Abstract
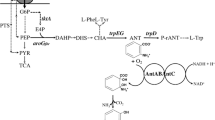
This work demonstrates the ring-cleavage pathways of catechol on Pseudomonas cepacia ATCC 29351, formed upon its growth on salicylate and benzoate, each as a sole carbon source. When grown on salicylate, P. cepacia induces only the catechol ortho pathway by its induction of catechol 1,2-dioxygenase. However, interestingly, benzoate-grown cells induce the ortho and meta pathways for the biodegradation of catechol, by inducing simultaneously catechol 1,2-dioxygenase and 2,3-dioxygenase, respectively, in the ratio of 7:1. The results indicate that P. cepacia ATCC 29351 possesses the genetic capacity for enzymes of both the ortho- and meta-cleavage pathways of benzoate degradation, although the phenotypic expression for the ortho pathway is higher. The simultaneous induction of catechol 1,2- and 2,3-dioxygenase is not detected in salicylate degradation. Although catechol is the metabolic intermediate for both salicylate and benzoate, catechol did not induce either pathway when used as a sole carbon source.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ballard RW, Palleroni NJ, Doudoroff M, Stainer RY, Mandel M (1970) Taxonomy of the aerobic pseudomonads: Pseudomonas cepacia, P. marginata, P. alliicola, and P. caryophylli. J Gen Microbiol 60:199–214
Cain RB, Farr DR (1968) Metabolism of arylsulfonates by micro-organisms. Biochem J 106:859–877
Dagley S (1978) Pathways for the utilization of organic growth substrates. In: Ornston LN, Sokatch JR (eds) The bacteria, vol 6. Academic Press, New York, pp 305–388
Dagley S (1982) The role of flavoproteins in aromatic catabolism. In: Massey V, Williams CH (eds) Flavins and flavoproteins. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 311–317
Dagley S (1986) Biochemistry of aromatic hydrocarbon degradation by pseudomonads. Bacteria 10:527–555
Davies JI, Evans WC (1964) Oxidative metabolism of naphthalene by soil pseudomonads. Biochem J 91:251–261
Dorn E, Knackmuss H-J (1978) Chemical structure and biodegradability of halogenated aromatic compounds: two catechol 1,2-dioxygenases from a 3-chlorobenzoate grown pseudomonad. Biochem J 174:73–84
Feist CF, Hegeman GD (1969a) Phenol and benzoate metabolism by Pseudomonas putida: regulation of tangenital pathways. J. Bacteriol 100:869–877
Feist CF, Hegeman GD (1969b) Regulation of the meta cleavage pathway for benzoate oxidation by Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol 100:1121–1123
Gonzalez CF, Vidaver AK (1979) Bacteriocin, plasmid, and pectolytic diversity in Pseudomonas cepacia of clinical and plant origin. J Gen Microbiol 110:161–170
Hamzah RY (1984) Differential induction and characterization of flavoprotein hydroxylases in Pseudomona cepacia. Ph.D. Dissertation, University of Houston-University Park, USA
Hamzah RY, Tu S-C (1981) Determination of the position of mono-oxygenation in the formation of catechol catalyzed by salicylate hydroxylase. J Biol Chem 256:6392–6394
Kemp MB, Hegeman GD (1968) Genetic control of β-ketoadipate pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Biol Chem 96:1488–1499
Kim Y, Tu S-C (1989) Molecular cloning of salicylate hydroxylase genes from Pseudomonas cepacia and Pseudomonas putida. Arch Biochem Biophys 269:295–304
Lessie TG, Gaffnew T (1986) Catabolic potential of Pseudomonas cepacia. In: Sokatch JR, Ornston LN (eds) The bacteria: the biology of Pseudomonas, vol 10. Academic Press, Orlando, Fla., pp 439–481
Lessie TG, Wood MS, Byrne A, Ferrante A (1990) Transposable gene-activating elements in Pseudomonas cepacia. In: Silver S, Chakrabarty AM, Iglewski B, Kaplan S (eds) Pseudomonas bio-transformations, pathogenesis, and evolving biotechnology. American Society of Microbiology, Washington, D.C., pp 279–291
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Farr AL, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with the Folin-phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Massey V, Hemmerich P (1975) Flavin and pteridine monooxygenases. In: Boyer PD (ed) The enzymes, vol 12. Part B. Academic Press, New York, pp 191–252
Nakazawa T, Nakazawa A (1970) Pyrocatechase (Pseudomonas). Methods Enzymol 17A:518–522
Nakazawa T, Yokota T (1973) Benzoate metabolism in Pseudomonas putida (arvilla) mt-2: demonstration of two benzoate pathways. J Bacteriol 115:262–267
Nozaki M (1974) Nonheme iron dioxygenase. In: Hayaishi O (ed) Molecular mechanisms of oxygen activation. Academic Press, London, pp 135–162
Nozaki M, Kagamiyama H, Hayaishi O (1963) Metapyrocatechase. I. Purification, crystallization and some properties. Biochem Z 338:582–590
Nozaki M, Ono K, Nakazawa T, Kotani S, Hayaishi O (1968) Metapyrocatechase. II. The role of iron and sulfhydryl groups. J. Biol Chem 243:2682–2690
Ornston LN (1971) Regulation of catabolic pathways in Pseudomonas. Bacteriol Rev 35:87–116
Sala-Trepat JM, Evans WC (1971) The meta-cleavage of catechol by Azotobacter species. 4-Oxalocronate ptthway. Eur J Biochem 20:400–413
Smith MR (1990) The biodegradation of aromatic hydrocarbons by bacteria. Biodegradation 1:191–206
Stainer RY, Ornston LN (1973) The β-ketoadipate pathway. Adv Microb Physiol 9:89–151
Stainer RY, Sleeper BP, Tsuchida M, McDonald DL (1950) Bacterial oxidation of aromatic compounds. III. The enzymatic oxidation of catechol and protocatechuic acid to β-ketoadipate acid. J Bacteriol 59:137–151
Stainer RY, Palleroni NJ, Doudoroff M (1966) The aerobic pseudomonads: a taxonomic study. J Gen Microbiol 43:159–271
Wang L-H, Hamzah RY, Yu Y, Tu S-C (1987) Pseudomonas cepacia 3-hydroxybenzoate-6-hydroxylase: induction, purification, and characterization. Biochemistry 26:1099–1104
White-Stevens RH, Kamin H (1972) Studies of a flavoprotein, salicylate hydroxylase: 1. Preparation, properties, and the uncoupling of oxygen reduction from hydroxylation. J Biol Chem 247:2358–2370
Yamaguchi M, Fujisawa H (1980) Purification and characterization of an oxygenase component in benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase system from Pseudomonas arvilla c-1. J Biol Chem 255:5058–5063
Yamaguchi M, Fujisawa F (1982) Subunit structure of oxygenase component in benzoate 1,2-dioxgenase system from Pseudomonas arvilla c-1. J Biol Chem 257:12497–12502
Yamaguchi M, Yamauchi T, Fujisawa H (1975) Studies on mechanism of double hydroxylation I. Evidence for participation of NADH-cytochrome c reductase in the reaction of benzoate 1,2-dioxygenase (benzoate hydroxylase). Biochem Biophys Res Commun 67:264–271
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamzah, R.Y., Al-Baharna, B.S. Catechol ring-cleavage in Pseudomonas cepacia: the simultaneous induction of ortho and meta pathways. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 41, 250–256 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186968
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00186968