p-phenylene-diamine
References
Ameyama M, Matsushita K, Shinagawa E, Adachi O(1987) Sugar-oxidizing respiratory chain of Gluconobacter suboxydans. Evidence for a branched respiratory chain and characterization of respiratory chain-linked cytochromes. Agric Biol Chem 51:2943–2950
Beardmore-Gray M, Anthony C (1986) The oxidation of glucose by Acinetobacter calcoaceticus: interaction of the quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase with the electron transport chain. J Gen Microbiol 132:1257–1268
Belaich JP, Senez JC (1965) Influence of aeration and of pantothenate on growth yields of Zymomonas mobilis. J Bacteriol 89:1195–1200
Bergmeyer HU, Graßl M, Walter HE (1983a) Catalase. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Graßl M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 2, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 165–166
Bergmeyer HU, Graßl M, Walter HE (1983b) Alcohol oxidase. In: Bergmeyer HU, Bergmeyer J, Graßl M (eds) Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 2, 3rd edn. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 143–144
Bouvet OMM, Grimont PAD (1988) Extracellular oxidation of d-glucose by some members of the enterobacteriaceae. Ann Inst Pasteur/Microbiol 139:59–77
Bringer S, Finn RK, Sahm H (1984) Effect of oxygen on the metabolism of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 139:376–381
Bringer S, Härtner T, Poralla K, Sahm H (1985) Influence of ethanol on the hopanoid content and the fatty acid pattern in batch and continuous cultures of Zymomonas mobilis. Arch Microbiol 140:312–316
Collins MD (1985) Analysis of isoprenoid quinones. Methods Microbiol 18:329–366
Collins MD, Jones D (1981) Distribution of isoprenoid quinone structural types in bacteria and their taxonomic implications. Microbiol Rev 45:316–354
Dawes EA, Ribbons DW, Large PJ (1966) The route of ethanol formation in Zymomonas mobilis. Biochem J 98:795–803
Duine JA, Jongejan JA (1989) Quinoproteins, enzymes with pyrrolo-quinoline quinone as cofactor. Annu Rev Biochem 58:403–426
Ensley BD, Finnerty WR (1980) Influences of growth substrates and oxygen on the electron transport chain system in Acinetobacter sp. HO1-N. J Bacteriol 142:859–868
Ernster L, Glaser E, Norling B (1978) Extraction and reincorporation of ubiquinone in submitochondrial particles. Methods Enzymol 53:573–579
Friedrich T, Strohdeicher M, Hofhaus G, Preis D, Sahm H, Weiss H (1990) The same domain motif for ubiquinone reduction in mitochondrial or chloroplast NADH dehydrogenase and bacterial glucose dehydrogenase. FEBS Lett 265:37–40
Jagow Gvon, Link TA (1986) Use of specific inhibitors on the mitochondrial bc 1 complex. Methods Enzymol 126:253–271
Jeng M, Hall C, Crane Fl, Takahashi N, Tamura S, Folkers K (1968) Inhibition of mitochondrial electron transport by piericidin A and related compounds. Biochemistry 7:1311–1321
Leigh D, Scopes RK, Rogers PL (1984) A proposed pathway for sorbitol production by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20:413–415
Matsushita K, Ohno Y, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1982) Membrane-bound, electron transport-linked, d-glucose dehydrogenase of Pseudomonas fluorescens. Interaction of the purified enzyme with ubiquinone or phospholipid. Agric Biol Chem 46:1007–1011
Matsushita K, Nonobe M, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1987a) Reconstitution of pyrroloquinoline quinone-dependent d-glucose oxidase respiratory chain of Escherichia coli with cytochrome o oxidase. J Bacteriol 169:205–209
Matsushita K, Ohnishi T, Kaback HR (1987b) NADH-ubiquinone oxidoreductases of the Escherichia coli aerobic respiratory chain. Biochemistry 26:7732–7737
