Summary
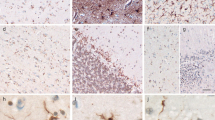
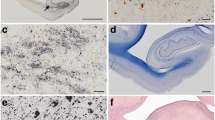
The previously reported unusual, Tau-positive glia with astrocytic morphology seen in brain tissues from cases of progressive supranuclear palsy (PSP) were re-examined immunohistochemically using antibodies to CD44 and vimentin, as well as Alz-50. Four brains of PSP cases, one of whom had atypical clinical features, were examined. All four cases showed the unusual glia which were positive to Alz-50 and anti-CD44 antibodies, but negative to anti-vimentin antibody. Ultrastructurally, they had either paired nucleated or lobulated nuclei and the cytoplasm frequently contained lipofuscin pigment. The CD44 was located on the surface of the cell bodies and their processes. Such glia were most numerous in the striatum in all cases. They also appeared in the cortex and some subcortical nuclei in the three typical cases. They were not seen in the lower brain stem or cerebellum. In their morphological characteristics and regionally specific appearance, these unusual glia seemed similar to the Alzheimer type I glia which are commonly seen in hepatic encephalopathy or Wilson's disease.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aruffo A, Stamenkovic I, Melnick M, et al (1990) CD44 is the principal cell surface receptor for hyaluronate. Cell 61:1303–1313
Astrom KE, Mancalol EL, Richardson EP (1958) Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. A hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain 81:93–111
Butterworth RF, Giguere JF, Michaud J, et al (1987) Ammonia: key factor in the pathogenesis of hepatic encephalopathy. Neurochem Pathol 6:1–12
Cavanagh JB, Kyu MH (1971) On the mechanism of type I Alzheimer abnormality in the nuclei of astrocytes. J Neurol Sci 12:241–261
Couche D, Fages C, Bridoux AM, et al (1985) Microtubule-associated proteins and in vitro astrocyte differentiation. J Cell Biol 101:2095–2103
Damsma G, Boisvert DP, Mudrick L, Wenkstern D, Fibiger HC (1990) Effects of transient forebrain ischemia and pargyline on extracellular concentrations of dopamine, serotonin, and their metabolites in the rat striatum as determined by in vivo microdialysis. J Neurochem 54:801–808
Davis PH, Bergeron C, McLachlan DR (1985) Atypical presentation of progressive supranuclear palsy. Ann Neurol 17:337–343
Diemer NH, Klinken E (1976) Astrocyte mitoses and Alzheimer type I and II astrocytes in anoxic encephalopathy. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 2:313–321
Dubas F, Gray F, Escroulle R (1983) Maladie de Steele-Richardson-Olszewski sans opthalmoplégie: six cas anatomocliniques. Rev Neurol (Paris) 139:407–416
Duchen LW, Jakob JM (1984) Nutritional deficiencies and metabolic disorders. In: Adams JH, Corsellis JAN, Duchen LW (eds) Greenfield's neuropathology. Edward Arnold, London, pp 597–600
Gallatin WM, Wayner EA, Hoffman PA, et al (1989) Structual homology between lymphocyte receptors for high endothelium and class III extracellular matrix receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4654–4658
Girgrah N, Letarte M, Becker LE, et al (1991) Localization of the CD44 glycoprotein to fibrous astrocytes in normal white matter and to reactive astrocytes in active lesions in multiple sclerosis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 50:778–792
Gregorios JB, Mozes LW, Norenberg LO, et al (1985) Morphologic effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. 1. Light microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 44:397–403
Gregorios JB, Mozes LW, Norenberg MD (1985) Morphologic effects of ammonia on primary astrocyte cultures. II. Electron microscopic studies. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 44:404–414
Hauw JJ, Verny M, Delaère P (1990) Constant neurofibrillary changes in the neocortex in progressive supranuclear palsy. Basic differences with Alzheimer's disease and aging. Neurosci Lett 119:182–186
