Summary
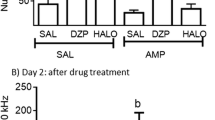
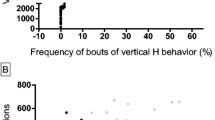
The stereotyped behaviour was analysed in Mastomys natalensis, a species of desert rat recently introduced in laboratory practice. The components of stereotyped behaviour were similar to rat characterised by repetitive sniffing, rearing, licking, head movements and biting. Apomorphine (0.5–2.0 mg/kg), amphetamine (2.5–10 mg/kg), methylphenidate (10 – 30 mg/kg) and adamantanamine (10 – 50 mg/kg) administered intraperitoneally, induced stereotyped behaviour in dose-dependent manner. Positive response was also obtained by other drugs acting on dopamine receptors like 1-dopa, GBR 12909, piribedil, tyramine, BS 9648, BS 9641 and BS 8824. Yohimbine (2 mg/kg) failed to produce any response. Apomorphine (2 mg/kg), amphetamine (10 mg/kg), methylphenidate (30 mg/kg) and piribedil (12 mg/kg) induced stereotypy which could be blocked by dopamine receptor blockers haloperidol (1 mg/kg) or pimozide (1 mg/kg) but yohimbine (2 mg/kg) an alpha adrenoceptor blocker was ineffective. Adamantanamine, piribedil and GBR 12909 enhanced the stereotypy induced by low doses of apomorphine, amphetamine and methylphenidate. The data shows that the stereotyped behaviour in Mastomys natalensis is mediated through dopaminergic mechanisms. It appears that both excitatory and inhibitory types of dopamine receptors are involved.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browne RG, Segal DS (1977) Metabolic and experimental factors in the behavioural response to repeated amphetamine. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:545–552
Carlson KG, Almasi J (1978) Sensitivity to apomorphine in the guinea pig as function of age and body weight. Psychopharmacology 57:279–282
Cools AR, Van Rossum JM (1970) Caudate dopamine and stereotyped behaviour of cats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn 187:163–173
Cools AR, Van Rossum JM (1976) Excitation mediating and inhibition mediating dopamine receptors, a new concept towards a better understanding of electrophysiological, biochemical, pharmacological, functional and clinical data. Psychopharmacology 45:243–254
Cools AR, Van Rossum JM (1980) Mini review: Multiple receptors for brain dopamine in behavioural regulation: concept of dopamine E and dopamine I receptors. Life Sci 27:1237–1253
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1973) On the mode of action of apomorphine. Eur J Pharmaco1 21:350–361
Costall B, Naylor RJ (1974) Stereotyped and circling behaviour induced by dopamine agonists after lesion of the midbrain raphe nuclei. Eur J Pharmaco1 29:206–222
Costall B, Naylor RJ, Cannon JG, Lee T (1977) Differentiation of the dopamine mechanisms mediating stereotyped behaviour and hyperactivity in the nucleus accumbens and caudate putamen. J Pharm Pharmacol 29:337–342
Dhawan BN, Patnaik GK (1976) Evidence for non-dopaminergic nature of apomorphine induced pecking in pigeons. In: Bradley PB, Dhawan BN (eds) Drugs and central synaptic transmission. MacMillan, London, pp 301–307
Dhawan BN, Srimal RC (1977) Drug induced stereotyped behaviour in guinea pig. In: Subramanyam S (ed) Neurohumoral correlates of behaviour. Thompson Press, Faridabad, pp 153–160
Dourish CT (1983) Piribedil: Behavioural, neurochemical and clinical profile of a dopamine agonist. Prog Neuropsychopharmacol Biol Psychiat 7:3–27
Durcan MJ, Fulker DW, Campbell IC (1984) Differences in the stereotypy response but not the motility response to apomorphine in the Roman high and Roman low avoiding strains of rats. Psychopharmacology 82:215–220
Einon DF, Sahakian BJ (1979) Environmentally induced differences in susceptibility of rats to CNS stimulants and CNS depressants: Evidence against a unitary explanation. Psychopharmacology 61:299–307
