Abstract
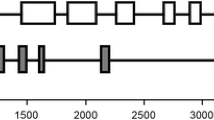
Recently, two distinct cDNA clones encoding the catalytic subunit of the vacuolar H+-ATPase (V-ATPase) were isolated from the allotetraploid cotton species Gossypium hirsutum L. cv ‘Acala SJ-2’ (Wilkins 1992, 1993). Differences in the nucleotide sequence of these clones were used as molecular markers to explore the organization and structure of the V-ATPase catalytic subunit genes in the A and D genomes of diploid and allotetraploid cotton species. Nucleotide sequencing of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) products amplified from G. arboreum (A2, 2n=26), G. raimondii (D5, 2n=26), and G. hirsutum cv ‘Acala SJ-2’ [(AD)1, 2n=4x=52] revealed a V-ATPase catalytic subunit organization more complex than indicated hitherto in any species, including higher plants. In the genus Gossypium, the V-ATPase catalytic subunit genes are organized as a superfamily comprising two diverse but closely related multigene families, designated as vat69A and vat69B, present in both diploid and allotetraploid species. As expected, each vat69 subfamily is correspondingly more complex in the allotetraploid species due to the presence of both A and D alloalleles. Because of this, about one-half of the complex organization of V-ATPase catalytic subunit genes predates polyploidization and speciation of New World tetraploid species. Comparison of plant and fungal V-ATPase catalytic subunit gene structure indicates that introns accrued in the plant homologs following the bifurcation of plant and fungi but prior to the gene duplication event that gave rise to the vat69A and vat69B genes approximately 45 million years ago. The structural complexity of plant V-ATPase catalytic subunit genes is highly conserved, indicating the presence of at least ten introns dispersed throughout the coding region.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham P (1940) Cytological studies in Gossypium. I. Chromosome behavior in interspecific hybrid G. arboreum × G. stocksii. Indian J Agric Sci 10:285–298
Beasley JO (1942) Meiotic chromosome behavior in species, species hybrids, haploids and induced polyploids of Gossypium. Genetics 27:25–54
Bowman BJ, Vázquez-Laslop N, Bowman EJ (1992) The vacuolar ATPase of Neurospora crassa. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24:361–370
Bowman EJ, Tenney K, Bowman BJ (1988) Isolation of genes encoding the Neurospora vacuolar ATPase. J Biol Chem 263:13994–14001
Chanson A, Taiz L (1985) Evidence for an ATP-dependent proton pump on the Golgi of corn coleoptiles. Plant Physiol 78:232–240
Darlington CD, Wylie AP (1955) Chromosome atlas of flowering plants, 2nd edn. George Allen and Unwin, London
Davie JH (1933) Cytological studies in the Malvaceae and certain related families. J Genet 28:33–67
Depta H, Holstein SEH, Robinson DG, Lutzelschwab M, Michalke W (1991) Membranes markers in highly purified clathrin-coated vesicles from Cucurbita hypocotyls. Planta 183:434–442
Dupont FM, Tanaka CK, Hurkman WJ (1988) Separation and immunological characterization of membrane fractions from barley roots. Plant Physiol 86:717–724
Ehrendorfer F, Krendl F, Habeier E, Sauer W (1968) Chromosome numbers and evolution in primitive angiosperms. Taxon 17:337–468
Endrizzi JE, Turcotte EL, Kohel RJ (1985) Genetics, cytology, and evolution of Gossypium. Adv Genet 23:271–375
Feinberg AP, Vogelstein B (1983) A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem 132:6–13
Fryxell PA (1979) The natural history of the cotton tribe. Texas A&M University Press, College Station, Tex
