Summary
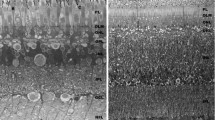
The mudpuppy retina was investigated with the histofluorescence method of Falck and Hillarp in normal animals and in animals injected intraocularly with α-methylnoradrenaline, 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine, or a combination of the two drugs. Catecholaminergic amacrine cells were found to form a thin layer of terminals at the border between the inner nuclear and the inner plexiform layers. Catecholaminergic interplexiform cells were not found. Indoleamine-accumulating amacrine cells were also observed. They are fifteen to twenty times more numerous than the catecholaminergic cells, and their terminals occur diffusely throughout the inner plexiform layer. In a number of eyes the majority of the indoleamine-accumulating terminals were eliminated with intraocular injections of the neurotoxin, 5,7-dihydroxytryptamine, but the reproducibility of this effect was not consistent. Intravitreal injections of 5,6-dihydroxytryptamine were used to label both types of neurons for electron microscopy. They were found to make conventional type synapses on amacrine cells and, less frequently, on bipolar cells.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Björklund A (1972) Fluorescence microscopic and microspectrofluorometric techniques for the cellular localization and characterization of biogenic amines. In: Rall JE, Kopin, I (eds) Methods of Investigative and Diagnostic Endocrinology, North Holland Publ Comp, pp 318–368
Bortoff A (1964) Localization of slow potential responses in the Necturus retina. Vision Res 4:626–635
Dowling JE, Boycott BB (1966) Organization of the primate retina: electron microscopy. Proc R Soc (Biol) 166:80–111
Dowling JE, Werblin FS (1969) Organization of retina of the mudpuppy. J Neurophysiol 32:315–318
Dowling JE, Ehinger B (1975) Synaptic organization of the amine-containing interplexiform cells of the goldfish and Cebus monkey retinas. Science 188:270–273
Dowling JE, Ehinger B (1978a) Synaptic contacts of dopaminergic neurons in the rabbit retina. J Comp Neurol 180:203–220
Dowling JE, Ehinger B (1978b) Synapses of the dopaminergic interplexiform neurons in goldfish retina. Proc R Soc Ser B 201:7–26
Dowling JE, Ehinger B, Florén I (1980) Fluorescence and electron microscopical observations on the amine accumulating neurons of the Cebus monkey retina. J Comp Neurol (In press)
Ehinger B (1978) Biogenic monoamines and amino acids as retinal neurotransmitters. In: Cool SJ, Smith III EL, (eds) Frontiers in Visual Science, Springer Series in Optical Sciences, New York, Heidelberg, Berlin, pp 42–53
Ehinger B, Florén I (1978) Chemical removal of indoleamine accumulating terminals in rabbit and goldfish retina. Exp Eye Res 26:321–328
Ehinger B, Florén I (1980) Retinal indoleamine accumulating neurons. Neurochem Internat 1:209–228
Ehinger B, Holmgren I (1979) Electron microscopy of the indoleamine accumulating neurons in the rabbit retina. Cell Tissue Res 197:175–194
Famiglietti EV, Kolb H (1976) Structural basis for on and off-center responses in retinal ganglion cells. Science 194:193–195
Hökfelt T (1968) In vitro studies on central and peripheral monoamine neurons at the ultrastructural level. Z Zellforsch 91:1–74
Jacoby JH, Lytle LD (1978) Serotonin neurotoxins. Ann NY Acad Sci 305:1–702
Nelson R, Famiglietti EV, Kolb H (1978) Intracellular staining reveals different levels of stratifications for on-and off-center ganglion cells in cat retina. J Neurophysiol 41:472–483
Thomas TN, Redburn DA (1979) 5-hydroxytryptamine —a neurotransmitter of bovine retina. Exp Eye Res 28:55–61
Tranzer JP, Richards JG (1971) Fine structural effects of 6-OH-DA in the periphery. In: Malmfors T, Thoenen H (eds) 6-hydroxytryptamine and Catecholamine Neurons. North-Holland Publ Comp Amsterdam-London, pp 15–32
Werblin FS, Dowling JE (1969) Organization of the retina of the mudpuppy. J Neurophysiol 32:339–355
West R, Dowling JE (1972) Synapses onto different morphological types of retinal ganglion cells. Science 178:510–512
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Adolph, A., Dowling, J.E. & Ehinger, B. Monoaminergic neurons of the mudpuppy retina. Cell Tissue Res. 210, 269–282 (1980). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237615
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00237615