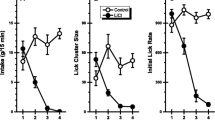
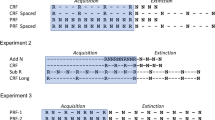
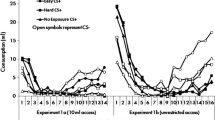
Abstract
The conditioned taste aversion (CTA) literature is extensive, yet little is known about the mechanisms by which treatments induce CTA. This paper describes and evaluates Garcia's hypothesis (e.g., Garcia et al. 1985) that treatments produce taste aversions by activating the receptors and neural pathways proposed by Borison and Wang (1953) to underlie emesis. Research on the mechanisms by which various treatments induce emesis is reviewed and compared with similar research on CTA. Emetic mechanisms appear to be involved in the formation of CTAs produced by some treatments, but there is contrary evidence for other treatments. This suggests that some CTAs are mediated by emetic mechanisms and others are not, so that Garcia's hypothesis is not generally correct. However, methodological and theoretical ambiguities make it premature to draw this conclusion.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ashe JH, Nachman M (1980) Neural mechanisms in taste aversion learning. In: Sprague JM, Epstein AN (eds) Progress in psychobiology and physiological psychology, vol 9. Academic, New York, pp 233–262
Baldessarini RJ (1980) Drugs and the treatment of psychiatric disorders. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th ed. Macmillan, New York, pp 391–447
Bechara A, van der Kooy D (1985) Opposite motivational effects of endogenous opioids in brain and periphery. Nature 314:533–534
Berger BD (1972) Conditioning of food aversions by injections of psychoactive drugs. J Comp Physiol Psychol 81:21–26
Berger BD, Wise CD, Stein L (1973) Area postrema damage and baitshyness. J Comp Physiol Psychol 82:475–479
Berk AM, Miller RR (1978) LiCl-induced aversions to audiovisual cues as a function of response measure and CS-US interval. Behav Biol 24:185–208
Best PJ, Best MR, Mickley GA (1973) Conditioned aversion to distinct environmental stimuli resulting from gastrointestinal distress. J Comp Physiol Psychol 85:250–257
Bhargava KP, Dixit KS (1968) Role of the chemoreceptor trigger zone in histamine-induced emesis. Br J Pharmacol 34:508–513
Bhargava KP, Gupta PC, Chandra O (1961) Effect of ablation of the chemoreceptor trigger zone (CT zone) on the emetic response to intraventricular injection of apomorphine and emetine in the dog. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 134:329–331
Bhargava KP, Dixit KS, Palit G (1976) Nature of histamine receptors in the emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone. Br J Pharmacol 57:211–213
Bhargava KP, Dixit KS, Gupta YK (1981) Enkephalin receptors in the emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone of the dog. Br J Pharmacol 72:471–475
Booth DA, D'Mello GD, Pilcher CWT, Stolerman IP (1977) Comparative potencies of amphetamine, fenfluramine and related compounds in taste aversion experiments in rats. Br J Pharmacol 61:669–677
Borison HL (1958) Influence of area postrema ablation on the emetic effect of adrenaline, apomorphine and pilocarpine administered by cerebral intraventricular injection in the cat. J Physiol 143:14P
Borison HL (1974) Area postrema: Chemoreceptor trigger zone for vomiting — is that all? Life Sci 14:1807–1817
Borison HL (1983) A 1983 neuropharmacologic perspective of space sickness. Brain Behav Evol 23:7–13
Borison HL (1984) History and status of the area postrema. Fed Proc 43:2937–2940
Borison HL, Fairbanks VF (1952) Mechanism of veratrum-induced emesis in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 105:317–325
Borison HL, McCarthy LE (1983) Neuropharmacologic mechanisms of emesis. In: Laszlo J (ed) Antiemetics and cancer chemotherapy. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore MD, pp 6–20
Borison HL, Sampson SR (1961) The vagal body: Receptor site for emetic action of veratrum alkaloids? Fed Proc 20:169
