Abstract
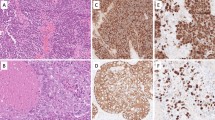
Molecular, histopathological, and clinical studies were carried out on a series of 79 laryngeal papillomas (LP) from 36 patients in order to investigate the hypothesis that juvenile and adult LP may represent a biological entity causally related to Human papilloma virus (HPV) infection. Using in situ hybridization with biotin-labelled probes and polymerase chain reaction, we detected human papilloma virus (HPV) 6/11 in 28 of 29 juvenile LP, in 26 of 30 adult multiple, and in 17 of 20 adult solitary LP. None of LP was found to harbour HPV types 16, 18, 31, 33, and 51. There were no clear-cut histological differences between juvenile and adult LP, the presence of koilocytosis was equally observed in both, and there was no prevalent type of epithelial hyperplasia in either form, except that all three cases of atypical hyperplasias (precancerous lesions) were found among adult patients. During a 14 year follow-up, no carcinomatous transformation of LP was observed. All juvenile LP in our study had frequent recurrences of the disease, however, numerous surgical procedures were also required in 16 of 27 adult patients. Our study supports Lindeberg's hypothesis of a similar pathogenesis for all forms of LP caused by the HPV types 6/11.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abramson AL, Steinberg BM, Winkler B (1987) Laryngeal papillomatosis: clinical, histopathologic and molecular studies. Laryngoscope 97:678–685
Brandsma JL, Lewis AJ, Abramson A, Manos MM (1990) Detection and typing of papillomavirus DNA in formaldehydefixed paraffin-embedded tissue. Arch Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg 116:844–848
Burkhardt A, Meyer Breiting E (1988) General conditions and risk factors of carcinogenesis, precancerous lesions. In: Meyer-Breiting E, Burkhardt A. Tumours of the larynx. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 57–77
Chang F (1990) The role of papillomaviruses. J Clin Pathol 43:269–276
Chang F, Wang L, Syrjanen S, Syrjanen K (1992) Human papillomavirus infections in the respiratory tract. Am J Otolaryngol 13:210–225
Cohen SR, Geller KA, Seltzer S, et al. (1989) Papilloma of the larynx and tracheobronchial tree in children. A retrospective study. Ann Otolaryngol 89:497–503
Dickens P, Srivastava G, Loong Loke S, Larkin S (1991) Human papillomavirus 6, 11 and 16 in laryngeal papillomas. J Pathol 165:243–246
Friedmann I, Ferlito A (1993) Precursors of squamous cell carcinoma. In: Ferlito A (ed) Neoplasms of the larynx. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 97–111
Kambič V, Gale N (1986) Significance of keratosis and dyskeratosis for classifying hyperplastic aberrations of laryngeal mucosa. Am J Otolaryngol 7:323–333
Kambič V, Gale N, Ferluga D (1992) Laryngeal hyperplastic lesions, follow-up study and application of lectins and anticytokeratins for their evaluation. Pathol Res Pract 188:1067–1077
Kwok S, Higushi R (1990) Avoiding false positives with PCR. Nature 339:237–238
Levi JE, Delcelo R, Alberti VN, Torloni H, Villa LL (1989) Human papillomavirus DNA in respiratory papillomatosis detected by in situ hybridization and the polymerase chain reaction. Am J Pathol 135:1179–1184
Lindeberg H (1991) Laryngeal papillomas: histomorphometric evaluation of multiple and solitary lesions. Clin Otolaryngol 16:257–260
Lindeberg H, Elbrond O (1989) Laryngeal papillomas: clinical aspects in a series of 231 patients. Clin Otolaryngol 14:333–342
Lindeberg H, Johansen L (1990) The presence of human papillomavirus (HPV) in solitary adult laryngeal papillomas demonstrated by in situ DNA hybridization with sulphonated probes. Clin Otolaryngol 15:367–371
Lindeberg H, Oster S, Oxlund I, Elbrond O (1986) Laryngeal papillomas: classification and course. Clin Otolaryngol 11:423–429
Padovan IF (1974) Premalignant laryngeal lesions — a laryngologyst's viewpoint. Can Otolaryngol 34:543–545
Poljak M, Cerar A (1993) Human papillomavirus type 16 DNA in oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Anticancer Res 13:2113–2116
Poljak M, Cerar A (1994) Detection of human papilloma virus type 6 DNA in an esophageal squamous cell papilloma. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis 13:188–189
Quiney RE, Wells M, Lewis FA, Terry RM, Michaels L, Croft CB (1989) Laryngeal papillomatosis: correlation between severity of disease and presence of HPV 6 and 11 detected by in situ DNA hybridisation. J Clin Pathol 42:694–698
Rimell F, Maisel R, Dayton V (1992) In situ hybridization and laryngeal papillomas. Ann Otol Rhinol Laryngol 101:119–126
Shibata DK, Arnheim N, Martin WJ (1988) Detection of human papillomavirus in paraffin — embedded tissue using the polymerase chain reaction. J Exp Med 167:225–230
Shanmugarathnam K, Sobin LH (1991) Histological typing of tumours of the upper respiratory tract and ear. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 20–21
Terry RM, Lewis FA, Griffiths S, Wells M, Bird CC (1987) Demonstration of human papillomavirus types 6 and 11 in juvenile laryngeal papillomatosis by in situ DNA hybridization. J Pathol 153:245–248
Terry RM, Lewis FA, Robertson S, Blythe D, Wells M (1989) Juvenile and adult laryngeal papillomata: classification by in situ hybridization for human papillomavirus. Clin Otolaryngol 14:135–139
Ting Y, Manos MM (1990) Detection and typing of genital human papillomaviruses. In: Innis MA, Gelfant DH, Sninsky JJ, White TJ (eds) PCR protocols: a guide to methods and applications. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 356–367
Tsutsumi K, Nakajima T, Gotoh M, Shimosato Y, Tsunokawa Y, Terada M, Ebihara S, Ono I (1989) In situ hybridization and immunohistochemical study of human papillomavirus infection in adult laryngeal papillomas. Laryngoscope 99:80–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gale, N., Ferluga, D., Poljak, M. et al. Laryngeal papillomatosis: molecular, histopathological, and clinical evaluation. Vichows Archiv A Pathol Anat 425, 291–295 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196152
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00196152