Horoupian DS (1990) Cytoplasmic oligodendroglial inclusions in a patient with striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and “atypical” Pick's disease (abstract). Neurobiol Aging 11:272
Jellinger K, Riederer P, Tomonaga M (1980) Progressive supranuclear palsy: clinico-pathological and biochemical studies. J Neural Transm [Suppl] 16:111–128
Klavins J (1963) Central pontine myelinolysis. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 22:302–317
Linenberg R, Haymaker W (1982) Neuroglia and their reactions. In: Haymarker W, Adams RD (eds), Histology and histopathology of the nervous system. Charles Thomas, Springfield, pp1088–1091
Lowry OH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
McGeer EG, Singh EA, McGeer PL (1987) γ-Glutamyl transferase: normal control levels in Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer Dis Assoc Disord 1:38–42
McGeer PL, Akiyama H, Itagaki S, McGeer EG (1989) Immune system response in Alzheimer's disease. Can J Neurol Sci 16:516–527
McKee AC, Kosik KS, Kowall NW (1991) Neuritic pathology and dementia in Alzheimer's disease. Ann Neurol 30:156–165
Nakazato Y, Yamzaki H, Hirato J, et al (1990) Oligodendroglial microtubular tangles in olivopontocerebellar atrophy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 49:521–530
Norenberg MD (1981) The astrocyte in liver disease. Adv Cell Neurobiol 2:303–352
O'Kusky JR, Boyes BE, McGeer EG (1988) Methylmercury-induced movement and postural disorders in developing rat: regional analysis of brain catecholamines and indoleamines. Brain Res 439:138–146
Papp MI, Kahn JE, Lantos PL (1989) Glial cytoplasmic inclusions in the CNS of patients with multiple system atrophy (striatonigral degeneration, olivopontocerebellar atrophy and Shy-Drager syndrome). J Neurol Sci 94:79–100
Probst A, Langui C, Ulrich J, et al (1988) Progressive supranuclear palsy: extensive neuropil threads in addition to neurofibrillary tangles. Acta Neuropathol 77:61–68
Sobel RA, De Armond SJ, Forno LS, Eng LF (1981) Glial fibrillary acidic protein in hepatic encephalopathy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 40:625–632
Steele JC, Richardson JC, Olszewski T (1964) Progressive supranuclear palsy. A heterogenous degeneration involving the brain stem, basal ganglia and cerebellum, with vertical gaze and pseudobulbar palsy, nuchal dystonia and dementia. Arch Neurol 10:333–359
Stoll M, Dalchau R, Schmidt RE (1989) Cluster report: CD44. In: Knapp W, et al (eds) Leukocytes Typing IV, White cell differentiation antigens. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp616–622
Vogel H, Butcher EC, Picker LJ (1992) H-CAM expression in the human nervous system: evidence for a role in diverse glial interactions. J Neurocytol 21:363–373
Yamada T, McGeer PL (1990) Oligodendroglial microtubular masses: an abnormality observed in some human neurodegenerative diseases. Neurosci Lett 120:163–166
Yamada T, McGeer PL, McGeer EG (1992) Appearance of paired nucleated, tau-positive glia in progressive supranuclear palsy brain tissue. Neurosci Lett 135:99–102
Yamada T, Walker DG, McGeer PL (1992) Vimentin immunoreactivity in human brains with normal and pathological states. Acta Neuropathol 84:157–162
Yamamoto T, Hirano A (1986) A comparative study of modified Bielschowski, Bodian and thioflavin stains on Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangles. Neuropathol Appl Neurobiol 12:3–9
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by grants from the Parkinson Foundation of Canada, the Medical Research Council of Canada, and the Alzheimer Society of B.C., as well as donations from individual British Columbians
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamada, T., Calne, D.B., Akiyama, H. et al. Further observations on Tau-positive glia in the brains with progressive supranuclear palsy. Acta Neuropathol 85, 308–315 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227727
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227727