Borison HL, Wang SC (1949) Functional localization of central coordinating mechanism for emesis in the cat. J Neurophysiol 12:305–313
Borison HL, Wang SC (1953) Physiology and pharmacology of vomiting. Pharmacol Rev 5:193–230
Borison HL, Harris TD, Schmidt AM (1956) Central emetic action of pilocarpine in the cat. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 15:485–491
Borison HL, Brand ED, Orkand RK (1958) Emetic action of nitrogen mustard (mechlorethamine hydrochloride) in dogs and cats. Am J Physiol 192:410–416
Borison HL, Rosenstein R, Clark WG (1960) Emetic effect of intraventricular apomorphine after ultrasonic decerebration in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 130:427–430
Borison HL, Fishburn BR, Bhide NK, McCarthy LE (1962) Morphine-induced hyperglycemia in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 138:229–235
Borison HL, Hawken MJ, Hubbard JI, Sirett NE (1975) Unit activity from cat area postrema influenced by drugs. Brain Res 92:153–156
Borison HL, Borison R, McCarthy LE (1981) Phylogenic and neurologic aspects of the vomiting process. J Clin Pharmacol 21:23S–29S
Borison HL, Borison R, McCarthy LE (1984) Role of the area postrema in vomiting and related functions. Fed Proc 43:2955–2958
Bradbury M (1979) The concept of a blood-brain barrier. Wiley, Chichester
Braveman NS (1977) What studies on preexposure to pharmacological agents tell us about the nature of the aversion-inducing treatment. In: Barker LM, Best MR, Domjan M (eds) Learning mechanisms in food selection. Baylor University Press, Waco TX, pp 511–530
Braveman NS (1979) The role of blocking and compensatory conditioning in the treatment preexposure effect. Psychopharmacology 61:177–189
Brizzee KR (1956) Effect of localized brain stem lesions and supra-diaphragmatic vagotomy on X-irradiation emesis in the monkey. Am J Physiol 187:567–570
Brizzee KR, Dunlap WP (1983) Motion-induced alterations in 2-deoxyglucose uptake in brainstem nuclei of squirrel monkeys: Autoradiographic and liquid scintillation studies. Brain Behav Evol 23:14–25
Brizzee KR, Neal LM, Williams PM (1955) The chemoreceptor trigger zone for emesis in the monkey. Am J Physiol 180:659–662
Brizzee KR, Ordy JM, Mehler WR (1980) Effect of ablation of area postrema on frequency and latency of motion sickness-induced emesis in the squirrel monkey. Physiol Behav 24:849–853
Brooks MJ, Hubbard JI, Sirett NE (1983) Extracellular recording in rat area postrema in vitro and the effects of cholinergic drugs, serotonin, and angiotensin II. Brain Res 261:85–90
Cappell H, LeBlanc AE (1977) Gustatory avoidance conditioning by drugs of abuse: Relationships to general issues in research on drug dependence. In: Milgram NW, Krames L, Alloway TM (eds) Food aversion learning. Plenum, New York, pp 133–167
Cappell H, LeBlanc AE, Endrenyi L (1973) Aversive conditioning by psychoactive drugs: Effects of morphine, alcohol and chlordiazepoxide. Psychopharmacologia 29:239–246
Carpenter DO, Briggs DB, Strominger N (1984a) Behavioral and electrophysiological studies of peptide-induced emesis in dogs. Fed Proc 43:2952–2954
Carpenter DO, Briggs DB, Strominger N (1984b) Peptide-induced emesis in dogs. Behav Brain Res 11:277–281
Carr GD, White NM (1986) Anatomical disassociation of amphetamine's rewarding and aversive effects: An intracranial micro-injection study. Psychopharmacology 89:340–346
Chinn HI, Wang SC (1954) Locus of emetic action following irradiation. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 85:472–474
Coil JD, Garcia J (1977) Conditioned taste aversions: The illness US. In: Biological approaches to learning. Papers presented at the Northeastern Regional Meeting of the Animal Behavior Society, October, St John's, Newfoundland, Canada, pp 1–32
Coil JD, Norgren R (1981) Taste aversions conditioned with intravenous copper sulfate: Attenuation by ablation of the area postrema. Brain Res 212:425–433
