Abstract
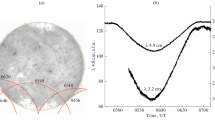
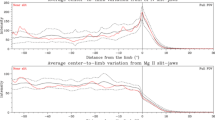
The total solar eclipse of February 26, 1979 was monitored at far infrared wavelengths from the NASA Lear Jet Observatory flying at 12.9 km in the eclipse shadow. The resultant eclipse curve for radiation within a bandwidth of 20 cm−1 centered upon 25 cm−1 (400 μm) was measured and analysed at an equivalent angular resolution of 1 arc sec over a 100 arc sec region adjacent to the limb to provide information on the intensity distribution of continuum radiation close to this limb. The curve has been compared to predictions derived from models of the solar atmosphere for the specific geometry of this eclipse, and is shown to match most closely that derived from a uniform distribution of radiation across the disk. This is in distinct contrast to the result obtained in the only other comparable experiment, carried out over Africa in 1973 from a supersonic Concorde aircraft, in which an intense but narrow ‘spike’ of far infrared radiation at the extreme solar limb was inferred from the data. The absence also in the present observations of the significant limb brightening predicted by the HSRA model (in which homogeneity within the source region is assumed) is in substantial agreement with lower resolution results from mountain altitudes. This result is interpreted as further evidence for the presence in the Sun's lower chromosphere of significant inhomogeneity with a scale size of at least 1000 km at this depth.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ade, P. A. R., Beckman, J. E., and Clark, C. D.: 1971, Nature 231, 55.
Allen, C. W.: 1973, Astrophysical Quantities, 3rd ed., Athlone Press.
Beckman, J. E. and Clark, C. D.: 1971, Solar Phys. 16, 87.
Beckman, J. E. and Ross, J.: 1976, in M. Rowan-Robinson (ed.), Far Infrared Astronomy, Pergamon.
Beckman, J. E., Clark, C. D., and Ross, J.: 1973, Solar Phys. 31, 319.
Beckman, J. E., Lesurf, J. C. G., and Ross, J.: 1975, Nature 254, 38.
Coffey, H. E. (ed.): 1979, Solar-Geophysical Data Prompt Reports 416, Part 1, p. 101.
Kundu, M. R. and Liu, S. Y.: 1975, Solar Phys. 44, 361.
Labrum, N. R., Archer, J. W., and Smith, C. J.: 1978, Solar Phys. 59, 331.
Lantos, P. and Kundu, M. R.: 1972, Astron. Astrophys. 21, 119.
Lindsey, C. and Hudson, H. S.: 1976, Astrophys. J. 203, L95.
Lindsey, C., Hildebrand, R., and de Graauw, Th.: 1980, Bull. Am. Astron. Soc. 12, 474.
Shimabukuro, F. I., Wilson, W. J., Mori, T. T., and Smith, P. L.: 1975, Solar Phys. 40, 359.
Simon, M. and Zirin, H.: 1969, Solar Phys. 9, 317.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Clark, T.A., Boreiko, R.T. Airborne total eclipse observation of the extreme solar limb at 400 μm. Sol Phys 76, 117–128 (1982). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214133
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00214133