Abstract
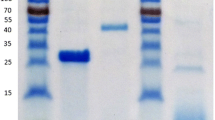
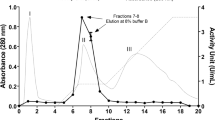
The induction of arabinases in Aspergillus niger N400 was studied on different simple and complex carbon sources. Sugar beet pulp was found to be an inducer of three arabinan degrading enzymes (α-l-arabinofuranosidase A, α-l-arabinofuranosidase B and endoarabinase). These enzymes were purified from A. niger culture fluid after growth of the fungus in medium employing sugar beet pulp as the carbon source and were characterised both physico-chemically (Mw 83 000, 67 000, 43 000 Da and, pI 3.3, 3.5 and 3.0 for α-l-arabinofuranosidases A and B and endo-arabinase, respectively) and kinetically (K m on p-nitrophenyl-α-l-arabinofuranoside 0.68 and 0.52 mM for α-l-arabinofuranosidases A and B, resp.; K m on sugar beet arabinan 0.24 and 3.7 g/l for α-l-arabinofuranosidase B and endoarabinase, resp.). The amino acid compositions of the three enzymes were determined also. The enzymic properties were compared with those of arabinases purified from a commerical A. niger enzyme preparation. Differences were found though the kinetic data suggest considerable similarity between the enzymes from the different sources. Antibodies raised in mice against the three enzymes were found to be highly specific and no crossreactivity with other proteins present in culture filtrates was observed. A mixture of these antibodies has been used to analyze specific induction of these individual enzymes on simple and complex substrates by Western blotting.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- PNA:
-
p-nitrophenyl-α-l-arabinofuranoside
References
Amons R (1987) Vapor-phase modification of sulfhydryl groups in proteins. FEBS Lett 212:68–72
Bidlingmeyer BA, Cohen SA, Tarvin TL (1984) Rapid analysis of amino acids using precolumn derivatization. J Chromatogr 336:93–104
Dijkema C, Kester HCM, Visser J (1985) Carbon-13 NMR studies of carbon metabolism in the hyphal fungus Aspergillus nidulans. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:14–18
Hirst EL, Jones JKN (1948) Pectic substances. VIII. Araban component of sugar beet pectin. J Chem Soc 2311–2313
Janssen PSL, Nipsen JWvan, Melgers PATA, Bogaart HWMvan den, Hamelink RLAE, Goverde BC (1986) HPLC analysis of phenylthiocarbamyl (PTC) amino acids. I. Evaluation and optimization of the procedure. Chromatographia 22:345–350
Kaji A, Tagawa K (1970) Purification, crystalization and amino acid composition of α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger. Biochim Biophys Acta 207:456–464
Kaji A (1984) l-Arabinosidases. Adv Carbohydr Chem Biochem 42:283–394
Kaji A, Saheki T (1975) Endo-arabinase from Bacillus subtilis F-11. Biochim Biophys Acta 410:354–360
Komae K, Kaji A, Sato M (1982) An α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Streptomyces purpurascens IFO 3389. Agric Biol Chem 46:1899–1905
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227:680–685
Rombouts FM, Voragen AGJ, Searle-van Leeuwen MF, Geraeds CCJM, Schols HA, Pilnik W (1988) The arabinases of Aspergillus niger — Purification and characterisation of two α-l-arabinofuranosidases and an endo-1,5-α-l-arabinanase. Carbohydr Polymers 9:25–47
Siliha HAI (1985) Studies on cloud stability of apricot nectar. Ph.D. Thesis, Agric. Univ. Wageningen, The Netherlands
Stephen AM (1983) Other plant polysaccharides. In: Aspinall GO (ed) The poylsaccharides, vol 2. Academic Press, New York, pp 97–193
Stephens BG, Felkel HJJr, Spinelli WM (1974) Spectrophotometric determination of copper and iron subsequent to the simultaneous extraction of bis(2,9-dimethyl-1,10-phenanthroline)copper(I) and bis[2,4-tri-(2-pyridyl)-1,3,5-triazine]iron(II) into propylene carbonate. Anal Chem 46:692–696
Voragen AGJ, Geerst F, Pilnik W (1982) Hemi-cellulase in enzymic fruit processing. In: Dupuy P (ed) Use of enzymes in food technology. Technique et Documentation Lavoisier, Paris, pp 497–502
Waibel R, Amado R, Neukom H (1980) Purification of an α-l-arabinofuranosidase from Aspergillus niger by substrate affinity chromatography. J Chromatogr 197:86–91
Weinstein L, Albersheim P (1979) Structure of plant cell walls. Purification and partial characterisation of a wall-degrading endo-arabanase and an arabinosidase from Bacillus subtillis. Plant Physiol 63:425–432
Witteveen CFB, Busink R, Vondervoort Pvan de, Dijkema C, Swart K, Visser J (1989) l-Arabinose and d-xylose catabolism in Aspergillus niger. J Gen Microbiol 135:2163–2171
Yoshikara O, Kaji A (1983) An endo-1,5-α-l-arabinase, which can disintegrate potato tissue. Agric Biol Chem 47:1935–1940
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
v. d. Veen, P., Flipphi, M.J.A., Voragen, A.G.J. et al. Induction, purification and characterisation of arabinases produced by Aspergillus niger . Arch. Microbiol. 157, 23–28 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00245330
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00245330