Summary
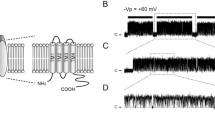
The plasma membrane of the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae has been investigated by patch-clamp techniques, focusing upon the most conspicuous ion channel in that membrane, a K+-selective channel. In simple observations on inside-out patches, the channel is predominantly closed at negative membrane voltages, but opens upon polarization towards positive voltages, typically displaying long flickery openings of several hundred milliseconds, separated by long gaps (G). Elevating cytoplasmic calcium shortens the gaps but also introduces brief blocks (B, closures of 2–3 msec duration). On the assumption that the flickery open intervals constitute bursts of very brief openings and closings, below the time resolution of the recording system, analysis via the beta distribution revealed typical closed durations (interrupts, I) near 0.3 msec, and similar open durations. Overall behavior of the channel is most simply described by a kinetic model with a single open state (O), and three parallel closed states with significantly different lifetimes: long (G), short (B) and very short (I). Detailed kinetic analysis of the three open/closed transitions, particularly with varied membrane voltage and cytoplasmic calcium concentration, yielded the following stability constants for channel closure: K I =3.3 · e −zu in which u=eV m /kT is the reduced membrane voltage, and z is the charge number; K G = 1.9 · 10−4([Ca2+] · e zu )−1; and K B =2.7 · 103([Ca2+] · e zu )2. Because of the antagonistic effects of both membrane voltage (V m ) and cytoplasmic calcium concentration ([Ca2+]cyt) on channel opening from the B state, compared with openings from the G state, plots of net open probability (P 0 ) vs. either V m or [Ca2+] are bell-shaped, approaching unity at low calcium (μ m) and high voltage (+150 mV), and approaching 0.25 at high calcium (10 mm) and zero voltage. Current-voltage curves of the open channel are sigmoid vs. membrane voltage, saturating at large positive or large negative voltages; but time-averaged currents, along the rising limb of P 0 (in the range 0 to +150 mV, for 10 μ m [Ca2+]) make this channel a strong outward rectifier. The overall properties of the channel suggest that it functions in balancing charge movements during secondary active transport in Saccharomyces.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adrian, R.H. 1969. Rectification in muscle. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 19:341–369
Anderson, J.A., Huprikar, S.S., Kochian, L.V., Lucas, W.J., Gaber, R.F. 1992. Functional expression of a probable Arabidopsis thaliana potassium channel in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 89:3736–3740
Armstrong, C.M., Cota, G. 1991. Calcium ion as a cofactor in Na channel gating. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88:6528–6531
Armstrong, C.M., Matteson, D.R. 1986. The role of calcium ions in the closing of K channels. J. Gen. Physiol. 87:817–832
Bertl, A. 1989. Current-voltage relationships of a sodium-sensitive potassium channel in the tonoplast of Chara corallina. J. Membrane Biol. 109:9–19
Bertl, A., Gradmann, D. 1987. Current-voltage relationships of potassium channels in the plasmalemma of Acetabularia. J. Membrane Biol 99:41–49
Bertl, A., Gradmann, G., Slayman, C.L. 1992a. Calcium- and voltage-dependent ion channels in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. London B, 338:63–72
Bertl, A., Blumwald, E., Coronado, R., Eisenberg, R., Findlay, G., Gradmann, D., Hille, B., Köhler, K., Kolb, H.-A., MacRobbie, E., Meissner, G., Miller, C., Neher, E., Palade, P., Pantoja, O., Sanders, D., Schroeder, J., Slayman, C.L., Spanswick, R., Williams, A. 1992b. Electrical measurements on endomembranes. Science 258:873–874
Bertl, A., Klieber, H.G., Gradmann, D. 1988. Slow kinetics of a potassium channel in Acetabularia. J. Membrane Biol. 102:141–152
Bertl, A., Slayman, C.L. 1990. Cation-selective channels in the vacuolar membrane of Saccharomyces: Dependence on calcium, redox state, and voltage. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:7824–7828
Bertl, A., Slayman, C.L. 1993. Complex modulation of cation channels in the tonoplast and plasma membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae: Single-channel studies. J. Exp. Biol. 172:271–287
Bisson, L.F., Fraenkel, D.G. 1982. Involvement of kinases in glucose and fructose uptake by Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80:1730–1734
