Abstract
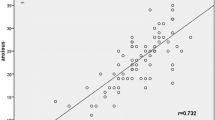
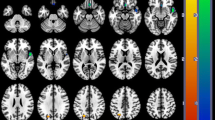
Regional cerebral blood flow was investigated in 14 patients with major depression diagnosed according to the DSM-III-R criteria (six patients with single and eight patients with recurrent episodes) and in ten healthy volunteers. The mean ages of the patients and the controls were 33.5 ± 2.7 and 31.6 ± 2.6 years, respectively. The severity of the depression was assessed using the 17-item Hamilton Depression Scale (mean: 23.2 ± 1.5). None of the patients was under medication. After administration of 500 MBq technetium-99m hexamethylpropylene amine oxime, a single photon emission tomography study was performed and then transaxial, sagittal and coronal slices were obtained. For the semiquantitative analysis of the data, the ratios of the mean counts/pixel to the whole slice were calculated for 24 regions on three consecutive transaxial slices in the orbitomeatal plane. Additionally, left/right and frontal/occipital ratios were calculated. Both sides of the temporal region had a significantly decreased cerebral blood flow (CBF) when compared to the controls. The left/right ratio of the prefrontal region was also significantly lower in the patients than in the controls. The Hamilton score had a negative correlation with blood flow in the anterofrontal and left prefrontal regions. According to our results, regional CBF seems to be decreased in the left prefrontal and in both temporal regions in major depression. The severity of depression is correlated with the reduction in CBF in the regions of the anterofrontal and left prefrontal cortex.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Psychiatric Association (1987) DSM III. Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders. Third edition, revised. American Psychiatric Association, Washington, DC
Andreasen NC, Swayze V, Flaum M, Alliger R, Cohen G (1990) Ventricular abnormalities in affective disorder: clinical and demographic correlates. Am J Psychiatry 147:893–900
Baxter LR Jr, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Schwartz JM, Gerner RH, Selin CE, Sumida RM (1985) Cerebral metabolic rates for glucose in mood disorders: studies with positron emission tomography and fluorodeoxyglucose. Arch Gen Psychiatry 42:441–447
Baxter LR Jr, Schwarz JM, Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Guze BH, Selin CE, Gerner RH, Sumida RM (1989) Reduction of prefrontal cortex glucose metabolism common to three types of depression. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:243–250
Buchsbaum MS, Ingvar DH, Kesslar R, Waters RN, Capellatti J, van Kammen DP, King AC, Johnson JL, Manning RG, Flyn RW, Mann LS, Bunney WE, Sokoloff L (1982). Cerebral glucography with positron emission tomography. Arch Gen Psychiatry 39:251–259
Buchsbaum MS, DeLisi LE, Holcomb HH, Capellatti J, King AC, Johnson J, Hazlett E, Dowling-Zimmerman S, Post RM, Morihisa J, Carpenter W, Cohen R, Pickar D, Weinberger DR, Margolin R, Kessler RM (1984) Anteroposterior gradients in cerebral glucose use in schizophrenia and affective disorder. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:1159–1166
Buchsbaum MS, Wu J, DeLisi LE, Holcomb H, Kessler R, Johson J, King AC, Hazlett E, Lanston K, Post RM (1986) Frontal cortex and basal ganglia rates assessed by positron emission tomography with (F 18) 2-deoxyglucose in affective illness. J Affective Disord 10:137–152
Costa DC, Ell PJ, Cullum ID, Jarritt PH (1986) The in vivo distribution of 99mTc-HMPAO in normal man. Nucl Med Commun 7:647–658
Delvenne V, Delecluse F, Hubain PP, Schoutens A, De-Maertetlaer V, Mendlewicz J (1990) Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with affective disorders. Br J Psychiatry 157:359–365
Devous MD, Rush AJ, Schlesser MA, Debus J, Raese JD, Chehabi HH, Bonte FJ (1984) Single photon tomographic determinants of regional cerebral blood blood flow in psychiatric disorders (abstract). J Nucl Med 25:57–58
