Summary
Morphology and calcium metabolism have been studied on five different cell cultures from human normal adult temporal-bone biopsies obtained during five stapedectomies. Control cell cultures were obtained from normal human skin.
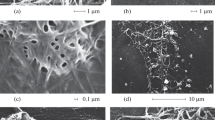
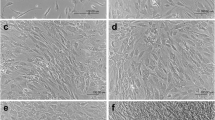
Four different cell types were observed in the bone biopsies: 1) osteoblast-like cells; 2) osteoclast-like cells; 3) fibroblast-like cells; 4) intermediate cells. However, morphology by itself is inadequate for clear differentiation of the four cell types.
Hormonal stimulation with calcitonin and dibutyryl-cAMP in presence of 45Ca++ showed a clear-cut difference in 45Ca++ uptake between cultured cells deriving from bone and skin. Functional responses to hormonal stimulation are therefore more specific than cell shape and morphology in differentiating fibroblasts from bone cells.
Since responses to hormonal stimulation confirm that temporal-bone cell cultures actually contain bone cells, such cultures seem to be a good experimental model for the study of bone morphology and physiology.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bard DR, Dickens MJ, Smith AU, Zarek JM (1972) Isolation of living cells from mature mammalian bone. Nature 236:314–315
Bindermann I, Duskin D, Harrell A, Katzir E, Sachs L (1974) Formation of bone tissue in culture from isolated bone cells. J Cell Biol 61:427–439
Borle A (1968) Calcium metabolism in HeLa cells and the effects of parathyroid hormone. J Cell Biol 36:567–581
Borle A (1969) Effects of thyrocalcitonin on calcium transport in kidney cells. Endocrinology 85:194–199
Borle A (1975) Regulation of cellular calcium metabolism and calcium transport by calcitonin. J Membr Biol 21:125–146
Dziak R, Brand JS (1974) Calcium transport in isolated bone cells. 2. Calcium transport studies. J Cell Physiol 84:85–96
Dziak R, Stern PH (1975) Calcium transport in isolated bone cells. 3. Effects of parathyroid hormone and cyclic 3′,5′ AMP. Endocrinology 97:1281–1287
Hall BK (1975) The origin and fate of osteoclasts. Anat Rec 183:1–11
Harrell A, Bindermann I, Rodan GA (1973) The effect of calcium concentration on calcium uptake by bone cells treated with thyrocalcitonin. Endocrinology 92:550–552
Heersche JNM, Marcus R, Aurbach GD (1974) Calcitonin and formation of 3′5′ AMP in bone and kidney. Endocrinology 94:241–246
Lawrence M, Arbor A (1965) In vitro culture of osteoblasts from the otosclerotic foci. Arch Otolaryngol 82:136–144
Lowry OH, Roserough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–267
Luben RA, Cohn DV (1976) Effects of parathormone and calcitonin on citrate and hyaluronate metabolism in cultured bone. Endocrinology 98:413–419
Luben RA, Wong GL, Cohn DV (1976) Biochemical characterization with parathormone and calcitonin of isolated bone cells: provisional identification of osteoblasts and osteoclasts. Endocrinology 99:526–534
Miller SS, Wolf AM, Arnaud CD (1976) Bone cells in culture: morphologic transformation by hormones. Science 192:1340–1343
Nguyen TL, Eb F, Drouet S (1976) Mise au point d'une technique de culture de cellules osseuses. CR Acad Sci Paris 283:543–545
Peck WA, Carpenter J, Messinger K (1974a) Cyclic 3′,5′-adenosine monophosphate in isolated bone cells. 2. Responses to adenosine and parathyroid hormone. Endocrinology 94:148–154
Peck WA, Messinger K, Kimmich G, Carpenter J (1974b) Stimulation of uridine incorporation in isolated bone cells by parathyroid hormone and cyclic AMP. Endocrinology 95:289–298
Peck WA, Burks JK, Wilkins J, Rodan SB, Rodan GA (1977) Evidence for preferential effects of parathyroid hormone, calcitonin and adenosine on bone and periosteum. Endocrinology 100:1357–1364
Raisz LG (1977) In: Avioli LV, Krane SM (ed) Metabolic bone disease. Academic Press. NY. pp 1–48
Rasmussen H, Tenenhouse A (1970) Cyclic adenosine monophosphate, Ca++, and membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wesl.) 59:1364–1370
Smith OM, Johnston CC Jr (1975) Cyclic 3′,5′ adenosine monophosphate levels in separated bone cells. Endocrinology 96:1261–1269
Swaminathan R, Ker J, Care AA (1974) Calcitonin and intestinal calcium absorption. J Endocrinol 61:83–88
Talmage RV, Cooper CW, Park HH (1980) Regulation of calcium transport in bone by parathyroid hormone. Vitam Horm 28:103–140
Wong GL, Cohn DV (1974) Separation of parathyroid hormone and calcitonin-sensitive cells from non-responsive bone cells. Nature 252:713–715
Wong GL, Cohn DV (1975) Target cells in bone for parathormone and calcitonin are different: enrichment for each cell type by sequential digestion of mouse calvaria and selective adhesion to polymeric overfaces. Proc Natl Acad Sci (Wesh.) 72:3167–3171
Wong GL, Kent GN, Ku KY, Cohn DV (1978) The interaction of parathormone and calcium on the hormone regulated synthesis of hyaluronic acid citrate decarboxylation in isolated cells. Endocrinology 103:2274–2282
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maurizi, M., Binaglia, L., Donti, E. et al. Morphological and functional characteristics of human temporal-bone cell cultures. Cell Tissue Res. 229, 505–513 (1983). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207694
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207694