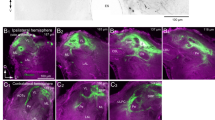
Abstract
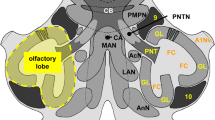
Neurons in the olfactory deutocerebrum of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus, were recorded intracellularly and filled with biocytin. Recorded neurons arborized in the olfactory lobe (OL), a glomerular neuropil innervated by olfactory and some presumptive mechanosensory antennular afferents. The neurons responded to chemosensory input from the lateral antennular flagellum bearing the olfactory sensilla but not the medial flagellum bearing many non-olfactory chemosensory sensilla. Many neurons received additional mechanosensory input. Thus the OL integrates specifically olfactory with mechanosensory input. OL neurons had multiglomerular arborizations restricted to one or two of the three horizontal layers of the columnar glomeruli. OL local interneurons comprised “core” neurons with tree-like neurites and terminals in the base of the glomeruli and “rim” neurons with neurites surrounding the OL and terminals in the cap/subcap. The somata of OL local interneurons lay in the medial soma cluster (100000 somata). OL projection neurons arborized in the base of the glomeruli and ascended via the olfactory glomerular tract to the lateral protocerebrum. A parallel projection pathway is constituted by projection neurons of the accessory lobe, a glomerular neuropil without afferent innervation but intimate links to the OL. The projection neuron somata constituted the lateral soma cluster (200000 somata).
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AC :
-
anterior cluster (cluster 6,7)
- AL :
-
accessory lobe
- aMC :
-
anterior subcluster of medial cluster (cluster 9)
- A lNv:
-
main antenna I (antennular) nerve
- A lNM:
-
antenna I (antennular) motor nerve
- A llNv:
-
main antenna II (antennal) nerve
- CB :
-
central body
- CL :
-
central layer of accessory lobe
- DC :
-
deutocerebral commissure
- DCN :
-
deutocerebral commissure neuropil
- dDUMC :
-
dorsal subcluster of dorsal unpaired median cluster (cluster 17)
- dMC :
-
dorsal subcluster of medial cluster (cluster 11)
- dVPALC :
-
dorsal subcluster of ventral paired anterolateral cluster (cluster 8) G glomerulus
- IDUMC :
-
lateral subcluster of dorsal unpaired median cluster (cluster 16)
- LC :
-
lateral cluster (cluster 10)
- LF :
-
lateral flagellum of antenna I (antennule)
- LL :
-
lateral layer of accessory lobe
- MF :
-
medial flagellum of antenna I (antennule)
- ML :
-
medial layer of accessory lobe
- MPN :
-
anterior and posterior median protocerebral neuropils
- OGT :
-
olfactory globular tract
- OGTN :
-
olfactory globular tract neuropil
- OL :
-
olfactory lobe
- OLALT :
-
olfactory lobe-accessory lobe tract
- PB :
-
protocerebral bridge
- pMC :
-
posterior subcluster of medial cluster (cluster 9)
- PT :
-
protocerebral tract
- TNv :
-
tegumentary nerve
- VPMC :
-
ventral paired medial cluster (cluster 12)
- VUMC :
-
ventral unpaired medial cluster (cluster 13)
- vVPALC :
-
ventral subcluster of ventral paired anterolateral cluster (cluster 8)
- ASW :
-
artificial sea water
- M3 :
-
mixture 3
- PRO :
-
L-proline
- TM :
-
TetraMarin extract
References
Arbas EA, Humphreys CJ, Ache BW (1988) Morphology and physiological properties of interneurons in the olfactory midbrain of the crayfish. J Comp Physiol A 164: 231–241
Bauchau AG, Passelecq-Gérin (1984) Ultrastructure des aesthetascs du crabe Carcinus maenas, L. Cahiers de Biologie Marine 25: 333–341
Blaustein DN, Derby CD, Simmons RB, Beall AC (1988) Structure of the brain and medulla terminalis of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus and the crayfish Procambarus clarkii, with an emphasis on olfactory centers. J Crust Biol 8: 493–519
Boeckh J, Ernst KD, Sass H, Waldow U (1984) Anatomical and physiological characteristics of individual neurons in the central antennal pathway of insects. J Insect Physiol 30: 15–26
Chambille I, Rospars JP (1985) Neurons and identified glomeruli of antennal lobes during postembryonic development in the cockroach Blaberus craniifer Burm. (Dictyoptera: Blaberidae). Int J Insect Morphol Embryol 14: 203–226
Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1987) Male-specific, sex pheromone-selective projection neurons in the antennal lobes of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 160: 553–569
Christensen TA, Waldrop BR, Harrow ID, Hildebrand JG (1993) Eocal interneurons and information processing in the olfactory glomeruli of the moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 173: 385–399
Devine DV, Atema J (1982) Function of chemoreceptor organs in spatial orientation of the lobster, Homarus americanus: differences and overlap. Biol Bull 163: 144–153
