Abstract
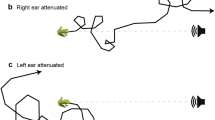
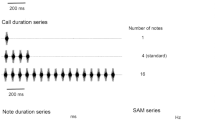
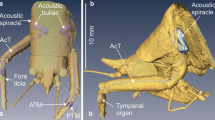
Unlike most praying mantises that have a single region of auditory sensitivity, species in the genus Creobroter have equally sensitive hearing at 2–4 and at 25–50 kHz and and are relatively insensitivity at 10–15 kHz — they have a W-shaped audiogram. Ultrasonic sensitivity originates from an auditory organ in the ventral midline of the metathorax that closely resembles the ear of other mantises. Ablation experiments demonstrate that low frequency sensitivity derives from a serially homologous mesothoracic auditory organ. Extracellular recordings suggest that these two ears operate largely, if not entirely, independently of one another in the thorax. The low frequency response has a longer latency, more action potentials per stimulus, and different patterns of change with increasing SPL than the high frequency response. Separate interneurons mediate responses in the two frequency ranges, but our evidence suggests that they are two serially homologous sets of cells. Neither auditory organ shows any physiological evidence of directional sensitivity. Ultrasound triggers a set of behaviors in flying hymenopodid mantises much like those in other mantises, but the behavioral significance of low frequency hearing in these animals is still unknown.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- SPL :
-
sound pressure level
- dB SPL :
-
sound pressure level re: 20 μPa
- HF :
-
high frequency
- LF :
-
low frequency
References
Annandale N (1900) On the insects of the “Skeat Expedition”. Proc Zool Soc Lond 1900: 837–854
Arntz B (1975) Das Hörvermögen von Nepa cinerea L. J Comp Physiol 96: 53–72
Beier M (1934) Mantodea. Hymenopodinae. In: Wytsman P (ed) Genera Insectorum. vol 196. Louis Desmet-Verteneuil, Brussels, pp 1–36
Beier M (1968) Mantodea (Fangheuschrecken). In: Helmcke J-G, Starck D, Wermuth H (eds) Handbuch der Zoologie. Band IV, Hälfte 2, Teil 2/12. De Gruyter, Berlin, pp 1–47
Boyan GS (1985) Auditory input to the flight system of the locust. J Comp Physiol A 156: 79–91
Boyan G (1992) Common synaptic drive to segmentally homologous interneurons in the locust. J Comp Neurol 321: 544–554
Boyan GS (1993) Another look at insect audition: the tympanic receptors as an evolutionary specialization of the chordotonal system. J Insect Physiol 39: 187–200
Davis NT (1982) Improved methods for cobalt filling and silver intensification of insect motor neurons. Stain Technol 57: 239–244
Davis NT (1983) Serial homologies of the motor neurons of the dorsal intersegmental muscles of the cockroach, Periplaneta americana (L.). J Morp 176: 197–210
Edmunds M (1975) Courtship, mating and possible sex pheromones in three species of Mantodea. Entomol Monthly Mag 111: 53–58
Haszprunar G (1992) The types of homology and their significance for evolutionary biology and phylogenetics. J Evol Biol 5: 13–24
Jansson A (1973) Stridulation and its significance in the genus Cenocorixa (Hemiptera, Corixidae). Behaviour 46: 1–36
Kalmring K, Rössler W, Unrast C (1994) Complex tibial organs in fore-, mid-, and hindlegs of the bushcricket Gampsocleis gratiosa (Tettigoniidae): Comparison of physiology of the organs. J Exp Zool 270: 155–161
Kutsch W, Heckmann R (1995) Homologous structures, exemplified by motoneurones of Mandibulata. In: Breidbach O, Kutsch W (eds) The nervous system of invertebrates: An evolutionary and comparative approach. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 221–248
Libersat F, Hoy RR (1991) Ultrasonic startle behavior in bushcrickets (Orthoptera; Tettigoniidae). J Comp Physiol A 169: 507–514
Lin Y, Rössler W, Kalmring K (1994) Complex tibial organs in fore-, mid-, and hindlegs of the bushcricket Gampsocleis gratiosa (Tettigoniidae): Comparison of morphology of the organs. J Morphol 221: 191–198
Loxton RG (1979) On display behavior and courtship in the praying mantis Ephestiasula amoena (Bolivar). Zool J Linn Soc 65: 103–110
MacKinnon J (1970) Indications of territoriality in mantids. Z Tierpsychol 27: 150–155
Meier T, Reichert H (1990) Embryonic development and evolutionary origin of the orthopteran auditory organs. J Neurobiol 21: 592–610
Meier T, Reichert H (1991) Serially homologous development of the peripheral nervous system in the mouthparts of the grasshopper. J Comp Neurol 305: 201–214
Meier T, Reichert H (1995) Developmental mechanisms, homology and evolution of the insect peripheral nervous system. In: Breidbach O, Kutsch W (eds) The nervous system of invertebrates: An evolutionary and comparative approach. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 249–272
Meier T, Chabaud F, Reichert H (1991) Homologous patterns in the embryonic development of the peripheral nervous system in the grasshopper Schistocerca gregaria and the fly Drosophila melanogaster. Development 112: 241–253
Mesce KA, Amos TM, Clough SM (1993) A light-insensitive method for contrast enhancement of insect neurons filled with cobaltlysine complex. Biotech Histochem 68: 222–228
