Abstract
-
1.
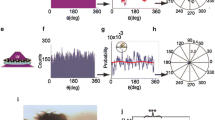
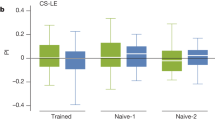
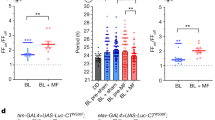
Wildtype Oregon-R Drosophila melanogaster were trained in the ambient magnetic field to a horizontal gradient of 365 nm light emanating from one of the 4 cardinal compass directions and were subsequently tested in a visually-symmetrical, radial 8-arm maze in which the magnetic field alignment could be varied. When tested under 365 nm light, flies exhibited consistent magnetic compass orientation in the direction from which light had emanated in training.
-
2.
When the data were analyzed by sex, males exhibited a strong and consistent magnetic compass response while females were randomly oriented with respect to the magnetic field.
-
3.
When tested under 500 nm light of the same quantal flux, females were again randomly oriented with respect to the magnetic field, while males exhibited a 90° clockwise shift in magnetic compass orientation relative to the trained direction.
-
4.
This wavelength-dependent shift in the direction of magnetic compass orientation suggests that Drosophila may utilize a light-dependent magnetic compass similar to that demonstrated previously in an amphibian. However, the data do not exclude the alternative hypothesis that a change in the wavelength of light has a non-specific effect on the flies' behavior, i.e., causing the flies to exhibit a different form of magnetic orientation behavior.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arendse MC (1978) Magnetic field detection is distinct from light detection in the invertebrates Tenebrio and Talitrus. Nature 274:358–362
Arendse MC, Vrins JCM (1975) Magnetic orientation and its relation to photic orientation in Tenebrio molitor L. (Coleoptera, Tenebrionidae). Netherlands J Zool 25(4): 407–437
Batschelet E (1981) Circular statistics in biology. Academic Press, London New York
Feiler R, Harris WA, Kirschfeld K, Wehrhahn C, Zuker CS (1988) Targeted misexpression of a Drosophila opsin gene leads to altered visual function. Nature 333:737–741
Feiler R, Bjornson R, Kirschfeld K, Mismer D, Rubin GM, Smith DP, Socolich M, Zuker CS (submitted) Ectopic expression of ultraviolet-rhodopsins in the blue photoreceptor cells of Drosophila: visual physiology and photochemistry of transgenic animals. J Neurosci
Harris WA, Stark WS, Walker JA (1976) Genetic dissection of the photoreceptor system in the compound eye of Drosophila melanogaster. J Physiol (Lond) 256:414–439
Kirschfeld K, Franceschini N, Minke B (1977) Evidence for a sensitizing pigment in fly photoreceptors. Nature 269:386–390
Kirschfeld K, Feiler R, Hardie R, Vogt D, Franceschini N (1983) The sensitizing pigment in fly photoreceptors. Properties and candidates. Biophys Struct Mech 10:81–92
Kirschfeld K, Hardie R, Lenz G, Vogt K (1988a) The pigment system of the photoreceptor 7 yellow in the fly, a complex photoreceptor. J Comp Physiol A 162:421–433
Kirschfeld K, Feiler R, Vogt K (1988b) Evidence for a sensitizing pigment in the ocellar photoreceptors of the fly (Musca, Calliphora). J Comp Physiol A 163:421–423
Kirschvink JL, Jones DS, MacFadden BJ (1985) Magnetite biomineralization and magnetoreception in organisms: a new biomagnetism. Plenum Press, New York
Leask MJM (1977) A physicochemical mechanism for magnetic field detection by migrating birds and homing pigeons. Nature 267:144–145
Merritt R, Prucell C, Stroink G (1983) Uniform magnetic field produced by three, four, and five square coils. Rev Sci Instrum 54:879–882
Olcese J, Reuss S, Semm P (1988) Geomagnetic field detection in rodents. Life Sci 42:605–613
Phillips JB (1986) Two magnetoreception pathways in a migratory salamander. Science 233:765–767
Phillips JB (1986) Magnetic compass orientation in the Eastern red-spotted newt (Notophthalmus viridescens). J Comp Physiol A 158:103–109
Phillips JB (1987) Specialized visual receptors respond to magnetic field alignment in the blowfly (Calliphora vicina). Soc Neurosci Abstr 13:397
Phillips JB, Borland SC (1992) Behavioral evidence for the use of a light-dependent magnetoreception mechanism by a vertebrate. Nature 359:142–144
Schulten K (1982) Magnetic field effects in chemistry and biology. Adv Solid State Phys 22:61–83
Semm P, Demaine C (1986) Neurophysiological properties of magnetic cells in the pigeon's visual system. J Comp Physiol A 159:619–625
Semm P, Nohr D, Demaine C, Wiltschko W (1984) Neural basis of the magnetic compass: Interactions of visual, magnetic and vestibular inputs in the pigeon's brain. J Comp Physiol A 155:283–288
Stark WS (1977) Sensitivity and adaption in R7, an ultraviolet photoreceptor in the Drosophila retina. J Comp Physiol 115:47–59
Wiltschko W, Wiltschko R (1972) Magnetic compass of European robins. Science 176:62–64
Zuker CS, Mismer D, Hardy R, Rubin GM (1988) Ectopic expression of a minor Drosophila opsin in the major photoreceptor cell class: Distinguishing the role of primary receptor and cellular context. Cell 55:475–482
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Phillips, J.B., Sayeed, O. Wavelength-dependent effects of light on magnetic compass orientation in Drosophila melanogaster . J Comp Physiol A 172, 303–308 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216612
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00216612