Abstract
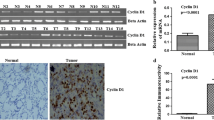
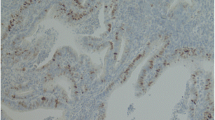
The expression of cyclin E in human colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas was examined immunohistochemically to elucidate the role of cyclin E in the colorectal carcinogenesis. The expression of cyclin E was detected in 25% (91/358) of the adenomas and 56% (149/267) of the adenocarcinomas. The incidence of strongly positive cases was significantly higher in the adenocarcinomas (20%) than in the adenomas (5%) (P<0.01). Among adenomas, a significant correlation was noticed between the expression of cyclin E and the grade of atypia. The incidence of cyclin E expression was significantly higher in the adenocarcinomas without an adenoma component (62%; 104/169) than in those with this component (46%; 45/98) (P<0.05). Furthermore, the incidence of the cyclin E expression was higher in stages 1 and 2 carcinoma than in stage 0 and stages 3 and 4 carcinoma. The expression of cyclin E was the most prominent in tumors invading the submucosa and muscularis propria. The expression of cyclin E was significantly correlated with the proliferative activity of the tumor cells measured by Ki-67 antigen expression (P<0.01). It was also correlated with the expression of p53 protein in the tumor cells (P<0.01). Overexpression of cyclin E and subsequent deregulation of cell cycle may contribute to the development and early progression of the colorectal carcinomas.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akama Y, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Kuniyasu H, Kitahara K, Ishikawa T, Tahara E (1995) Frequent amplification of the cyclin E gene in human gastric carcinomas. Jpn J Cancer Res 86: 617–621
Ayhan A, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Ito H, Tahara E (1992) Genetic abnormalities and expression of p53 in human colon carcinomas. Int J Oncol 1: 431–437
Buckley MF, Sweeney KJ, Hamilton JA, Sini RL, Manning DL, Nicholson RI, deFazio A, Watts CK, Musgrove EA, Sutherland RL (1993) Expression and amplification of cyclin genes in human breast cancer. Oncogene 8: 2127–2133
Dutta A, Chandra R, Leiter LM, Lester S (1995) Cyclins as markers of tumor proliferation: immunohistochemical studies in breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 92: 5386–5390
El-Deiry WS, Tokino T, Velculescu VE, Levy DB, Parsons R, Trent JM, Lin D, Mercer E, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1993) WAF1, a potential mediator of p53 tumor suppression. Cell 75: 817–825
Hannon GJ, Beach D (1994) p15INK4B is a potent effector of TGF-β induced cell cycle arrest. Nature 371: 257–261
Harper JW, Adami GR, Wei N, Keyomarsi K, Elledge SJ (1993) The p21 Cdk-interacting protein Cip1 is a potent inhibitor of G1 cyclin-dependent kinases. Cell 75: 805–816
Heichman KA, Roberts JM (1994) Rules to replicate by. Cell 79: 557–562
Hunter T, Pines J (1994) Cyclins and cancer. II. Cyclin D and CDK inhibitors come of age. Cell 79: 573–582
Japanese Research Society for Cancer of the Colon and Rectum (1994) General rules for clinical and pathological studies on cancer of the colon, rectum and anus, 5th edn. Kanehara, Tokyo
Jiang W, Kahn CM, Tomita N, Zhang Y-J, Lu SH, Weinstein IB (1992) Amplification and expression of the human cyclin D gene in esophageal cancer. Cancer Res 52: 2980–2983
Kamb A, Gruis NA, Weaver-Feldhaus J, Liu Q, Harshman K, Tavtigian SV, Stockert E, Day RSI, Johnson BE, Skolnick MH (1994) A cell cycle regulator potentially involved in genesis of many tumor types. Science 264: 436–440