Coil JD, Rogers RC, Garcia J, Novin D (1978) Conditioned taste aversions: Vagal and circulatory mediation of the toxic unconditioned stimulus. Behav Biol 24:509–519
Corrigall WA, Linseman MA, D'Onofrio R, Lei H (1986) Analysis of the paradoxical effect of morphine on runway speed and food consumption. Psychopharmacology 89:327–333
Costello DJ, Borison HL (1977) Naloxone antagonizes narcotic self-blockade of emesis in the cat. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 203:222–230
Coussens WR (1974) Conditioned taste aversion: Route of drug administration. In: Singh JM, Lal H (eds) Drug addiction: Neurobiology and influences on behavior, vol 3. Stratton International Medical Book, New York, pp 241–248
Crampton GH, Daunton NG (1983) Evidence for a motion sickness agent in cerebrospinal fluid. Brain Behav Evol 23:36–41
Davis CJ, Harding RK, Leslie RA, Andrews PLR (1986) The organisation of vomiting as a protective reflex: A commentary on the first day's discussions. In: Davis CJ, Lake-Bakaar GY, Grahame-Smith DG (eds) Nausea and vomiting: Mechanisms and treatment. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 65–75
Domjan M, Best MR (1980) Interference with ingestional aversion learning produced by preexposure to the unconditioned stimulus: Associative and nonassociative aspects. Learn Motiv 11:522–537
Farber PD, Gorman JE, Reid LD (1976) Morphine injections in the taste aversion paradigm. Physiol Psychol 4:365–368
Ford KA, Riley AL (1984) The effects of LiCl preexposure on amphetamine-induced taste aversions: An assessment of blocking. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:643–645
Gaitondé BB, McCarthy LE, Borison HL (1965) Central emetic action and toxic effects of digitalis in cats. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 147:409–415
Gamzu E (1977) The multifaceted nature of taste-aversion-inducing agents: Is there a single common factor? In: Barker LM, Best MR, Domjan M (eds) Learning mechanisms in food selection. Baylor University Press, Waco TX, pp 477–509
Gamzu E, Vincent G, Boff E (1985) A pharmacological perspective of drugs used in establishing conditioned food aversions. Ann NY Acad Sci 443:231–249
Garcia J, Ervin FR (1968) Gustatory-visceral and telereceptor-cutaneous conditioning: Adaptation in internal and external milieus. Commun Behav Biol A1:389–415
Garcia J, Koelling RA (1966) Relation of cue to consequence in avoidance learning. Psychon Sci 4:123–124
Garcia J, Kimeldorf DJ, Hunt EL (1961) The use of ionizing radiation as a motivating stimulus. Psychol Rev 68:383–395
Garcia J, Ervin FR, Koelling RA (1967) Bait-shyness: A test for toxicity with N=2. Psychon Sci 7:245–246
Garcia J, Hankins WG, Rusiniak KW (1974) Behavioral regulation of the milieu interne in man and rat. Science 185:824–831
Garcia J, Lasiter PS, Bermudez-Rattoni F, Deems DA (1985) A general theory of aversion learning. Ann NY Acad Sci 443:8–21
Gerstner HB (1960) Reaction to short-term radiation in man. Ann Rev Med 11:289–302
Goudie AJ (1979) Aversive stimulus properties of drugs. Neuropharmacology 18:971–979
Greenberg D, Dowdy EE, Peacock LJ (1977) Disruption of lithium-chloride-induced taste aversion by subdiaphragmatic vagotomy. Bull Psychon Soc 10:254
Greenshaw AJ, Burešová O (1982) Learned taste aversion to saccharin following intraventricular or intraperitoneal administration of d,1-amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 17:1129–1133
Griffiths RR, Bigelow GE, Henningfield JE (1980) Similarities in animal and human drug-taking behavior. In: Mello NK (ed) Advances in substance abuse, vol 1. JAI Press, Greenwich CT, pp 1–90
Gylys JA, Doran K, Szaraz M (1974) Antagonism of morphine and apomorphine in dogs and rats. Fed Proc 33:515
Hartley PL (1977) Motion-induced learned taste aversions in rats and the role of the area postrema. Diss Abstr Int 38:2925B
Ionescu E, Burešová O (1977) Failure to elicit conditioned taste aversion by severe poisoning. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:251–254