Matsushita K, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1988) Quinoprotein d-glucose dehydrogenase in Acinetobacter calcoaceticus LMD 79.41: the membrane-bound enzyme is distinct from the soluble enzyme. FEMS Microbiol Lett 55:53–58
Matsushita K, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1989a) Quinoprotein d-glucose dehydrogenase of the Acinetobacter calcoaceticus respiratory chain: membrane-bound and soluble forms are different molecular species. Biochemistry 28:6276–6280
Matsushita K, Shinagawa E, Adachi O, Ameyama M (1989b) Reactivity with ubiquinone of quinoprotein glucose dehydrogenase from Gluconobacter suboxydans. J Biochem 105:633–637
McGill DJ, Dawes EA (1971) Glucose and fructose metabolism in Zymomonas anaerobia. Biochem J 125:1059–1068
Möllering H, Bergmeyer HU (1974) Gluconat. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed) Methoden der enzymatischen Analyse, vol. 2. Verlag Chemie, Weinheim, pp 1288–1292
Müller RH, Babel W (1986) Glucose as an energy donor in acetate growing Acinetobacter calcoaceticus. Arch Microbiol 144:62–66
Pankova LM, Shvinka JE, Beker ME, Slava ÉÉ (1985) Effect of aeration on Zymomonas mobilis. Mikrobiologiya 54:120–124
Prochaska HJ (1988) Purification and crystallization of rat liver NAD(P)H:(quinone-acceptor) oxidoreductase by cibacron blue affinity chromatography: identification of a new potent inhibitor. Arch Biochem Biophys 267:529–538
Shimomura Y, Kawada T, Suzuki M (1989) Capsaicin and its analogs inhibit the activity of NADH-coenzyme Q oxidoreductase of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Arch Biochem Biophys 270:573–577
Shvinka JE, Pankova LM, Mezbarde IN, Licis LJ (1989) Hydrogen peroxide production by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 31:240–245
Smith PK, Krohn RI, Hermanson GT, Mallia AK, Gartner FH, Provenzano MD, Fujimoto EK, Goeke NM, Olson BJ, Klenk DC (1985) Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal Biochem 150:76–85
Strohdeicher M, Schmitz B, Bringer-Meyer S, Sahm H (1988) Formation and degradation of gluconate by Zymomonas mobilis. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 27:378–382
Strohdeicher M, Bringer-Meyer S, Neuß B, van derMeer R, Duine JA, Sahm H (1989) Glucose dehydrogenase from Zymomonas mobilis: evidence for a quinoprotein. In: Jongejan JA, Duine JA (eds) PQQ and quinoproteins. Kluwer, Dordrecht, pp 103–105
Swings J, DeLey J (1977) The biology of Zymomonas. Bacteriol Rev 41:1–46
Truesdale GA, Downing AL, Lowden GF (1955) The solubility of oxygen in pure water and sea-water. J Appl Chem 5:53–62
vanSchie BJ, Hellingwerf KJ, vanDijken JP, Elferink MGL, vanDijl JM, Kuenen JG, Konings WN (1985) Energy transduction by electron transfer via pyrrolo-quinoline quinone-dependent glucose dehydrogenase in Escherichia coli, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, and Acinetobacter calcoaceticus (var. wolffi). J Bacteriol 163:493–499
Yamada Y, Aida K, Uemura T (1968) Distribution of ubiquinone 10 and 9 in acetic acid bacteria and its relation to the classification of genera Gluconobacter and Acetobacter, especially of so-called intermediate strains. Agric Biol Chem 32:786–788
Zachariou M, Scopes RK (1986) Glucose-fructose oxidoreductase, a new enzyme isolated from Zymomonas mobilis that is responsible for sorbitol production. J Bacteriol 167:863–869
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Strohdeicher, M., Neuß, B., Bringer-Meyer, S. et al. Electron transport chain of Zymomonas mobilis . Arch. Microbiol. 154, 536–543 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248833
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00248833