Summary
The upper limits of striatal and hypothalamic dopamine formation and metabolism in the rat were defined after acute levodopa/carbidopa (100/100 mg/kg) in combination with MAO (clorgyline; 32 mg/kg or pargyline; 100 mg/kg) and/or COMT inhibitors (OR-462, OR-611, Ro 41-0960, 30 mg/kg).
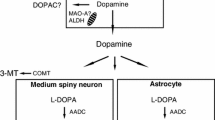
Striatal and hypothalamic dopa and 3-OMD levels increased several hundred times after levodopa/carbidopa treatment alone. Dopamine, DOPAC, HVA and 3-MT levels elevated also but noradrenaline and 5-HT did not. Clorgyline further increased 3-OMD, dopamine and 3-MT concentrations while DOPAC and HVA levels decreased. These changes were even more pronounced after pargyline. In the striatum, all COMT inhibitors (with levodopa/carbidopa) blocked 3-OMD formation but elevated neither dopamine nor DOPAC levels. OR 462 increased dopa levels. Only Ro 41-0960, the brain penetrating compound, blunted HVA levels. All three COMT inhibitors decreased high 3-OMD levels evoked by MAO inhibitors (+ levodopa/carbidopa). In pargyline-treated rats, COMT inhibitors did not alter dopamine, DOPAC or HVA levels but all of them decreased significantly 3-MT levels, particularly Ro 41-0960. Striatal dopamine levels increased maximally 6 times compared to those in the saline-treated controls. In the hypothalamus, COMT inhibitors decreased 3-OMD levels to 1/5-1/30 of those after levodopa/carbidopa alone. COMT inhibitors suppressed 3-OMD formation also in clorgyline and pargyline (+ levodopa/carbidopa) treated rats. After clorgyline, OR-611 and Ro 41-0960 increased high dopamine levels but only Ro 41-0960 suppressed HVA and 3-MT levels. None of the COMT inhibitors changed the high dopamine and low DOPAC levels after pargyline. 3-MT was decreased by OR-462 and Ro 41-0960. Hypothalamic dopamine was maximally 45 times higher than that in the control rats. COMT inhibitors did not have any significant hormonal effects.
In conclusion, formation of 3-OMD was well inhibited by all COMT inhibitors, but their effect on the brain dopamine levels was limited compared to the very pronounced effect of the two MAO inhibitors. Inhibition of COMT outside the brain (as with OR-462) contributed about equally to the brain dopamine levels as inhibition that occurred also in the brain (as with Ro 41-0960).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azzaro AJ, King J, Kotzuk J, Schoepp DD, Frost J, Schochet S (1985) Guinea pig striatum as a model of human dopamine deamination: the role of monoamine oxidase isozyme ratio, localization, and affinity for substrates in synaptic dopamine metabolism. J Neurochem 45:949–956
Bäckström R, Honkanen E, Pippuri A, Kairisalo P, Pystynen J, Heinola K, Nissinen E, Linden I-B, Mannisto PT, Kaakkola S, Pohto P (1989) Synthesis of some novel potent and selective catechol-O-methyltransferase inhibitors. J Med Chem 32:841–846
Borgulya J, Bruderer H, Bernauer K, Zürcher G, Da Prada M (1989) Catechol-O-methyltransferase-inhibiting pyrocatechol derivatives — synthesis and structure-activity studies. Hely Chim Acta 72:952- 968
Butcher SP, Fairbrother IS, Kelly JS, Arbuthnott GW (1990) Effects of selective monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the in vivo release and metabolism of dopamine in the rat striatum. J Neurochem 55:981–988
Buu NT, Angers M (1987) Effects of different monoamine oxidase inhibitors on the metabolism of L-dopa in the rat brain. Biochem Pharmacol 36:1731–1735
Cedarbaum JM (1987) Clinical pharmacokinetics of anti-parkinsonian drugs. Clin Pharmacokin 13:141–178
Dzoljic MR, Bruinvels J, Bonta IL (1977) Desynchronization of electrical activity in rats induced by deprenyl — an inhibitor of monoamine oxidase B — and relationship with selective increase of dopamine and beta-phenylalanine. J Neural Transm [Gen Sect] 40:1–12
