Abstract
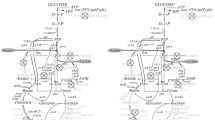
The activation of alternative respiration with an internal electron acceptor during anaerobic glucose utilization in E. coli strains with impaired fermentation ability has been studied. It was found out that respiration processes utilizing pyruvic acid as an endogenous electron acceptor can markedly contribute to the maintenance of the anaerobic redox balance in E. coli strains deficient in mixed acid fermentation pathways. The sequential inactivation of the pathways of anaerobic dissimilation of pyruvate and impairment of the functionality of the reductive branch of the tricarboxylic acid cycle led to an increase in the contribution (from 11 to 54%) of the respiratory formation of lactic acid and alanine to the biosynthesis of the reduced products of anaerobic glucose utilization by the strains. Analysis of the enantiomeric composition of the lactic acid and alanine secreted by the strains demonstrated that D-lactate dehydrogenase (Dld), L-lactate dehydrogenase (LctD), and D-alanine dehydrogenase (DadA) participated in the biosynthesis of the respective compounds.
Similar content being viewed by others
REFERENCES
Becker, J. and Wittmann, C., From systems biology to metabolically engineered cells—an omics perspective on the development of industrial microbes, Curr. Opin. Microbiol., 2018, vol. 45, pp. 180–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mib.2018.06.001
Chen, X., Zhou, L., Tian, K., et al., Metabolic engineering of Escherichia coli: a sustainable industrial platform for bio-based chemical production, Biotechnol. Adv., 2013, vol. 31, no. 8, pp. 1200–1223. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biotechadv.2013.02.009
Neidhardt, F. and Curtiss, R., Escherichia Coli and Salmonella: Cellular and Molecular Biology, 2nd ed., Washington, DC: ASM Press, 1996.
Sauer, U. and Eikmanns, B.J., The PEP-pyruvate-oxaloacetate node as the switch point for carbon flux distribution in bacteria, FEMS Microbiol. Rev., 2005, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 765–794. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.femsre.2004.11.002
Matsumoto, T., Tanaka, T., and Kondo, A., Engineering metabolic pathways in Escherichia coli for constructing a “microbial chassis” for biochemical production, Bioresour. Technol., 2017, vol. 245B, pp. 1362–1368. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.05.008
Unden, G. and Bongaerts, J., Alternative respiratory pathways of Escherichia coli: energetics and transcriptional regulation in response to electron acceptors, B-iochim. Biophys. Acta, 1997, vol. 1320, pp. 217–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0005-2728(97)00034-0
Morzhakova, A.A., Skorokhodova, A.Yu., Gule-vich, A.Yu., and Debabov, V.G., Recombinant Escherichia coli strains deficient in mixed acid fermentation pathways and capable of rapid aerobic growth on glucose with a reduced crabtree effect, Appl. Biochem. Micro-biol., 2013, vol. 49, no. 2, pp. 113–119. https://doi.org/10.7868/S0555109913020116
Sambrook, J., Fritsch, E., and Maniatis, T., Molecular Cloning: A Laboratory Manual, 2nd ed., New York, USA: Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, 1989.
Katashkina, J.I., Skorokhodova, A.Yu., Zimenkov, D.V., et al., Tuning the expression level of a gene located on a bacterial chromosome, Mol. Biol. (Moscow), 2005, vol. 39, no. 5, pp. 719–726.
Datsenko, K.A. and Wanner, B.L., One-step inactivation of chromosomal genes in Escherichia coli K-12 using PCR products, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A., 2000. V. 97, no. 12, pp. 6640–6645. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.120163297
Gulevich, A.Yu, Skorokhodova, A.Yu., Ermishev, V.Yu., et al., A new method for the construction of translationally coupled operons in a bacterial chromosome, Mol. Bio-l. (Moscow), 2009, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 505–514.
Fischer, C.R., Tseng, H.C., Tai, M., et al., Assessment of heterologous butyrate and butanol pathway activity by measurement of intracellular pathway intermediates in recombinant Escherichia coli,Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol., 2010, vol. 88, no. 1, pp. 265–275. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00253-010-2749-2
Dong, J.M., Taylor, J.S., Latour, D.J., et al., Three overlapping lct genes involved in L-lactate utilization by Escherichia coli,J. Bacteriol., 1993, vol. 75, no. 20, pp. 6671–6678.
Wallace, B.J. and Young, I.G., Role of quinones in electron transport to oxygen and nitrate in Escherichia coli. Studies with a ubiA- menA- double quinone mutant, Biochim. Biophys. Acta, 1977, vol. 461, no. 1, pp. 84–100.
Jones, H. and Venables, W.A., Effects of solubilisation on some properties of the membrane-bound respiratory enzyme D-amino acid dehydrogenase of Escherichia coli,FEBS Lett., 1983, vol. 151, no. 2, pp. 189–192.
Soini, J., Falschlehner, C., Liedert, C., et al., Norvaline is accumulated after a down-shift of oxygen in Escherichia coli W3110, Microb. Cell. Fact., 2008, vol. 7, no. 30. https://doi.org/10.1186/1475-2859-7-30
Zhang, Z., Gosset, G., Barabote, R., et al., Functional interactions between the carbon and iron utilization regulators, Crp and Fur, in Escherichia coli,J. Bacteriol., 2005, vol. 187, no. 3, pp. 980–990. https://doi.org/10.1128/JB.187.3.980-990.2005
de Mattos, M.J., The steady-state internal redox state (NADH/ NAD) reflects the external redox state and is correlated with catabolic adaptation in Escherichia coli,J. Bacteriol., 1999, vol. 181, no. 8, pp. 2351–2357.
Maklashina, E., Berthold, D.A., and Cecchini, G., Anaerobic expression of Escherichia coli succinate dehydrogenase: functional replacement of fumarate reductase in the respiratory chain during anaerobic growth, J. Bacteriol., 1998, vol. 180, no. 22, pp. 5989–5996.
Steinsiek, S., Frixel, S., and Stagge, S., SUMO, and Bettenbrock, K., Characterization of E. coli MG1655 and frdA and sdhC mutants at various aerobiosis levels, J. Biotechnol., 2011, vol. 154, no. 1, pp. 35–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbiotec.2011.03.015
Funding
The work was supported by a grant from the Russian Foundation for Basic Research (project no. 18-04-01222).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The authors declare that they have no conflicts of interest.
This article does not contain any studies involving animals or human participants performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Translated by I. Gordon
Abbreviations: cAMP, cyclic adenosine monophosphate; CL—culture liquid; Cm—chloramphenicol; CRP—cAMP receptor protein; GS—glyoxylate shunt; HPLC—high-performance liquid chromatography; NADH—nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide reduced; OAA—oxaloacetic acid; PCR—polymerase chain reaction; PEP—phosphoenolpyruvate; TCA cycle—tricarboxylic acid cycle.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Skorokhodova, A.Y., Sukhozhenko, A.V., Gulevich, A.Y. et al. Activation of Alternative Respiration with Internal Electron Acceptor during Anaerobic Glucose Utilization in Escherichia coli Strains with Impaired Fermentation Ability. Appl Biochem Microbiol 55, 870–876 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683819090072
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1134/S0003683819090072