Blatt, M.R., Slayman, C.L. 1983. KCl leakage from microelectrodes and its impact on the membrane parameters of a nonexcitable cell. J. Membrane Biol. 72:223–234
Boult, M., Elliott, D.C., Findlay, G.P., Terry, B.R., Tyerman, S.D. 1989. A multi-state anion channel in the plasmalemma of Amaranthus tricolor. In: Plant Membrane Transport: The Current Position. J. Dainty, M.I. de Michelis, E. Marrè, and F. Rasi-Caldogno, editors; pp. 517–520. Elsevier, Amsterdam
Caldwell, J.H., VanBrunt, J., Harold, F.M., 1986. Calcium-dependent anion channel in the water mold, Blastocladiella emersonii. J. Membrane Biol. 89:85–97
Camancho, M., Ramos, J., Rodriguez-Navarro, A. 1981. Potassium requirements of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Curr. Microbiol. 6:295–299
Catterall, W.A., 1977. Activation of the action potential Na+ ionophore by neurotoxins: An allosteric model. J. Biol. Chem. 23:8669–8676
Ciani, S., Krasne, S., Miyazaki, S., Hagiwara, S. 1978. A model for anomalous rectification: Electrochemical-potential-dependent gating of membrane channels. J. Membrane Biol. 44:103–134
Cirillo, V.P. 1961. Sugar transport in microorganisms. Annu. Rev. Microbiol. 15:197–218
Cirillo, V.P. 1989. Sugar transport in normal and mutant yeast cells. Meth. Enzymol. 174:617–622
Draber, S., Schultz, R., Hansen, U.-P. 1991. Patch-clamp studies on the anomalous mole fraction effect of the K+ channel in cytoplasmic droplets of Nitella: An attempt to distinguish between a multi-ion single-file pore and an enzyme kinetic model with lazy state. J. Membrane Biol. 123:183–190
Eilam, Y., Chernichovsky, D. 1987. Uptake of Ca2+ driven by the membrane potential in energy-depleted yeast cells. J. Gen. Microbiol. 133:1641–1649
Eilam, Y., Othman, M. 1990. Activation of Ca2+ influx by metabolic substrates in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: role of membrane potential and cellular ATP levels. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136:861–866
Eilam, Y., Othman, M., Halachmi, D. 1990. Transient increase in Ca2+ influx in Saccharomyces cerevisiae in response to glucose: effects of intracellular acidification and cAMP levels. J. Gen. Microbiol. 136:2537–2543
Eisenberg, R.S. 1990. Channels as enzymes. J. Membrane Biol. 115:1–12
Fairley, K., Laver, D., Walker, N. A. 1991. Whole-cell and single-channel currents across the plasmalemma of corn shoot suspension cells. J. Membrane Biol. 121:11–22
Findlay, I., Dunne, M.J., Petersen, O.H. 1985. High-conductance K+ channel in pancreatic islet cells can be activated and inactivated by internal calcium. J. Membrane Biol. 83:169–175
French, R.J., Shoukimas, J.J. 1985. An ion's view of the potassium channel. The structure of the permeation pathway as sensed by a variety of blocking ions. J. Gen. Physiol. 85:669–698
Fuller, F.B., Pickard, B.G. 1972. Spontaneous electrical activity in Coprinus. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 67:291–292
Gaber, R.F., Styles, C.A., Fink, G.R. 1988. TRK1 encodes a plasma membrane protein required for high-affinity potassium transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 8:2848–2859
Ghosh, A., Chance, B. 1964. Oscillations of glycolytic intermediates in yeast cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Comm. 16:174–181
Gillies, R.J. 1982. Intracellular pH and proliferation in yeast, Tetrahymena and sea urchin eggs. In: Intracellular pH: Its Measurement, Regulation, and Utilization in Cellular Functions. R. Nuticelli and D.W. Deamer, editors; pp. 341–359. A.R. Liss, New York
Gómez-Lagunas, F., Peña, A., Liévano, A., Darszon, A. 1989. Incorporation of ionic channels from yeast plasma membranes into black lipid membranes. Biophys. J. 56:115–119
Gradmann, D., Klieber, H.-G., Hansen, U.-P. 1987. Reaction kinetic parameters for ion transport from steady-state current-voltage curves. Biophys. J. 51:569–585
Gustin, M.C., Martinac, B., Saimi, Y., Culbertson, M.R., Kung, C. 1986. Ion channels in yeast. Science 233:1195–1197
Gustin, M.C., Zhou, X.-L., Martinac, B., Kung, C. 1988. A mechanosensitive ion channel in the yeast plasma membrane. Science 242:762–765
Hagiwara, S., Takahashi, K. 1974. The anomalous rectification and cation selectivity of the membrane of a starfish egg cell. J. Membrane Biol. 81:61–80
Halachmi, D., Eilam, Y. 1989. Cytosolic and vacuolar Ca2+ concentrations in yeast cells measured with the Ca2+-sensitive fluorescence dye indo-1. FEBS Lett. 256:55–61
Hamill, O.P., Marty, A., Neher, E., Sakmann, B., Sigworth, F.J. 1981. Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pfluegers Arch. 391:85–100