Keyomarsi K, Pardee AB (1993) Redundant cyclin overexpression and gene amplification in breast cancer cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 1112–1116
Keyomarsi K, O'Leary N, Molnar G, Lees E, Fingert HJ, Pardee AB (1994) Cyclin E, a potential prognostic marker for breast cancer. Cancer Res 54: 380–385
Kitahara K, Yasui W, Kuniyasu H, Yokozaki H, Akama Y, Yunotani S, Hisatsugu T, Tahara E (1995) Concurrent amplification of cyclin E and CDK2 genes in colorectal carcinomas. Int J Cancer 62: 25–28
Kitahara K, Yasui W, Yokozaki H, Semba S, Hamamoto T, Hisatsugu T, Tahara E (1996) Expression of cyclin D1, CDK4 and p27KIP1 is associated with the p16MTS1 gene status in human esophageal carcinoma cell lines. J Exp Ther Oncol 1: 7–12
Leach FS, Elledge SJ, Sherr CJ, Willson JK, Markowitz S, Kinzler KW, Vogelstein B (1993) Amplification of cyclin genes in colorectal carcinomas. Cancer Res 53: 1986–1989
Nobori T, Miura K, Wu DJ, Lois A, Takabayashi K, Carson DA (1994) Deletions of the cyclin-dependent kinase-4 inhibitor gene in multiple human cancers. Nature 368: 753–756
Polyak K, Kato JY, Solomon MJ, Sherr CJ, Massague J, Roberts JM, Koff A (1994) p27KIP1, a cyclin-Cdk inhibitor, links transforming growth factor-β and contact inhibition to cell cycle arrest. Gene Dev 8: 9–22
Schuuring E, Verhoeven E, Mooi WJ, Michalides RJAM (1992) Identification and cloning of two overexpressed genes, U21B31/PRAD1 and EMS1, within the amplified chromosome 11q13 region in human carcinomas. Oncogene 7: 355–361
Serrano M, Hannon GJ, Beach D (1993) A new regulatory motif in cell-cycle control causing specific inhibition of cyclin D/CDK4. Nature 366: 704–707
Sherr CJ (1994) G1 phase progression: cycling on cue. Cell 79: 515–555
Toyoshima H, Hunter T (1994) p27, a novel inhibitor of G1 cyclin-Cdk protein kinase activity, is related to p21. Cell 78: 67–74
Weidner N, Moore DH, Vartanian R (1994) Correlation of Ki-67 antigen expression with mitotic figure index and tumor grade in breast carcinomas using the novel “paraffin”-reactive MIB1 antibody. Hum Pathol 25: 337–342
Xiong Y, Hannon G, Zhang H, Casso D, Kobayashi R, Beach D (1993) p21 is a universal inhibitor of cyclin kinases. Nature 366: 701–704
Yasui W, Ji Z-Q, Kuniyasu H, Ayhan A, Yokozaki H, Ito H, Tahara E (1992) Expression of transforming growth factor alpha in human tissues: immunohistochemical study and Northern blot analysis. Virchows Arch [A] 421: 513–519
Yasui W, Akama Y, Kuniyasu H, Yokozaki H, Samba S, Shimamoto F, Tahara E (1996) Expression of cyclin E in human gastric adenomas and adenocarcinomas: correlation with proliferative activity and p53 status. J Exp Ther Oncol 1:88–94
Yokozaki H, Kuniyasu H, Kitadai Y, Nishimura K, Todo H, Ayhan A, Yasui W, Ito H, Tahara E (1992) p53 point mutations in primary human gastric carcinomas. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 119: 67–70
Yoshida K, Kawami H, Kuniyasu H, Nishiyama M, Yasui W, Hirai T, Toge T, Tahara E (1994) Coamplification of cyclin D, hst-1 and int-2 genes is a good biological marker of high malignancy for human esophageal carcinomas. Oncol Rep 1: 493–496
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yasui, W., Kuniyasu, H., Yokozaki, H. et al. Expression of cyclin E in colorectal adenomas and adenocarcinomas: correlation with expression of Ki-67 antigen and p53 protein. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 429, 13–19 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196815
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196815