Ernst AM (1967) Mode of action of apomorphine and dexamphetamine on gnawing compulsion in rats. Psychopharmacology 10:316–323
Ernst AM, Smelik P (1966) Site of action of dopamine and apomorphine in compulsive gnawing behaviour in rats. Experientia 22:837–838
Frommel ED (1965) The cholinergic mechanism of psychomotor agitation in apomorphine injected mice. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 154:231–234
Goodman I, Zacny J, Osman A, Azzaro A, Donovan C (1983) Dopaminergic nature of feeding induced behavioural stereotypies in stressed pigeons. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 18: 153–158
Grelak RP, Clark R, Stump JM, Vernier VG (1970) Amantadinedopamine interactions: Possible mode of action in Parkinsonism. Science 169:203–204
Gulati A, Dhawan BN (1984) Classification of central dopamine receptors. Ind J Pharmacol 16:182–188
Gulati A, Srimal RC, Dhawan KN, Dhawan BN (1987) On the mechanism of potentiation of apomorphine-induced stereotypy due to electroconvulsive shock. Neuropharmacology 26: 1733–1737
Gulati A, Hussain G, Srimal RC, Dhawan BN (1988) Comparison of cortical adrenergic, cholinergic and benzodiazepine receptors between albino rat and desert rat (Mastomys natalensis) using radioreceptor binding. Pharmacology (in press)
Hackman R, Pentikainen P, Neuvonen PJ, Vapaatalo H (1973) Inhibition of the apomorphine gnawing compulsion by amantadine. Experientia 29:1524–1525
Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJE, Jageneau AHM (1960) Apomorphine antagonism in rats. Arzneimittelforschung 10:1003–1005
Ljungberg T, Ungerstedt U (1977) Apomorphine-induced locomotion and gnawing: Evidence that the experimental design greatly influences gnawing while locomotion remains unchanged. Eur J Pharmacol 46:147–151
Mogilnicka E, Braestrup C (1976) Noradrenergic influence on the stereotyped behaviour induced by amphetamine, phenethylamine and apomorphine. J Pharm Pharmacol 28:253–255
Pandey SC, Dubey MP, Dhawan BN (1986) Ontogenic studies on brain biogenic amines in Mastomys natalensis. Ind J Med Res 84:405–412
Randrup A, Munkvad I (1967) Stereotyped activities produced by amphetamine in several animal species and man. Psychopharmacology 11:300–310
Randrup A, Munkvad I (1974) The pharmacology and physiology of stereotyped behaviour. J Psychiat Res 11:1–10
Scheel-Krüger J (1970) Central effects of anticholinergic drugs measured by apomorphine gnawing test in mice. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol 28:1–16
Shukla R, Srimal RC, Dhawan BN (1985) Centrally mediated effects of GBR 12909, a dopamine reuptake inhibitor on body temperature of pigeon, rabbit and Mastomys natalensis. Ind J Pharmacol 17:P077
Shukla R, Srimal RC, Dhawan BN (1981) The effect of intracerebroventricular administration of catecholamines and their antagonists on rectal temperature in Mastomys natalensis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318:38–42
Smith RC, Leelavathi DE, Lauritzen MA (1978) Behavioural effects of dopamine agonist increase with age. Commun Psychopharmacol 2:39–43
Srimal RC, Dhawan BN (1970) An analysis of methylphenidate induced gnawing in guinea pig. Psychopharmacology 18: 99–107
Van Beck MC, Timmerman H (1974) Some benzhydryl derivatives as central dopamine receptor stimulating agents. J Pharm Pharmacol 26: 57–58
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to A. Gulati
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gulati, A., Srima, R.C. & Dhawan, B.N. An analysis of stereotyped behaviour in Mastomys natalensis. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 337, 572–575 (1988). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182734
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00182734