Diebel CE, Ache BW (1993) Whole cell recordings from interneurons in the olfactory pathway of the CNS in the spiny lobster. Chem Senses 18: 544–545
Ernst KD, Boeckh J (1983) A neuroanatomical study on the organization of the central antennal pathways in insects. III. Neuroanatomical characterization of physiologically defined response types of deutocerebral neurons in Periplaneta americana. Cell Tissue Res 229: 1–22
Flanagan D, Mercer AR (1989) Morphology and response characteristics of neurones in the deutocerebrum of the brain of the honeybee Apis mellifera. J Comp Physiol A 164: 483–494
Fonta C, Sun X-J, Masson C (1993) Morphology and spatial distribution of bee antennal lobe interneurones responsive to odours. Chem Senses 18: 101–119
Fuzessery ZM (1978) Quantitative stimulation of antennular chemoreceptors of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Comp Biochem Physiol 60: 303–308
Grünert U, Ache BW (1988) Ultrastructure of the aesthetasc (olfactory) sensilla of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Cell Tissue Res 251: 95–103
Hanström B (1968) Vergleichende Anatomie des Nervensystems der wirbellosen Tiere. A. Asher & Co., Amsterdam
Helluy S, Sandeman R, Beltz B, Sandeman D (1993) Comparative brain ontogeny of the crayfish and clawed lobster: Implications of direct and larval development. J Comp Neurol 335: 343–354
Helm F (1928) Vergleichend-anatomische Untersuchungen über das Gehirn, insbesondere das “Antennalganglion” der Dekapoden. Z Morph Ökol Tiere 12: 70–134
Homberg U (1984) Processing of antennal information in extrinsic mushroom body neurons of the bee brain. J Comp Physiol A 154: 825–836
Homberg U, Christensen TA, Hildebrand JG (1989) Structure and function of the deutocerebrum in insects. Annu Rev Entomol 34: 477–501
Johansson KUI (1991) Identification of different types of serotoninlike immunoreactive olfactory interneurons in four infraorders of decapod crustaceans. Cell Tissue Res 264: 357–362
Kanzaki R, Arbas EA, Strausfeld NJ, Hildebrand JG (1989) Physiology and morphology of projection neurons in the antennal lobe of the male moth Manduca sexta. J Comp Physiol A 165: 427–453
Koontz MA, Schneider D (1987) Sexual dimorphism in neuronal projections from the antennae of silk moths (Bombyx mori, Antheraea polyphemus) and the gypsy moth (Lymantria dispar). Cell Tissue Res 249: 39–50
Laurent G, Naraghi M (1994) Odorant-induced oscillations in the mushroom bodies of the locust. J Neurosci 14: 2993–3004
Laverack MS (1964) The antennular sense organs of Panulirus argus. Comp Biochem Physiol 13: 301–321
Laverack MS, Ardill DJ (1965) The innervation of the aesthetasc hairs of Panulirus argus. Quart J MICR Sci 106: 45–60
Leise EM, Mulloney B (1986) The osmium-ethyl gallate procedure is superior to silver impregnations for mapping neuronal pathways. Brain Res 367: 265–272
Macrides F, Chorover SL (1972) Olfactory bulb units: activity correlated with inhalation cycles and odor quality. Science 175: 84–87
Matsumoto SG, Hildebrand JG (1981) Olfactory mechanisms in the moth Manduca sexta: response characteristics and morphology of central neurons in the antennal lobes. Proc R Soc Lond B 213: 249–277
Mellon D Jr, Alones V (1993) Cellular organization and growthrelated plasticity of the crayfish olfactory midbrain. Microsc Res Tech 24: 231–259
Mellon D Jr, Munger SD (1990) Nontopographic projection of olfactory sensory neurons in the crayfish brain. J Comp Neurol 296: 253–262
Mellon D Jr, Alones V, Lawrence MD (1992a) Anatomy and fine structure of neurons in the deutocerebral projection pathway of the crayfish olfactory system. J Comp Neurol 321: 93–111
Mellon D Jr, Sandeman DC, Sandeman RE (1992b) Characterization of oscillatory olfactory interneurones in the protocerebrum of the crayfish. J Exp Biol 167: 15–38
Orona E, Ache BW (1992) Physiological and pharmacological evidence for histamine as a neurotransmitter in the olfactory CNS of the spiny lobster. Brain Res 590: 136–143
Reeder PB, Ache BW (1980) Chemotaxis in the Florida spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Anim Behav 28: 831–839
Sandeman DC, Denburg JL (1976) The central projections of chemoreceptor axons in the crayfish revealed by axoplasmic transport. Brain Res 115: 492–496
Sandeman DC, Luff SE (1973) The structural organization of glomerular neuropile in the olfactory and accessory lobes of an Australian freshwater crayfish, Cherax destructor. Z Zellforsch 142: 37–61
Sandeman RE, Sandeman DC (1987) Serotonin-like immunoreactivity of giant olfactory interneurons in the crayfish brain. Brain Res 403: 371–374
Sandeman DC, Sandeman RE (1994) Electrical responses and synaptic connections of giant serotonin-immunoreactive neurons in crayfish olfactory and accessory lobes. J Comp Neurol 341: 130–144