Michelsen A, Larsen ON (1985) Hearing and sound. In: Kerkut GA, Gilbert LI (eds) Comprehensive insect physiology, biochemistry, and pharmacology. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 495–556
Minelli A, Peruffo B (1991) Developmental pathways, homology and homonomy in metameric animals. J Evol Biol 3: 429–445
Nolen TG, Hoy RR (1987) Postsynaptic inhibition mediates highfrequency selectivity in the cricket Teleogryllus oceanicus: Implications for flight phonotaxis behavior. J Neurosci 7: 2081–2096
Oldfield BP (1988) Tonotopic organization of the insect auditory pathway. Trends Neurosci 11: 267–270
Pantin CFA (1946) Notes on microscopical techniques for zoologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge
Pearson KG, Boyan GS, Bastiani M, Goodman CS (1985) Heterogeneous properties of segmentally homologous interneurons in the ventral nerve cord of locusts. J Comp Neurol 233: 133–145
Prager J (1976) Das mesothorakale Tympanalorgan von Corixa punctata Ill. (Heteroptera, Corixidae). J Comp Physiol 110: 33–50
Prager J (1981) Asymmetrical hearing in the water bug Corixa punctata observed with laser vibrometry. Naturwissenschaften 68: 579–580
Prager J, Theiss J (1982) The effect of tympanal position on the sound-sensitivity of the metathoracic scolopale organ of Corixa. J Insect Physiol 28: 447–452
Robinson MH, Robinson B (1979) By dawn's early light: Matutinal mating and sex attractants in a neotropical mantid. Science 205: 825–827
Römer H, Marquart V (1984) Morphology and physiology of auditory interneurons in the metathoracic ganglion of the locust. J Comp Physiol A 155: 249–262
Römer H, Marquart V, Hardt M (1988) Organization of a sensory neuropile in the auditory pathway of two groups of Orthoptera. J Comp Neurol 275: 201–215
Schwartzkopff J (1974) Mechanoreception. In: Rockstein M (ed) The physiology of Insecta. Academic Press, New York London, pp 273–352
Strausfeld NJ, Seyan NJ, Wohlers DW, Bacon JP (1983) Lucifer yellow histology. In: Strausfeld NJ (ed) Functional neuroanatomy. Springers, Berlin, pp 132–155
Thorne BL, Carpenter JM (1992) Phylogeny of the Dictyoptera. Syst Entomol 17: 253–268
Wagner GP (1989) The biological homology concept. Annu Rev Ecol Syst 20: 51–69
Wilson JA, Hoyle G (1978) Serially homologous neurons as concomitants of functional specialisation. Nature 264: 377–379
Wohlers DW, Huber F (1985) Topographical organization of the auditory pathway within the prothoracic ganglion of the cricket Gryllus campestris L. Cell Tissue Res 239: 555–565
Yack JE (1993) Janus Green B as a rapid, vital stain for peripheral nerves and chordotonal organs in insects. J Neurosci Methods 49: 17–22
Yack JE, Fullard JH (1990) The mechanoreceptive origin of insect tympanal organs: A comparative study of similar nerves in tympanate and atympanate moths. J Comp Neurol 300: pp 523–534
Yack JE, Fullard JH (1993) What is an insect ear? Ann Ent Soc Am 86: 677–682
Yack JE, Roots BI (1992) The metathoracic wing-hinge chordotonal organ of an atympanate moth, Actias luna (Lepidoptera, Saturniidae): a light- and electron-microscopic study. Cell Tissue Res 267: 455–471
Yager DD (1989) A diversity of mantis ears: Evolutionary implications. Proceedings of the 5th International Meetings of the Orthopterist's Society (Segovia, Spain; July, 1989), p 420
Yager DD (1990) Sexual dimorphism of auditory function and structure in praying mantises (Mantodea; Dictyoptera). J Zool, Lond 221: 517–537
Yager DD (1992) Ontogeny and phytogeny of the cyclopean mantis ear. J Acoust Soc Am 92: 2421
Yager DD (1995) Nymphal development of the auditory system in the praying mantis Hierodula membranacea (Dictyoptera, Mantidae). J Comp Neurol (in press)
Yager DD, Hoy RR (1987) The midline metathoracic ear of the praying mantis, Mantis religiosa. Cell Tissue Res 250: 531–541
Yager DD, Hoy RR (1989) Audition in the praying mantis, Mantis religiosa L.: Identification of an interneuron mediating ultrasonic hearing. J Comp Physiol A 165: 471–493
Yager DD, May ML (1990) Ultrasound-triggered, flight-gated evasive maneuvers in the praying mantis, Parasphendale agrionina (Gerst.). II. Tethered flight. J Exp Biol 152: 41–58
Yager DD, Scaffidi DJ (1993) Cockroach homolog of the mantis tympanal nerve. Soc Neurosci Abstr 19: 340
Yager DD, Spangler HG (1995) Characterization of auditory afferents in the tiger beetle, Cicindela marutha Dow. J Comp Physiol A 176: 587–600
Yager DD, May ML, Fenton MB (1990) Ultrasound-triggered, flight-gated evasive maneuvers in the praying mantis, Parasphendale agrionina (Gerst.). I. Free-flight. J Exp Biol 152: 17–39
Zheng J (1988) Description of two new species of the genus Creobroter Serville from China. Entomotaxonomia 10: 97–101
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yager, D.D. Serially homologous ears perform frequency range fractionation in the praying mantis, Creobroter (Mantodea, Hymenopodidae). J Comp Physiol A 178, 463–475 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190177
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00190177