Hansen, U.-P., Gradmann, D., Sanders, D., Slayman, C.L. 1981. Interpretation of current-voltage relationships for “active” ion transport systems: I. Steady-state reaction-kinetic analysis of Class-I mechanisms. J. Membrane Biol. 63:165–190
Heckmann, K, Lindemann, B., Schnakenberg, J. 1972. Current-voltage curves of porous membranes in the presence of poreblocking ions. Biophys. J. 12:683–702
Hedrich, R., Busch, H., Raschke, K. 1990. Ca2+ and nucleotide dependent regulation of voltage dependent anion channels in the plasma membrane of guard cells. EMBO J. 9:3889–3892
Hedrich, R., Schroeder, J.I. 1989. The physiology of ion channels and electrogenic pumps in higher plants. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 40:539–569
Heredia, C.F., Sols, A., De la Fuente, G. 1968. Specificity of the constitutive hexose transport in yeast. Eur. J. Biochem. 5:321–329
Hille, B. 1984. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sinauer, Sunderland, MA
Hille, B., Schwarz, W. 1978. Potassium channels in multi-ion single-file pores. J. Gen. Physiol. 72:409–442
Hodgkin, A.L., Horowicz, P. 1959. The influence of potassium and chloride ions on the membrane potentials of single muscle fibers. J. Physiol. 148:127–160
Iida, H., Yagawa, Y., Anraku, Y. 1990. Essential role for induced Ca2+ influx followed by [Ca2+]i rise in maintaining viability of yeast cells late in the mating pheromone response pathway: A study of [Ca2+]i in single Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells wth imaging of fura-2. J. Biol. Chem. 265:13391–13399
Iijima, T., Hagiwara, S. 1987. Voltage-dependent K channels in protoplasts of trap-lobe cells of Dionaea muscipula. J. Membrane Biol. 100:73–81
Jones, W.B.G., Rothstein, A., Sherman, F., Stannard, J.N. 1965. Variation of K+ and Na+ content during the growth cycle of yeast. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 104:310–312
Katsuhara, M., Mimura, T., Tazawa, M. 1989. Patch-clamp study on a Ca2+-regulated K+ channel in the tonoplast of the brackish characeae Lamprothamnium succinctum. Plant Cell Physiol. 30:549–555
Kitasato, H. 1973. K permeability of Nitella clavata in the depolarized state. J. Gen. Physiol. 62:535–549
Klieber, H.-G., Gradmann, D. 1993. Enzyme kinetics of the prime K+ channel in the tonoplast of Chara: Selectivity and inhibition. J. Membrane Biol. 132:253–265
Ko, C.H., Buckley, A.M., Gaber, R.F. 1990. TRK2 is required for low affinity K+ transport in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Genetics 125:305–312
Ko, C.H., Gaber, R.F. 1991. TRK1 and TRK2 encode structurally related K+ transporters in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol. Cell. Biol. 11:4266–4273
Larsson, P., Vacata, V., Lecar, H., Höfer, M. 1992. Multilevel cationic channel in the plasma membrane of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Biophys. J. 61:A512 (Abstr. 2957)
Latorre, R., Miller, C. 1983. Conduction and selectivity in potassium channels. J. Membrane Biol. 71:11–30
Latorre, R., Oberhauser, A., Labarca, P., Alvarez, O. 1989. Varieties of calcium-activated potassium channels. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 51:385–399
Läuger, P. 1976. Diffusion-limited ion flow through pores. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 455:493–509
Läuger, P. 1980. Kinetic properties of ion carriers and channels. J. Membrane Biol. 57:163–178
Läuger, P. 1983. Conformational transitions of ionic channels. In: Single-Channel Recording. B. Sakmann and E. Neher, editors; pp. 177–189. Plenum, New York
Laver, D.R. 1990. Coupling of K+-gating and permeation with Ca2+ block in the Ca2+-activated K+ channel in Chara australis. J. Membrane Biol. 118:55–67
Laver, D.R., Walker, N.A. 1991. Activation by Ca2+ and block by divalent ions of the K+ channel in the membrane of cytoplasmic drops from Chara australis. J. Membrane Biol. 120:131–139
Lühring, H. 1986. Recording of single K+ channels in the membrane of cytoplasmic drop of Chara australis. Protoplasma 133:19–28
Markin, V.S., Liu, D., Gimsa, J., Strobel, R., Rosenberg, M.D., Tsong, T.Y. 1992. Ion channel enzyme in an oscillating electric field. J. Membrane Biol. 126:137–145
McCleskey, E.W., Almers, W. 1985. The calcium channel in skeletal muscle is a large pore. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 82:7149–7153
Miller, A.J., Vogg, G., Sanders, D. 1990. Cytosolic calcium homeostasis in fungi: Roles of plasma membrane transport and intracellular sequestration of calcium. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 87:9348–9352
