Abstract
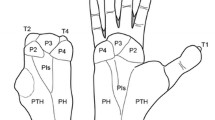
The physiological representation of the forepaw in rat primary somatosensory cortex (SI) is topographically organized. This representation is associated with the unique arrangement of barrels in layer IV of the forepaw barrel subfield (FBS) in SI and provides an example of a relationship between cortical structure and function. It has been reported that removal of peripheral afferent input to the FBS prior to postnatal day 5 or 6 results in a disorganized FBS, while deafferentation at later times produces little or no alteration of the FBS. Therefore, restricted deafferentations of individual digits in adult rats should result in little, if any, disruption of the FBS, while at the same time eliminating afferent input to the FBS from a localized region of the periphery. This manipulation is likely to create a mismatch between structure and function and offer insight into what barrels actually represent in the adult deafferent. In the present study, we amputated digit three (D3) in eight adult rats, allowed a 1-month survival time, physiologically mapped the representation of D2, D4, and the stump, and compared this physiological map to the underlying barrels in the FBS. Our results showed that FBS barrels formerly associated with the representation of D3 were now associated with the representation of surrounding digits D2 and D4, as well as the remaining stump. By superimposing the morphological and physiological map upon one another, it was clear that the D2 and D4 representations expanded into the former D3 barrel territory and septae between the barrels. The reorganized physiological map was somatotopically organized, even though the general configuration of the morphological map remained unaltered, as visualized with cytochrome oxidase staining. These results suggest that in the deafferent, neurons within FBS barrels previously associated with the representation of punctate regions of skin become associated with neighboring regions of skin. A morphological substrate to account for this cortical reorganization is described.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Armstrong-James M, Callahan CA (1991) Thalamo-cortical processing of vibrissal information in the rat. II. Spatiotemporal convergence in the thalamic ventroposterior medial nucleus (VPm) and its relevance to generation of receptive fields of S 1 cortical “barrel” neurones. J Comp Neurol 303:211–214
Armstrong-James M, Millar J (1979) Carbon fibre microelectrodes. J Neurosci Methods 1:279–287
Armstrong-James M, Callahan CA, Friedman MA (1991) Thalamo-cortical processing of vibrissal information in the rat. I. Intracortical origins of surround but not centre-receptive fields of layer IV neurones in the rat S1 barrel field cortex. J Comp Neurol 303:193–210
Calford MB, Tweedale R (1988) Immediate and chronic changes in responses of somatosensory cortex in adult flying-fox after digit amputation. Nature 332:446–448
Dawson DR, Killackey HP (1987) The organization and mutability of the forepaw and hindpaw representations in the somatosensory cortex of the neonatal rat. J Comp Neurol 256: 246–256
Horikawa K, Armstrong WE (1988) A versatile means of intracellular labeling: injection of biocytin and its detection with avidin conjugates. J Neurosci Methods 25:1–11
Iggo A, Andres H (1982) Morphology of cutaneous receptors. Annu Rev Neurosci 5:1–31
Istvan PJ, Zarzecki P (1994) Intrinsic discharge patterns and somatosensory inputs for neurons in raccoon primary somatosensory cortex. J Neurophysiol 6:2827–2839
Jeanmonod D, Rice FL, Van der Loos H (1977) Mouse somatosensory cortex: development of the alterations in the barrelfield which are caused by injury to the vibrissal follicles. Neurosci Lett 6:151–156
Jeanmonod D, Rice FL, Van der Loos H (1981) Mouse somatosensory cortex: alterations in the barrelfield following receptor injury at different postnatal ages. Neuroscience 6:1503–1535
Kelahan AM, Doetsch GS (1984) Time-dependent changes in the functional organization of somatosensory cerebral cortex following digit amputation in adult raccoons. Somatosens Res 1:49–81
Kelahan AM, Ray RH, Carson LV, Massey CE, Doetsch GS (1981) Functional reorganization of adult raccoon somatosensory cerebral cortex following neonatal digit amputation. Brain Res 223:152–159
Killackey HP, Belford GR, Ryugo G, Ryugo D (1976) Anomalous organization of thalamocortical projections consequent to vibrissae removal in the newborn rat and mouse. Brain Res 104:309–315
Li C, Waters RS (1995) A possible substrate for immediate cortical reorganization is observed in layer IV neurons of rat forepaw barrel subfield (FBS) that send their dendrites into neighboring barrel bands: an intracellular recording and labeling study. Soc Neurosci Abstr 21:124
Merzenich MM, Kaas JH, Wall J, Nelson RJ, Sur M, Felleman D (1983) Topographic reorganization of somatosensory cortical areas 3b and 1 in adult monkey following restricted deafferentation. Neuroscience 8:33–55
Merzenich MM, Nelson RJ, Stryker MP, Cynader MS, Schoppman A, Zook JM (1984) Somatosensory cortical map changes following digit amputation in adult monkeys. J Comp Neurol 224:591–605
Munger BL, Rice FL (1986) Successive waves of differentiation of cutaneous afferents in mystacial skin. J Comp Neurol 252: 404–414
Simons DJ (1978) Response properties of vibrissa units in the rat SI somatosensory neocortex. J Neurophysiol 41:798–820
Turnbull BG, Rasmusson DD (1991) Chronic effects of total or partial digit denervation on raccoon somatosensory cortex. Somatosens Mot Res 8:201–213
Waite PME, Cragg BG (1979) The effect of destroying the whisker follicles in mice on the sensory nerve, the thalamocortical radiation and cortical barrel development. Proc R Soc Lond 204:41–55
Wall JT, Cusick CG (1984) Cutaneous responsiveness in primary somatosensory (S-I) hindpaw cortex before and after partial handpaw deafferentation in adult rats. J Neurosci 6:1499–1515
Waters RS, Li CX (1992) Evidence for rapid changes in the receptive field organization of SI cortex in squirrel monkey: an intracellular recording study combined with reversible deafferentation. Soc Neurosci Abstr 18:1543
Waters RS, McCandlish CA, Cooper NGF (1990) Early development of SI cortical barrel subfield representation of forelimb in normal and deafferented neonatal rat as delineated by peroxidase conjugated lectin, peanut agglutinin (PNA). Exp Brain Res 81:234–240
Waters RS, Li CX, McCandlish CA (1995a) Relationship between the organization of the forepaw barrel subfield (FBS) and the representation of the forepaw in layer IV of rat somatosensory (SI) cortex. Exp Brain Res 103:183–197
Waters RS, McCandlish CA, Li CX (1995b) Organization and development of the forepaw representation in rodent barrel subfield (FBS) in somatosensory cortex of rat. Jones EG, Diamond JT (eds) Cerebral cortex, vol 11. Plenum Press, New York London
Welker C (1976) Receptive fields of barrels in the somatosensory neocortex of the rat. J Comp Neurol 166:173–190
Weller WL, Johnson JI (1975) Barrels in cerebral cortex altered by receptor disruption in newborn, but not in five-day old mice (Cricetidae and Muridae). Brain Res 83:504–508
Wong-Riley MT, Welt C (1980) Histochemical changes in cytochrome oxidase of cortical barrels after removal in neonatal and adult mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 77:2333–2337
Woolsey TA, Wann JR (1976) Areal changes in mouse cortical barrels following vibrissal damage at different postnatal ages. J Comp Neurol 170:53–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
McCandlish, C.A., Li, C.X., Waters, R.S. et al. Digit removal leads to discrepancies between the structural and functional organization of the forepaw barrel subfield in layer IV of rat primary somatosensory cortex. Exp Brain Res 108, 417–426 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227264
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00227264