Abstract
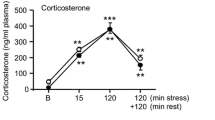
Subchronic (6 days) but not acute injections of nicotine (0.4 mg/kg SC) increased spontaneous activity (P<0.01) in an elevated X-maze composed of two open and two enclosed runways. Neither acute nor subchronic nicotine altered significantly the ratio of open: enclosed runway entries (O/E ratio). Diazepam (5 mg/kg PO) had no significant effects on spontaneous activity but increased the O/E ratio (P<0.05). Acute nicotine increased (P<0.01) whereas subchronic nicotine caused a small decrease (P<0.05) in the plasma corticosterone concentration. Both acute and subchronic diazepam decreased the levels of the hormone (P<0.01 and P<0.05, respectively) although the reduction elicited by chronic diazepam was less than that caused by acute diazepam (P<0.05). In the experiments with diazepam the plasma corticosterone concentration correlated negatively with the O/E ratio (r=−0.58; P<0.05), whereas in the experiments with nicotine plasma corticosterone correlated negatively (r=−0.46; P<0.05) with enclosed runway entries. Nicotine injections were associated with a regionally-selective reduction in the 5-hydroxyindole acetic acid (5-HIAA) concentration in the hippocampus (P<0.05) and a reduction in hippocampal 5-hydroxytryptamine (5-HT) which approached statistical significance. Chronic, but not acute, diazepam increased (P<0.01) hypothalamic 5-HT. The changes in 5-HT and 5-HIAA did not appear to be directly related to the behavioural or adrenocortical responses to either of the drugs.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balfour DJK (1984) The pharmacology of nicotine dependence: a working hypothesis. In: Balfour DJK (ed) Nicotine and the tobacco smoking habit. Pergamon Oxford, pp 101–112
Bättig K, Driscoll P, Schlatter J, Uster HJ (1975) Effects of nicotine on the exploratory locomotion patterns of female high- and low-avoidance rats. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 4:435–439
Benwell MEM, Balfour DJK (1979) Effects of nicotine administration and its withdrawal on plasma corticosterone and brain 5-hydroxyindoles. Psychopharmacology 63:7–11
Benwell MEM, Balfour DJK (1982a) Effects of chronic nicotine administration on the respone and adaptation to stress. Psychopharmacology 76:160–162
Benwell MEM, Balfour DJK (1982b) The effects of nicotine administration on 5-HT uptake and biosynthesis in rat brain. Eur J Pharmacol 84:71–77
FitzGerald RE, Oettinger R, Bättig K (1985) Reduction of nicotine-induced hyperactivity by pCPA. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 23:279–284
Handley SL, Mithani S (1983) Effects of drugs acting on β-adrenoceptors in an animal model of anxiety. Br J Pharmacol 78:110P
Hendry JS, Rosecrans JA (1984) Effects of nicotine on conditioned and unconditioned behaviours in experimental animals. In: Balfour DJK (ed) Nicotine and the tobacco smoking habit. Pergamon, Oxford, pp 75–79
Keenan A, Johnson FN (1972) Development of behavioural tolerance to nicotine in the rat. Experientia 28:428–429
Keim KL, Sigg EB (1977) Plasma corticosterone and brain catecholamines in stress: effect of psychotropic drugs. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 6:79–85
Le Fur G, Guilloux F, Mitrani N, Mizoule J, Uzan A (1979) Relationships between plasma corticosteroids and benzodiazepines in stress. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 211:305–308
Mattingly D (1962) A simple fluorometric method for the estimation of 11-hydroxycorticosteroids in human plasma. J Clin Pathol 15:375–379
Morrison CF (1974) Effects of nicotine and its withdrawal on the performance of rats on signalled and unsignalled avoidance schedules. Psychopharmacologia 28:25–35
Morrison CF, Stephenson JA (1970) Drug effects on a measure of unconditioned avoidance in the rat. Psychopharmacologia 18:133–143
Morrison CF, Stephenson JA (1972) Occurrence of tolerance to a central depressant effect of nicotine. Br J Pharmacol 46:151–156
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open: closed arm antries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Meth 14:149–167
Reinhard JF, Moskowitz MA, Sved AF, Fernstrom JD (1980) A simple sensitive and reliable assay for serotonin and 5-HIAA in brain tissue using liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. Life Sci 27:905–911
Stolerman IF, Fink R, Jarvik ME (1973) Acute and chronic tolerance to nicotine measured by activity in rats. Psychopharmacologia 30:329–342
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balfour, D.J.K., Graham, C.A. & Vale, A.L. Studies on the possible role of brain 5-HT systems and adrenocortical activity in behavioural responses to nicotine and diazepam in an elevated X-maze. Psychopharmacology 90, 528–532 (1986). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174073
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00174073