Kiefer SW (1985) Neural mediation of conditioned food aversions. Ann NY Acad Sci 443:100–109
Kiefer SW, Rusiniak KW, Garcia J, Coil JD (1981) Vagotomy facilitates extinction of conditioned taste aversions in rats. J Comp Physiol Psychol 95:114–122
Laffan RJ, Borison HL (1957) Emetic action of nicotine and lobeline. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 121:468–476
LeBlanc AE, Cappell H (1975) Antagonism of morphine-induced aversive conditioning by naloxone. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 3:185–188
Leslie RA, Gwyn DG (1984) Neuronal connections of the area postrema. Fed Proc 43:2941–2943
Lett BT (1985) The painlike effect of gallamine and naloxone differs from sickness induced by lithium chloride. Behav Neurosci 99:145–150
Levy CJ, Carroll ME, Smith JC, Hofer KG (1974) Antihistamines block radiation-induced taste aversions. Science 186:1044–1046
Lindstrom PA, Brizzee KR (1962) Relief of intractable vomiting from surgical lesions in the area postrema. J Neurosurg 19:228–236
Martin JR (1979) Coeliactomy: Differential toxiphobia conditioning with apomorphine and copper sulfate. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 11:331–334
Martin JR, Cheng FY, Novin D (1978) Acquisition of learned taste aversion following bilateral subdiaphragmatic vagotomy in rats. Physiol Behav 21:13–17
Mazur K, Borison HL (1968) Lack of directional selectivity of cassaine in excitation of the medullary emetic chemoreceptor trigger zone from blood and cerebrospinal fluid in cats. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 127:440–444
McCarthy LE, Borison HL (1983) Animal models for predicting antiemetic drug activity. In: Laszlo J (ed) Antiemetics and cancer chemotherapy. Williams and Wilkins, Baltimore MD, pp 21–33
McGlone JJ, Ritter S, Kelley KW (1980) The antiaggressive effect of lithium is abolished by area postrema lesion. Physiol Behav 24:1095–1100
Miller AD, Wilson VJ (1983) ‘Vomiting center’ reanalyzed: An electrical stimulation study. Brain Res 270:154–158
Money KE (1970) Motion sickness. Physiol Rev 50:1–39
Money KE, Cheung BS (1983) Another function of the inner ear: Facilitation of the emetic response to poisons. Aviat Space Environ Med 54:208–211
Nachman M, Hartley PL (1975) Role of illness in producing learned taste aversions in rats: A comparison of several rodenticides. J Comp Physiol Psychol 89:1010–1018
Nachman M, Rauschenberger J, Ashe JH (1977) Studies of learned aversions using non-gustatory stimuli. In: Barker LM, Best MR, Domjan M (eds) Learning mechanisms in food selection. Baylor University Press, Waco TX, pp 395–417
Niemegeers CJE (1982) Antiemetic specificity of dopamine antagonists. Psychopharmacology 78:210–213
Ossenkopp K-P (1983a) Area postrema lesions in rats enhance the magnitude of body rotation-induced conditioned taste aversions. Behav Neural Biol 38:82–96
Ossenkopp K-P (1983b) Taste aversions conditioned with gamma radiation: Attenuation by area postrema lesions in rats. Behav Brain Res 7:297–305
Parker LA (1982) Nonconsummatory and consummatory behavioral CRs elicited by lithium-and amphetamine-paired flavors. Learn Motiv 13:281–303
Parker LA (1986) Drug-specific blocking of lithium-, amphetamine-, and apomorphine-induced conditioned flavor avoidance. Learn Motiv 17:91–113
Pelchat ML, Grill HJ, Rozin P, Jacobs J (1983) Quality of acquired responses to tastes by rattus norvegicus depends on type of associated discomfort. J Comp Physiol Psychol 97:149–153
Peng MT (1963) Locus of emetic action of epinephrine and dopa in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 139:345–349
Peng MT, Pi WP (1967) Emesis in horse serum anaphylactic shock in dogs. Am J Physiol 212:131–134
Peng MT, Wang SC (1962) Emetic responses of monkeys to apomorphine, hydergine, deslanoside, and protoveratrine. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med 110:211–215
Prasad KN (1984) CRC handbook of radiobiology. CRC Press, Boca Ratan FL
