Summary
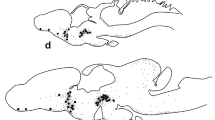
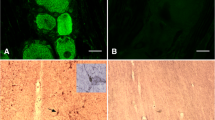
Luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH), vasopressin, and corticotropin systems were examined by immunocytochemical methods in male rats 2 to 20 days after deafferentation of the basal hypothalamus. Axonal degeneration of the vasopressin system (whose perikarya lie rostral to the island) and the corticotropin system (whose perikarya lie within the island) was examined and compared with the response of the LHRH system.
Vasopressin immunoreactive staining was absent in the internal zone of the median eminence 10 and 20 days after deafferentation. Disruption of the efferent projections of the opiocortin system caused the loss of almost all fiber staining outside the island by the 5th postoperative day. LHRH staining in the median eminence was modestly reduced in 5 days, considerably reduced in 10 days and negligible 20 days after deafferentation. At 10 and/or 20 days after deafferentation densely stained fibers of all three systems were observed on both sides of the cut. Invasive vasopressinergic fibers reached the lateral median eminence by the 20th postoperative day.
This study reports on the response of three neuropeptide systems after complete deafferentation and demonstrates that regeneration can occur across the knife cut.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barry J (1979) Immunohistochemistry of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone producing neurons of the vertebrates. Int Rev Cytol 60:179–221
Bennett-Clarke C, Joseph SA (1980) Immunocytochemical distribution of LHRH neurons and processes in the rat: Hypothalamic and extrahypothalamic locations. Cell Tissue Res (submitted)
Blake CA, Scaramuzzi RJ, Norman RL, Hillard J, Sawyer CH (1973) Effects of hypothalamic deafferentation on circulating levels of LH, FSH, prolactin and testosterone in the male rat. Endocrinology 92:1419–25
Carrillo AJ (1980) The medial basal hypothalamus and luteinizing hormone release in the rat: Where are the LH-RH neurons responsible for tonic gonadotropin secretion? Life Sci 27:179–83
Frizell M, McLean WG, Sjöstrand J (1976) Retrograde axonal transport of rapidly migrating labelled proteins and glycoproteins in regenerating peripheral nerves. J Neurochem 27:191–196
Halász B (1969) The endocrine effects of isolation of the hypothalamus from the rest of the brain. In: Ganong WF, Martini L (eds) Frontiers in Neuroendocrinology. Oxford Univ Press, New York, pp 307–42
Halász B, Pupp L (1965) Hormone secretion of the anterior pituitary gland after physical interruption of all nervous pathways to the hypophysiotrophic area. Endocrinology 77:553–62
Halász B, Florsheim WH, Corcorran NL, Gorski RA (1967) Thyrotrophic hormone secretion in rats after partial or total interruption of neural afferents to the medial basal hypothalamus. Endocrinology 80:1075–82
Joseph SA (1980) Immunoreactive adrenocorticotropin in rat brain: A neuroanatomical study using antiserum generated against synthetic ACTH 1–39. Am J Anat 158:533–48
Knigge KM (1980) Relationship of intracerebral pituitary grafts to central neuropeptide systems. Am J Anat 158:549–63
Knigge KM, Joseph SA, Nocton J (1981) Topography of the ACTH-immunoreactive neurons in the basal hypothalamus of the rat brain. Brain Res 215:333–340
Lieberman AR (1971) The axon reaction: A review of the principal features of perikaryal responses to axon injury. Int Rev Neurobiol 14:49–124
Merchenthaler I, Kovács G, Lovász G, Sétáló G (1980) The preoptico-infundibular LH-RH tract of the rat. Brain Res 198:63–74
Pelletier G, Leclerc R, Saavedra JM, Brownstein MJ, Vaudry H, Ferland L, Labrie F (1980) Distribution of b-lipotropin (b-LPH), adrenocorticotropin (ACTH) and a-melancocyte-stimulating hormone (a-MSH) in the rat brain. I. Origin of the extrahypothalamic fibers. Brain Res 192:433–440
Rodgers CH (1969) Total and partial surgical isolation of the male rat hypothalamus: Effects on reproductive behavior and physiology. Physiol Behav 4:465–470
Sétáló G, Vigh S, Schally AV, Arimura A, Flerkó B (1976) Immunohistological study of the origin of LH-RH-containing nerve fibers of the rat hypothalamus. Brain Res 103:597–602
Taketani Y, Nozaki M, Taga M, Minaguchi H, Kigawa T, Sakamoto S, Kobayashi H (1980) Effect of hypothalamic deafferentation on the distribution of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone (LHRH) in the rat brain. Endocrinol Jpn 27:297–305
Watson S, Akil H, Richard III C, Barchas J (1978) Evidence for two separate opiate peptide neuronal systems. Nature 275:226–228
Weiner RI, Pattou E, Kerdelhue B, Kordon C (1975) Differential effects of hypothalamic deafferentation upon luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone in the median eminence and organum vasculosum of the lamina terminalis. Endocrinology 97:1597–1600
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by: NIH Grants AM-22029 and Program Project NS-15345, and USPHS grant 5T32 GM-07136-06
The authors wish to express their appreciation to Ms. Barbara Dolf for her technical assistance.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Scott, P.M., Knigge, K.M. Immunocytochemistry of luteinizing hormone-releasing hormone, vasopressin, and corticotropin following deafferentation of the basal hypothalamus of the male rat brain. Cell Tissue Res. 219, 393–402 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210157
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00210157