Galau GA, Wilkins TA (1989) Alloplasmic male sterility in AD allotetraploid Gossypium hirtutum upon replacement of its resident A cytoplasm with that of D species G. harknessii. Theor Appl Genet 78:23–30
Galau GA, Bass HW, Hughes DW (1988) Restriction fragment length polymorphisms in diploid and tetraploid Gossypium: assigning the late embryogenesis abundant (Lea) alloalleles in G. hirsutum. Mol Gen Genet 211:305–314
Ghislain M, Bowman EJ (1992) Sequence of the genes encoding subuints A and B of the vacuolar H+-ATPase of Schizosaccharomyces pombe. Yeast 8:791–799
Gogarten JP, Taiz L (1992) Evolution of proton pumping ATPases: rooting the tree of life. Photosyn Res 33:137–146
Gogarten JP, Kibak H, Dittrich P, Taiz L, Bowman EJ, Bowman BJ, Manolson MF, Poole RJ, Date T, Oshima T, Konishi J, Denda K and Yoshida M (1989) Evolution of the vacuolar H+-ATPase: implication of the origin of eukaryotes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:6661–6665
Gogarten JP, Fishmann J, Braun Y, Morgan L, Styles P, Taiz SL, DeLapp K, Taiz L (1992a) The use of antisense mRNA to inhibit the tonoplast H+-ATPase in carrot. Plant Cell 4:851–864
Gogarten JP, Starke T, Kibak H, Fishmann J, Taiz L (1992b) Evolution and isoforms of V-ATPase subunits. J Exp Biol 172:137–147
Goldblatt P (1980) Polyploidy in angiosperms: monocotyledons. In: Lewis WH (ed) Polyploidy, biological relevance. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 219–239
Grant V (1981) Plant speciation, 2nd edn. Columbia University Press, New York
Hirata R, Ohsumi Y, Nakano A, Kawasaki H, Suzuki K, Anraku Y (1990) Molecular structure of a gene, VMA1, encoding the catalytic subunit of H+-translocating adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem 265:6726–6733
Hutchinson JB, Silow RA, Stephens SG (1947) The evolution of Gossypium. Oxford University Press, London
Iwabe N, Kuma K-I, Hasegawa M, Osawa S, Miyata T (1989) Evolutionary relationship of archaebacteria, eubacteria, and eukaryotes inferred from phylogenetic trees of duplicated genes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:9355–9359
Johnson BL (1975) Gossypium palmeri and a polyphyletic origin of the New World cottons. Bull Torrey Bot Club 102:340–349
Kibak H, Taiz L, Starke T, Bernasconi P, Gogarten JP (1992) Evolution of structure and function of V-ATPases. J Bioenerg Biomembr 24:415–424
Lawrence WJC (1931) The secondary association of chromosomes. Cytologia 2:352–384
Lewis WH (1980) Polyploidy in angiosperms: dicotyledons. In: Lewis WH (ed) Polyploidy, biological relevance. Plenum Press, New York London, pp 241–268
Narasimhan ML, Binzel ML, Perez-Prat E, Chen Z, Nelson DE, Singh NK, Bressan RA, Hasegawa PM (1991) NaCl regulation of tonoplast ATPase 70-kilodalton subunit mRNA in tobacco cells. Plant Physiol 97:562–568
Palmer JD, Logsdon JM Jr (1991) The recent origin of introns. Curr Opin Genet Dev 1:470–477
Phillips LL (1963) The cytogenetics of Gossypium and the origin of New World cottons. Evolution 17:460–469
Puopolo K, Kumamoto C, Adachi I, Forgac M (1991) A single gene encodes the catalytic-A subunit of the bovine vacuolar H+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 266:24564–24572
Randall SK, Sze H (1986) Properties of the partially purified tonoplast H+-pumping ATPase from oat roots. J Biol Chem 261:1364–1371
Raven PH (1975) The basis of angiosperm phytogeny: cytology. Ann Mo Bot Gard 62:724–764
Saiki RK, Scharf S, Faloona F, Mullis KB, Horn GT, Erlich HA, Arnheim N (1985) Enzymatic amplification of β-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science 230:1350–1354
Sambrook J, Fritsch EF, Maniatis T (1989) Molecular cloning: a laboratory manual, 2nd edn. Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, Cold Spring Harbor, N.Y.