Moczydlowski, E. 1986. Single-channel enzymology. In: Ion Channel Reconstitution. C. Miller, editor; pp. 75–111. Plenum, New York
Müller, U., Malchow, D., Hartung, K. 1986. Single ion channels in the slime mold Dictyostelium discoideum. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 857:287–290
Nakamura, Y., Nakajima, S., Grundfest, H. 1965. Analysis of spike electrogenesis and depolarizing K inactivation in electroplaques of Electrophorus electricus, L. J. Gen. Physiol. 49:321–349
Polakis, E.S., Bartley, W. 1966. Changes in the intracellular concentrations of adenosine phosphates and nicotinamide nucleotides during aerobic growth cycle of yeast on different carbon sources. Biochem. J. 99:521–533
Richard, E.A., Miller, C. 1990. Steady-state coupling of ion-channel conformations to a transmembrane ion gradient. Science 247:1208–1210
Ring, A., Sandblom, J. 1988. Modulation of gramicidin A open channel lifetime by ion occupancy. Biophys. J. 53:549–559
Schroeder, J.I. 1989. Quantitative analysis of outward rectifying K+ channel currents in guard cell protoplasts from Vicia faba. J. Membrane Biol. 107:229–235
Schroeder, J.I., Hagiwara, S. 1989. Cytosolic calcium regulates ion channels in the plasma membrane of Vicia faba guard cells. Nature 338:427–430
Schroeder, J.I., Hedrich, R., Fernandez, J.M. 1984. Potassium-selective single channels in guard cell protoplasts of Vicia faba. Nature 312:361–362
Sentenac, H., Bonneaud, N., Minet, M., Lacroute, F., Salmon, J.-M., Gaymard, F., Grignon, C. 1992. Cloning and expression in yeast of a plant potassium ion transport system. Science 256:663–665
Serrano, R. 1977. Energy requirements for maltose transport in yeast. Eur. J. Biochem. 80:97–102
Slayman, C.L. 1992. Channels, pumps, and osmotic machines in plants: A tribute to W.J.V. Osterhout. In: The Biological Century. R. Barlow, G. Weissmann, and J. Dowling, editors. Harvard, Cambridge
Slayman, C.L., Long, W.S., Gradmann, D. 1976. “Action potentials” in Neurospora crassa, a mycelial fungus. Biochim. Bio-phys. Acta 426:732–744
Spalding, E.P., Slayman, C.L., Goldsmith, M.H.M., Gradmann, D., Bertl, A. 1992. Ion channels in Arabidopsis plasma membrane: Transport characteristics and involvement in light-induced voltage changes. Plant Physiol. 99:96–102
Tanifuji, M., Sato, M., Wada, Y., Anraku, Y., Kasai, M. 1988. Gating behaviors of a voltage-dependent and Ca2+-activated cation channel of yeast vacuolar membrane incorporated into planar lipid bilayer. J. Membrane Biol. 106:47–55
Tester, M., 1990. Plant ion channels: whole-cell and single-channel studies. New Phytol. 114:305–340
Van de Mortel, J.B.J., Mulders, D., Korthout, H., Theuvenet, A.P.R., Borst-Pauwels, G.W.F.H. 1988. Transient hyperpolarization of yeast by glucose and ethanol. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 936:421–428
Vergara, C., Latorre, R. 1983. Kinetics of Ca2+-activated K+ channels from rabbit muscle incorporated into planar bilayers. J. Gen. Physiol. 82:543–568
Wada, Y., Ohsumi, Y., Tanifugi, M., Kasai, M., Anraku, Y. 1987. Vacuolar ion channel of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J. Biol. Chem. 262:17260–17263
Yellen, G.. 1984. Ionic permeation and blockade in Ca2+-activated K+ channels of bovine chromaffin cells. J. Gen. Physiol. 84:157–186
Yellen, G. 1987. Permeation in potassium channels: Implications for channel structure. Annu. Rev. Biophys. Biophys. Chem. 16:227–246
Zhou, X.-L., Stumpf, M.A., Hoch, H.C., Kung, C. 1991. A mechanosensitive channel in whole cells and in membrane patches of the fungus Uromyces. Science 253:1415–1417
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
The authors are indebted to Dr. Michael Snyder and Dr. Constance Copeland (Yale Department of Biology) for providing the tetraploid yeast strain and for initial assistance in handling the cells and preparing protoplasts; and to Dr. Esther Bashi for technical assistance throughout the experiments. The work was supported by Research Grant 85ER13359 from the United States Department of Energy (to C.L.S.), by Forschungs-Stipendium Be 1181/2-1 from the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (to A.B.), and by Akademie-Stipendium II/66647 from the Volkswagenstiftung (to D.G.).
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertl, A., Slayman, C.L. & Gradmann, D. Gating and conductance in an outward-rectifying K+ channel from the plasma membrane of Saccharomyces cerevisiae . J. Membarin Biol. 132, 183–199 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235737
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00235737