Pratt JA, Stolerman IP (1984) Pharmacologically specific pretreatment effects on apomorphine-mediated conditioned taste aversions in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 20:507–511
Rabin BM, Hunt WA (1986) Mechanisms of radiation-induced conditioned taste aversion learning. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 10:55–65
Rabin BM, Hunt WA, Lee J (1982) Studies on the role of central histamine in the acquisition of a radiation-induced conditioned taste aversion. Radiat Res 90:609–620
Rabin BM, Hunt WA, Lee J (1983) Attenuation of radiation-and drug-induced conditioned taste aversions following area postrema lesions in the rat. Radiat Res 93:388–394
Rabin BM, Hunt WA, Lee J (1984) Effects of dose and of partial body ionizing radiation on taste aversion learning in rats with lesions of the area postrema. Physiol Behav 32:119–122
Rabin BM, Hunt WA, Lee J (1985) Intragastric copper sulfate produces a more reliable conditioned taste aversion in vagotomized rats than in intact rats. Behav Neural Biol 44:364–373
Rabin BM, Hunt WA, Chedester AL, Lee J (1986) Role of the area postrema in radiation-induced taste aversion learning and emesis in cats. Physiol Behav 37:815–818
Reason JT, Brand JJ (1975) Motion sickness. Academic, London
Reicher MA, Holman EW (1977) Location preference and flavor aversion reinforced by amphetamine in rats. Anim Learn Behav 5:343–346
Revusky S (1968) Aversion to sucrose produced by contingent X-irradiation: Temporal and dosage parameters. J Comp Physiol Psychol 65:17–22
Revusky S (1984) Associative predispositions. In: Marler P, Terrace HS (eds) The biology of learning. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 447–460
Revusky S, Garcia J (1970) Learned associations over long delays. In: Bower G, Spence J (eds) Psychology of learning and motivation: Advances in research and theory, vol 4. Academic, New York, pp 1–84
Revusky S, Gorry T (1973) Flavor aversions produced by contingent drug injection: Relative effectiveness of apomorphine, emetine, and lithium. Behav Res Ther 11:403–409
Revusky S, Harding RK (1986) Pairing pentobarbital with one toxin causes it to attenuate taste aversions produced by a different toxin: Implications for conditioned antisickness theory. Behav Neurosci 100:685–694
Riley AL, Clarke CM (1977) Conditioned taste aversions: A bibliography. In: Barker LM, Best MR, Domjan M (eds) Learning mechanisms in food selection. Baylor University Press, Waco TX, pp 593–616
Riley AL, Jacobs WJ, LoLordo VM (1978) Morphine-induced taste aversions: A consideration of parameters. Physiol Psychol 6:96–100
Riley AL, Tuck DL (1985a) Conditioned food aversions: A bibliography. Ann NY Acad Sci 443:381–437
Riley AL, Tuck DL (1985b) Conditioned taste aversions: A behavioral index of toxicity. Ann NY Acad Sci 443:272–292
Ritter S, McGlone JJ, Kelley KW (1980) Absence of lithium-induced taste aversion after area postrema lesion. Brain Res 201:501–506
Rondeau DB, Jolicoeur FB, Merkel AD, Wayner MJ (1981) Drugs and taste aversion. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 5:279–294
Share NN, Chai CY, Wang SC (1965) Emesis induced by intracerebroventricular injections of apomorphine and deslanoside in normal and chemoreceptive trigger zone ablated dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 147:416–421
Sherman JE, Roberts T, Roskam SE, Holman EW (1980) Temporal properties of the rewarding and aversive effects of amphetamine in rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 13:597–599
Stefanini E, Clement-Cormier Y (1981) Detection of dopamine receptors in the area postrema. Eur J Pharmacol 74:257–260
Stolerman IP, D'Mello GD (1981) Oral self-administration and the relevance of conditioned taste aversions. In: Thompson T, Dews PB, McKim WA (eds) Advances in behavioral pharmacology, vol 3. Academic, New York, pp 169–214