Glowinski J, Iversen LL (1966) Regional studies on catecholamines in the rat brain. I. The disposition of 3H-norepinephrine, 3H-dopamine and 3H-dopa in various regions of the brain. J Neurochem 13:655–669
Kaakkola S, Tuomainen P, Wurtman RJ, Mannisto PT (1991) Effect of systemic carbidopa on dopamine synthesis in rat hypothalamus and striatum. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] (in press)
Kato T, Dong B, Ishii K, Kinemuchi H (1986) Brain dialysis: in vivo metabolism of dopamine and serotonin by monoamine oxidase A but not B in the striatum of unrestrained rats. J Neurochem 46:1277–1282
Kopin I (1985) Catecholamine metabolism: basic aspects and clinical significance. Pharmacol Rev 37:333–364
LeWitt PA (1989) The pharmacology of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease: an update. In: Calne DB (ed) Drugs for the treatment of Parkinson's disease (Handbook of experimental pharmacology), vol 88. Springer, Berlin Heidelberg New York, pp 325–384
Männistö PT (1983) Central regulation of thyrotropin secretion in rats: methodological aspects, problems and some progress. Med Biol 61:92–100
Männistö PT, Kaakkola S (1989) New selective COMT inhibitors: useful adjuncts for Parkinson's disease? Trends Pharmacol Sci 10:54–56
Männistö PT, Kaakkola S (1990) Rationale for selective COMT inhibitors as adjuncts in the drug treatment of Parkinson's disease. Pharmacol Toxicol 66:317–323
Männistö PT, Kaakkola S, Nissinen E, Linden I-B, Pohto P (1988) Properties of novel effective and highly selective inhibitors of catechol-O-methyl transferase. Life Sci 43:1465–1471
Männistö PT, Tuomainen P, Toivonen M, Törnwall M, Kaakkola S (1990) Effect of acute levodopa on brain catecholamines after selective MAO and COMT inhibition in male rats. J Neural Transm [P-D Sect] 2:31–43
Melamed E, Hefti F, Wurtman RJ (1980) Nonaminergic striatal neurons convert exogenous Lrdopa to dopamine. Ann Neurol 8:558–563
Nissinen E, Linden I-B, Schultz E, Kaakkola S, Mannisto PT, Pohto P (1988) Inhibition of catechol-O-methyltransferase activity by two novel disubstituted catechols in the rat. Eur J Pharmacol 153:263–269
Oreland L, Arai Y, Stenström A (1983) The effect of deprenyl (selegyline) on intra- and extraneuronal dopamine oxidation. Acta Neurol Scand [Suppl] 95:81–85
Porter CC, Watson LS, Titus DC, Totaro JA, Byer SS (1962) Inhibition of dopa decarboxylase by the hydrazino analog of alpha-methyl-dopa. Biochem Pharmacol 11:1067–1077
Turomisto J, Männistö PT (1985) Neurotransmitter regulation of anterior pituitary hormones. Pharmacol Rev 37:249–332
Wagner J, Vitali P, Palfreyman MG, Zraika M, Huot S (1982) Simultaneous determination of 3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine, 5-hydroxytryptamine, dopamine, 4-hydroxy-3-methoxy-phenylalanine, norepinephrine, 3,4-dihydroxyphenylacetic acid, homovanillic acid, serotonin, and 5-hydroxyindoleacetic acid in rat cerebrospinal fluid and brain by high-performance liquid chromatography with electrochemical detection. J Neurochem 38:1241–1254
Waldmeier PC (1987) Amine oxidases and their endogenous substrates (with special reference to monoamine oxidase and the brain). J Neural Transm [Gen Sect] 23:55–72
Yang HYT, Neff NH (1974) The monoamine oxidase of brain: selective inhibition with drugs and consequences for the metabolism of biogenic amines. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 189:733–740
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Send offprint requests to P.T. Männistö at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Männistö, P.T., Tuomainen, P. Effect of high single doses of levodopa and carbidopa on brain dopamine and its metabolites: modulation by selective inhibitors of monoamine oxidase and/or catechol-O-methyltransferase in the male rat. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344, 412–418 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172580
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172580