Devous MD, Gullion CM, Granneman B, Rush AJ (1991) Regional cerebral blood flow alterations in unipolar depression (abstract). J Nucl Med 32:951–952
Frackowiack RSJ, Pozilli C, Logg NJ (1981) Regional cerebral oxygen supply and utilization in dementia. A clinical and physiological study with oxygen-15 and positron tomography. Brain 104:753–778
Goldstein PC, Brown GG, Welch KMA, Marcus A, Ewing JR, Rosenbaum G (1985) Age-related decline of rCBF in schizophrenia and major affective disorder. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab 5 [Suppl]:203–204
Gur RE, Skolnick BE, Gur RC, Caroff S, Rieger W, Obrist WD, Younkin D, Reivich M (1984) Brain function in psychiatric disorders: II. Regional cerebral blood flow in medicated unipolar depressives. Arch Gen Psychiatry 41:695–699
Hamilton M (1967) Development of a rating scale for primary depressive illness. Br J Soc Psychol 6:278–296
Kling AS, Metter EJ, Riege WH, Kuhl DE (1986) Comparison of PET measurement of local brain glucose metabolism and CAT measurement of brain atrophy in chronic schizophrenia and depression. Am J Psychiatry 143:175–180
Mathew RS, Meyer JS, Francis DJ, Senchuk KM, Mortel K, Clarhorn JI (1980) Cerebral blood flow in depression. Am J Psychiatry 137:1449–1450
Mayberg HS, Jeffrey PJ, Wagner HN, Simpson SG (1991) Regional cerebral blood flow in patients with refractory unipolar depression measured with Tc-99m HMPAO/SPECT (abstract). J Nucl Med 32:951
Oldfield RC (1971) The assesment and analysis of handedness: The Edinburgh Inventory. Neuropsychologia 9:97–113
Phelps ME, Mazziotta JC, Baxter LR, Gerner R (1984) Positron emission tomographic study of affective disorders: problems and strategies. Ann Neurol 15 [Suppl]:149–132
Robins PV, Pearlson GD, Aylward E, Kumar AJ, Dowell K (1991) Cortical magnetic resonance imaging changes in elderly inpatients with major depression. Am J Psychiatry 148:617–620
Sackeim HA, Porhovnik I, Apter S, Lucas L, Decina P, Mukherjee S, Prudic J, Malitz S (1987) Regional cerebral blood flow in affective disorders: baseline and effect of treatment. In: Takahashi R, Flow-Henry P, Gruzelier J, Niwa S (eds) Cerebral dynamics, laterality, and psychopathology. Elsevier Science, New York
Sackeim HA, Porhovnik I, Moeller JR, Brown RP, Apter S, Prudic J, Devanand DP, Mukherjee S (1990) Regional cerebral blood flow in mood disorders. Arch Gen Psychiatry 47:60–70
Schlegel S, Aldenhoff JB, Eissner D, Lindner P, Nickel O (1989) Regional cerebral blood flow in depression: association with Psychopathology. J Affective Disord 17:211–218
Schwartz JM, Baxter LB, Mazziotta JC, Gerner RH, Phelps ME (1987) The differential diagnosis of depression. Relevance of positron emission tomography studies of cerebral glucose metabolism to the bipolar-unipolar dichotomy. JAMA 258:1368–1374
Silfverskiöld P, Risberg J (1989) Regional cerebral blood flow in depression and mania. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:253–259
Targum SD, Rosen SN, DeLisi LE, Weinberger DR, Citrin CM (1983) Cerebral ventricular size in major depression: association with delusional symptoms. Biol Psychiatry 18:329–336
Uytdenhoef P, Portelange P, Jacquy J, Charles G, Linkowski P, Mendlewicz J (1983) Regional cerebral blood flow and lateralized hemispheric dysfunction in depression. Br J Psychiatry 143:128–132
Warren LR, Butler RW, Katholi CR, McFarland CE, Crews EL, Hasley JH (1984) Focal changes in cerebral blood flow produced by monetary incentive during a mental mathematics task in normal and depressed subjects. Brain Cogn 3:71–85
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yazici, K.M., Kapucu, Ö., Erbas, B. et al. Assessment of changes in regional cerebral blood flow in patients with major depression using the 99mTc-HMPAO single photon emission tomography method. Eur J Nucl Med 19, 1038–1043 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180865
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00180865