Summary
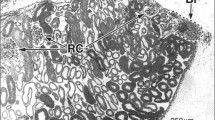
The ultrastructure of cat mesenteric Pacinian corpuscles in cross and longitudinal sections has been examined. The terminal ends of lamellar cells of the inner core have been identified in longitudinal sections through the proximal portion of the inner core. These terminal bulbous expansions contain characteristic concentric membranes of rough endoplasmic reticulum and in some cases masses of oval membranous inclusions. The central axon as seen in cross section is oval in profile, having X-(short) and Y-(long) axes, and each axonal face is characterized by specializations of the axolemma. At the X-axis, the inner lamellae of the inner core tightly abut a smooth axolemma, with no intervening connective tissue matrix, in a manner reminiscent of a neuroepithelium. The axolemma of the Y-axis has numerous axonal spines (microspikes) that project into the cleft in the inner core. The extent of the axolemma having axonal spines can only be appreciated in longitudinal sections. The clefts contain a specialized connective tissue with elastic and collagen fibrils. The connective tissue compartment of fibers and matrix separating individual inner core lamellae is unique, in that it contains extremely thin collagen fibrils measuring approximately 15 nm in diameter. The diameter of collagen fibrils increases as the cleft is approached. Here the fibrils resemble typical endoneural collagen.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andres KH (1966) Über die Feinstruktur der Rezeptoren an Sinushaaren. Z Zellforsch 75:339–385
Covaja N, Magherini PC, Pompeiano O (1967) Close apposition and junctions of plasma membranes of intrafusal muscle fibers in mammalian muscle spindles. Pflügers Arch Gen Physiol 296:337–345
English KB, Burgess PR, Norman DK-V (1980) Development of rat Merkel cells. J Comp Neurol 194:475–496
Halata Z (1975) The mechanoreceptors of the mammalian skin: Ultrastructure and morphological classification. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol 50:1–77
Halata M, Munger BL (1983) The sensory innervation of primate facial skin. II: Vermilion border and mucosa of lip. Brain Res Rev 5:81–107
Ide C (1976) The fine structure of the digital corpuscle of the mouse toe pad, with special reference to nerve fibers. Am J Anat 147:329–356
Ide C, Hayashi S (1988) Specialization of plasma membrane in Pacinian corpuscles: Implications of mechano-electric transduction. J Neurocytol (in press)
Ide C, Kumagai K, Hayashi S (1985) Freeze-fracture study of mechanoreceptive digital corpuscle of mice. J Neurocytol 14:1037–1052
Ide C, Yoshida Y, Hayasky S, Takashio M, Munger BL (1988) A re-evaluation of the cytology of Pacinian corpuscles. II. The extreme tip of the axon. Cell Tissue Res 253:95–103
Loewenstein WR (1971) Mechano-electric transduction in a Pacinian corpuscle: Initiation of sensory impulses in mechanoreceptors. In: Loewenstein WR (ed) Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 269–290
Munger BL (1971a) Pattern of organization of peripheral sensory receptors. In: Loewenstein WR (ed) Handbook of Sensory Physiology, Vol I. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 253–556
Munger BL (1971b) The comparative ultrastructure of slowly and rapidly adapting mechanoreceptors. In: Dubner R, Kawamura Y (eds) Oral-Facial Sensory and Motor Mechanism, AppletonCentury-Crofts, New York, pp 83–103
Munger BL, Ide C (1987) The enigma of sensitivity in Pacinian corpuscles. A critical review and hypothesis for mechano-electric transduction. Neurosci Res 5:1–15
Nafstad PH (1971) Comparative ultrastructural study on Merkel cells and dermal basal cells in poultry (Gallus domesticus). Z Zellforsch 116:342–348
Orfanos C (1967) Elektronenmikroskopischer Nachweis epithelioneuraler Verbindungen (Mechano-Receptoren) am Haarfollikelepithel des Menschen. Arch Klin Exp Dermatol 228:421–429
Osawa T, Ide C (1986) Changes in thickness of collagen fibrils in endoand epineurium of the mouse sciatic nerve during development. Acta Anat 125:245–351
Pease DC, Quilliam TA (1957) Electron microscopy of the Pacinian corpuscle. J Biopys Biochem Cytol 3:331–347
Spencer PS, Schaumburg HH (1973) An ultrastructural study of the inner core of the Pacinian corpuscle. J Neurocytol 2:217–235
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Munger, B.L., Yoshida, Y., Hayashi, S. et al. A re-evaluation of the cytology of cat Pacinian corpuscles. Cell Tissue Res. 253, 83–93 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221743
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00221743