Sandeman DC, Sandeman RE, Aitken AR (1988) Atlas of serotonin-containing neurons in the optic lobes and the brain of the crayfish, Cherax destructor. J Comp Neurol 269: 465–478
Sandeman D, Sandeman R, Derby C, Schmidt M (1992) Morphology of the brain of crayfish, crabs, and spiny lobsters: A common nomenclature for homologous structures. Biol Bull 183: 304–326
Sandeman DC, Scholtz G, Sandeman RE (1993) Brain evolution in decapod Crustacea. J Exp Zool 265: 112–133
Schildberger K (1984) Multimodal interneurons in the cricket brain: properties of identified extrinsic mushroom body cells. J Comp Physiol A 154: 71–79
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1991) FMRFamide-like immunoreactivity in the olfactory brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Chem Senses 16: 408
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1992) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lobster. II. Sensory innervation of the olfactory lobe. J Comp Neurol 318: 291–303
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1993) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lobster. III. Central arborizations of motoneurons. J Comp Neurol 336: 583–594
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1994) Descending neurons with dopamninelike or with substance P/FMRF-like immunoreactivity target the somata of olfactory interneurons in the brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. Cell Tissue Res 278: 337–352
Schmidt M, Ache BW (1996) Processing of antennular input in the brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus. I. Non-olfactory chemosensory and mechanosensory pathway of the lateral and median antennular neuropils. J Comp Physiol A
Schmidt M, Orona E, Waechter S, Batelle B-A, Ache BW (1990) Serotonin in the central olfactory system of the spiny lobster Panulirus argus. Chem Senses 15: 634–635
Schmidt M, Orona E, Ache BW (1991) Parallel processing of chemosensory input in the brain of the spiny lobster. Soc Neurosci Abstr 17: 1018
Schmidt M, Van Ekeris L, Ache BW (1992) Antennular projections to the midbrain of the spiny lobster. I. Sensory innervation of the lateral and medial antennular neuropils. J Comp Neurol 318: 277–290
Schmitt BC, Ache BW (1979) Olfaction: Responses of a decapod crustacean are enhanced by flicking. Science 205: 204–206
Spencer M (1986) The innervation and chemical sensitivity of single aesthetasc hairs. J Comp Physiol A 158: 59–68
Spencer M, Linberg KA (1986) Ultrastructure of aesthetasc innervation and external morphology of the lateral antennule setae of the spiny lobster Panulirus interruptus (Randall). Cell Tissue Res 245: 69–80
Stocker RF, Lienhard MC, Borst A, Fischbach K-F (1990) Neuronal architecture of the antennal lobe in Drosophila melanogaster. Cell Tissue Res 262: 9–34
Strausfeld NJ (1976) Atlas of an insect brain. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg, New York
Sun X-J, Fonta C, Masson C (1993) Odour quality processing by the antennal lobe interneurons. Chem Senses 18: 355–377
Takami S, Graziadei PPC (1990) Morphological complexity of the glomerulus in the rat accessory olfactory bulb-A Golgi study. Brain Res 510: 339–342
Tierney AJ, Thompson CS, Dunham DW (1986) Fine structure of aesthetasc chemoreceptors in the crayfish Orconectes propinquus. Can J Zool 64: 392–399
Wachowiak M, Ache BW (1993) Whole-cell recording from multiglomerular projection neurons in the olfactory lobe of the spiny lobster. Chem Senses 18: 645–646
Wachowiak M, Ache BW (1994) Morphology and physiology of multiglomerular olfactory projection neurons in the spiny lobster. J Comp Physiol A 175: 35–48
Waldow U (1975) Multimodale Neurone im Deutocerebrum von Periplaneta americana. J Comp Physiol 101: 329–341
Weissburg MJ, Zimmer-Faust RK (1993) Life and death in moving fluids: Hydrodynamic effects on chemosensory-mediated predation. Ecology 74: 1428–1443
Witthöft W (1967) Absolute Anzahl und Verteilung der Zellen im Hirn der Honigbiene. Z Morph Ökol Tiere 61: 160–184
Young SJ, Royer SM, Groves PM, Kinnamon JC (1987) Threedimensional reconstructions from serial micrographs using the IBM PC. J Electron Microsc Tech 6: 207–217
Zippel HP, Voigt R, Wächter T, Kühling-Thees J (1986) Goldfish olfactory bulb neurons respond to mechano- thermo- and nonolfactory stimuli applied to the olfactory mucosa. Chem Senses 11: 683
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schmidt, M., Ache, B.W. Processing of antennular input in the brain of the spiny lobster, Panulirus argus . J Comp Physiol A 178, 605–628 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227375
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227375