Abstract
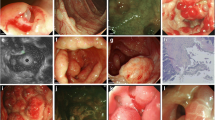
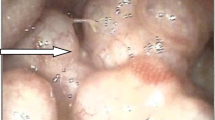
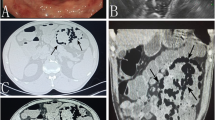
Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis (PCI), a condition involving submucosal or subserosal gas-containing cysts of the wall of the gastrointestinal tract, is a rare entity. It is mostly diagnosed between the third and fifth decades of life without a clear sexual predominance. Different aetiopathogenetic factors are under discussion, the most probable being a bacteriologic cause (Clostridium perfringens) in combination with minimal leaks in mucosal barrier. There are no pathognomonic symptoms; the clinical picture ranges from incidental findings to haematochezia. Diagnosis is based on plain abdominal film and X-ray following barium enema. Methods of treatment in symptomatic cases are oxygen and antibiotic (metronidazole) therapies and, in severe cases, resection of the diseased part of the intestine.
Zusammenfassung
Die Pneumatosis cystoides intestinii (PCI), das Auftreten submuköser oder subseröser, gasgefüllter Zysten in der Wand des Gastrointestinaltrakts, tritt als seltene Erkrankung ohne eindeutige Geschlechtspräferenz vorwiegend in der 3. bis 5. Lebensdekade auf. Atiopathogenetisch werden unterschiedliche Faktoren diskutiert, am wahrscheinlichsten ist eine bakterielle Ursache (Clostridium perfringens) in Verbindung mit einer minimalen Unterbrechung der Mukosaintegrität. Eine pathognomonische Symptomatik gibt es nicht, das klinische Bild reicht von asymptomatischen Zufallsbefunden bis zur Hämatochezie. Die Diagnose wird durch den Nachweis der Gaseinschlüsse mittels Abdomenübersichtsaufnahme und Kolonkontrasteinlauf gestellt. Als Behandlungsmethoden für symptomatische Patienten stehen Sauerstofftherapie, Antibiotikagabe (Metronidazol) und in schweren Fällen die Resektion des betroffenen Darmabschnitts zur Verfügung.
Similar content being viewed by others
Literatur
Alford JE, Galletti G, Culver GJ (1956) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Am J Surg 92:648–656
Bang BLF (1876) Luftholdige Kyster i Väggen of ileum og i nydannet Bindeväv pa sammes serosa. Nord Med Ark 8:1–16
Baumann-Schenker R (1939) Über Pneumatosis Cystoides Ventriculi et Jejuni. Acta Radiol 20:365–372
Bloch C (1977) The natural history of Pneumatosis coli. Radiology 123:311–314
Case WG, Hall R (1985) Surgical treatment of pneumatosis coli. Ann R Coll Surg Engl 67:368–369
Duvernoi JG (1730) Aer intestinorum tam sub extima quam intima tunica inclussus: observationes anatomicae: comment. Acad Acient Imp Petropol 5:213–225
Forgacs P, Wright PH, Wyatt AP (1973) Treatment of intestinal gas cysts by oxygen breathing. Lancet I:579–581
Galandiuk S, Fazio VW (1986) Pneumatosis Cystoides Intestinalis — A review of the literature. Dis Col Rect 29:358–363
Gillon J, Holt S, Sircus W (1979) Pneumatosis coli and sigmoid volvulus: a report of 4 cases. Br J Surg 66:802–805
Gruenberg JC, Grodsinky C, Ponka J (1979) Pneumatosis Intestinalis: A Clinical Classification Dis Col Rect 22:5–9
Hahn E (1899) Ueber Pneumatosis cystoides intestinorum hominis und einen durch Laparotomie behandelten Fall. Dtsch Med Wochenschr 25:657–660
Höflin F, Linden W van der (1974) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis treated by oxygen breathing. Scand J Gastroenterol 9:427–430
Hughes DTD, Gordon KCD, Swann JC, Bolt GL (1966) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Gut 7:553–557
Jamart J (1979) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis — A statistical study of 919 cases. Acta Hepatogastroenterol 26:419–422
Jauhonen P, Lehtola J, Karttunen T (1987) Treatment of pneumatosis coli with Metronidazole — endoscopic follow - up of one case. Dis Col Rect 30:800–801
Keyting W, McCarver RR, Kovarik J, Daywitt AL (1961) Pneumatosis intestinalis: A new concept. Radiology 76:733–741
Koss L (1952) Abdominal gas cysts (Pneumatosis cystoides intestinorum hominis) An analysis with a report of a case and a critical review of the literature. Arch Pathol 53:523–549
Marshak RH, Lipsay JJ, Friedman AI (1952) Pneumatosis of the colon. JAMA 148:1416–1418
Marshak RH, Lindner E, Maklansky D (1977) Pneumatosis cystoides coli. Gastrointest Radiol 2:85–89
Meyers MA, Ghahremani GG, Clements JL jr, Goodman K (1977) Pneumatosis intestinalis. Gastrointest Rdiol 2:91–105
Moote DJ, Fried LA, LeBrun GP, Fraser DB (1989) Pneumatosis coli: Is there a relationship with sigmoid colon reduncy? Gastrointest Radiol 14:79–82
Mujahed Z, Evans JA (1958) Gas cysts of the intestine (pneumatosis intestinalis). Surg Gynecol Obstet 107:151–160
O'Connell DJ, Dewbury KC, Green B, Wyatt AP (1976) The plain abdominal radiograph in pneumatosis coli. Clin Radiol 27:563–568
Read NW, Al-Janabi MN, Cann PA (1984) Is raised breath hydrogen related to the pathogenesis of pneumatosis coli? Gut 25:839–845
Simon NM, Nyman KE, Divertie MB, Rovelstad RA, King JE (1975) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis: Treatment with oxygen via close fitting mask. JAMA 231:1354–1356
Smith BH, Welter LH (1967) Pneumatosis intestinalis. Am J Clin Pathol 48:455–465
Smith WG, Anderson MJ jr, Pemberton HW (1958) Pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis involving left portion of colon: of four cases diagnosed at sigmoidoscopy. Gastroenterology 35:528–533
Spigelman AD, Williams CB, Ansell JC, Rutter CRP, Phillips] RCS (1990) Pneumatosis coli: a source of diagnostic confusion. Br J Surg 77:155
Stuart M (1984) Pneumatosis coli complicating carcinoma of the colon — Report of a case. Dis Col Rect 27:257–259
Van der Linden W, Marsell R (1979) Pneumatosis cystoides coli associated with high H2 excreation. Scand J Gastroenterol 14:173–174
Vernacchia FS, Jeffrey RB, Laing FC, Wing VW (1985) Sonographic recognition of pneumatosis intestinalis. AJR 145:51–52
Wyatt AP (1975) Prolonged symptomatic and radiological remission of colonic gas cysts after oxygen therapy. Br J Surg 62:837–839
Yale DE, Balish E, Madison JP (1974) The bacterial etiology of pneumatosis cystoides intestinalis. Arch Surg 109:89–94
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bertram, P., Treutner, K.H., Winkeltau, G. et al. Pneumatosis cystoides intestinii. Langenbecks Arch Chir 378, 249–254 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184367
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00184367