Testa TJ, Ternes JW (1977) Specificity of conditioning mechanisms in the modification of food preferences. In: Barker LM, Best MR, Domjan M (eds) Learning mechanisms in food selection. Baylor University Press, Waco TX, pp 229–253
Torack RM (1973) area postrema: A feedback control of choroid plexus function? In: Zimmerman HM (ed) Progress in neuropathology, vol 2. Grune and Stratton, New York, pp 115–127
van der Kooy D (1984) Area postrema: Site where cholecystokinin acts to decrease food intake. Brain Res 295:345–347
van der Kooy D, Koda LY (1983) Organization of the projections of a circumventricular organ: The area postrema in the rat. J Comp Neurol 219:328–338
van der Kooy D, Phillips AG (1977) Temporal analysis of naloxone attenuation of morphine-induced taste aversion. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:637–641
van der Kooy D, Swerdlow NR, Koob GF (1983) Paradoxical reinforcing properties of apomorphine: Effects of nucleus accumbens and area postrema lesions. Brain Res 259:111–118
Wagner GC, Foltin RW, Seiden LS, Schuster CR (1981) Dopamine depletion by 6-hydroxydopamine prevents conditioned taste aversion induced by methylamphetamine but not lithium chloride. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 14:85–88
Wang SC (1965) Emetic and antiemetic drugs. In: Root WS, Hoffman FG (eds) Physiological pharmacology: A comprehensive treatise, vol 2. Academic, New York, pp 255–328
Wang SC (1980) Physiology and pharmacology of the brainstem. Futura Publishing, Mount Kisco NY
Wang SC, Borison HL (1950) The vomiting center: A critical experimental analysis. Arch Neurol Psychiatry 63:928–941
Wang SC, Borison HL (1951a) Copper sulphate emesis: A study of afferent pathways from the gastrointestinal tract. Am J Physiol 164:520–526
Wang SC, Borison HL (1951b) The vomiting center: Its destruction by radon implantation in dog medulla oblongata. Am J Physiol 166:712–717
Wang SC, Borison HL (1952) A new concept of organization of the central emetic mechanism: Recent studies on the sites of action of apomorphine, copper sulfate and cardiac glycosides. Gastroenterology 22:1–12
Wang SC, Chinn HI (1954) Experimental motion sickness in dogs: Functional importance of chemoceptive emetic trigger zone. Am J Physiol 178:111–116
Wang SC, Chinn HI (1956) Experimental motion sickness in dogs: Importance of labyrinth and vestibular cerebellum. Am J Physiol 185:617–623
Wang SC, Glaviano VV (1954) Locus of emetic action of morphine and hydergine in dogs. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 111:329–334
Wang SC, Chinn HI, Renzi AA (1957) Experimental motion sickness in dogs: Role of abdominal visceral afferents. Am J Physiol 190:578–580
Wang SC, Renzi AA, Chinn HI (1958) Mechanism of emesis following X-irradiation. Am J Physiol 193:335–339
Weiner N (1980a) Atropine, scopolamine, and related antimuscarinic drugs. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th ed. Macmillan, New York, pp 120–137
Weiner N (1980b) Norepinephrine, epinephrine, and the sympathomimetic amines. In: Gilman AG, Goodman LS, Gilman A (eds) Goodman and Gilman's the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 6th ed. Macmillan, New York, pp 138–175
White N, Sklar L, Amit Z (1977) The reinforcing action of morphine and its paradoxical side effect. Psychopharmacology 52:63–66
Wise RA, Yokel RA, de Wit H (1976) Both positive reinforcement and conditioned aversion from amphetamine and from apomorphine in rats. Science 191:1271–1272
Wittlin WA, Brookshire KH (1968) Apomorphine-induced conditioned aversion to a novel food. Psychon Sci 12:217–218
Wood CD, Graybiel A (1972) Theory of antimotion sickness drug mechanisms. Aerospace Med 43:249–252
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grant, V.L. Do conditioned taste aversions result from activation of emetic mechanisms?. Psychopharmacology 93, 405–415 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207227
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207227