Sanger F, Nicklen S, Coulson AR (1977) DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 74:5463–5467
Shih C-K, Wagner R, Geinstein S, Kanik-Ennulat C, Neff N (1988) A dominant trifluoperazine resistance gene from Saccharomyces cerevisiae has homology with F0F1 ATP synthase and confers calcium-sensitive growth. Mol Cell Biol 8:3094–3103
Skovsted A (1933) Cytolotical studies in cotton. I. The mitosis and meiosis in diploid and triploid Asiatic cotton. Ann Bot 47:227–251
Skovsted A (1934) Cytological studies in cotton. II. Two interspecific hybrids between Asiatic and New World cotton. J Genet 28:407–424
Soltis DE, Soltis PS (1990) Isozyme evidence for ancient polyploidy in primitive angiosperms. Syst Bot 15:328–337
Starke T, Gogarten JP (1993) A conserved intron in the V-ATPase A subunit genes of plants and algae. FEBS Lett 315:252–258
Starke T, Linkkila TP, Gogarten JP (1991) Two separate genes encode the catalytic 70-kDa V-ATPase subunit in Psilotum and Equisetum. Z Naturforsch 46c:613–620
Stebbins GL (1947) Evidence on rates of evolution from the distribution of existing and fossil plant species. Ecol Monogr 17:149–158
Stebbins GL (1971) Chromosomal evolution in higher plants. Edward Arnold, London
Stephens SG (1944a) The genetic organization of leaf-shape development in the genus Gossypium. J Genet 46:28–51
Stephens SG (1944b) Phenogenetic evidence for amphidiploid origin of New World cotton. Nature 153:53–54
Stephens SG (1950) The internal mechanism of speciation in Gossypium. Bot Rev 16:115–149
Struve I, Rausch T, Bernasconi P, Taiz L (1990) Structure and function of the promoter of the carrot V-type H+-ATPase catalytic subunit gene. J Biol Chem 265:7927–7932
Suiter KA (1988) Genetics of allozyme variation in Gossypium arboreum L. and Gossypium herbaceum L. (Malvaceae) Theor Appl Genet 75:259–271
Vieira J, Messing J (1987) Production of single-stranded plasmid DNA. Method Enzymol 153:3–11
Wan C-Y, Wilkins TA (1993) Spermidine facilitates PCR amplification of target DNA. PCR Method Applic 3:208–210
Wang Y, Sze H (1985) Similarities and differences between the tonoplast-type and the mitochondrial H+-ATPases of oat roots. J Biol Chem 260:10434–10443
Wendel JF (1989) New World tetraploid cottons contain Old World cytoplasm. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:4132–4136
Wilkins TA (1992) Role of proton pumps in cotton fiber development. In: Benedict CR (ed) Proc Cotton Fiber Cellulose Conf. Savannah GA, pp 141–145
Wilkins TA (1993) Vacuolar H+-ATPase 69-kilodalton catalytic subunit cDNA from developing cotton (Gossypium hirsutum) ovules. Plant Physiol 102:679–680
Wolfe KH, Sharp PM, Li W-H (1989) Rates of synonomous substitution in plant nuclear genes. J Mol Evol 29:208–211
Zimniak L, Dittrich P, Gogarten JP, Kibak H, Taiz L (1988) The cDNA sequence of the 69-kDa subunit of the carrot vacuolar H+-ATPase. J Biol Chem 263:9102–9112
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Communicated by G. S. Khush
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wilkins, T.A., Wan, CY. & Lu, CC. Ancient origin of the vacuolar H+-ATPase 69-kilodalton catalytic subunit superfamily. Theoret. Appl. Genetics 89, 514–524 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225389
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00225389