Summary
The present study aimed at determining the modulation by adenosine of the release of noradrenaline in the epididymal portion of the rat vas deferens. The tissues were treated with pargyline and perifused in the presence of desipramine and yohimbine. Up to four periods of electrical stimulation were applied (5 Hz, 9 min).
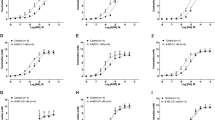
The A1-adenosine receptor selective agonist R-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine (R-PIA; 100–900 nmol·l−1) reduced, whereas the A2A-receptor selective agonist 2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino-5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine (CGS21680; 3–30nmol·l−1) increased the electrically-evoked noradrenaline overflow in a concentration-dependent manner. The nonselective agonist 5′-N-ethy1carboxamidoadenosine (NECA; 30–300 nmol·l−1) reduced noradrenaline overflow, but the effect did not depend on the concentration. Adenosine deaminase at the concentration of 0.5 μ·ml−1 decreased but at that of 2.0 μ·ml−1 increased noradrenaline overflow. The inhibitors of adenosine uptake, S-(4-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine (NBTI; 50 nmol·l−1) and dipyridamole (3 μmol·l−1), increased the electrically-evoked noradrenaline overflow. The A1-adenosine receptor antagonist 1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine (DPCPX; 20 nmol·l−1) caused an increase whereas the A2-adenosine receptor antagonist 3,7-dimethyl-1-(2-propynyl)xanthine (DMPX; 0.1 μmol·l−1) caused a decrease. NBTI (50 nmol·l−1), partially antagonized the effect of both DPCPX (20 nmol·l−1) and DMPX (0.1 μmol·l−1).
It is concluded that, in the epididymal portion of the rat vas deferens, endogenous adenosine tonically modulates the release of noradrenaline evoked by electrical stimulation, through activation of both inhibitory (A1) and facilitatory (A2A) adenosine receptors.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CGS 21680:
-
2-p-(2-carboxyethyl)phenethylamino-5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine
- DMPX:
-
3,7-dimethyl-l-(2-propynyl)xanthine
- DPCPX:
-
1,3-dipropyl-8-cyclopentylxanthine
- NBTI:
-
S-(4-nitrobenzyl)-6-thioinosine
- NECA:
-
5′-N-ethylcarboxamidoadenosine
- R-PIA:
-
R-N6-phenylisopropyladenosine
References
Ballard HJ (1991) The influence of lactic acid on adenosine release from skeletal muscle in anaesthetized dogs. J Physiol (Lond) 433:95–108
Brown SJ, James S, Reddington M, Richardson PJ (1990) Both A1 and A2a purine receptors regulate striatal acetylcholine release. J Neurochem 55:31–38
Burnstock G (1990) Noradrenaline and ATP as cotransmitters in sympathetic nerves. Neurochem Int 17:357–368
Clanachan AS, Parkinson FE (1990) Transport systems for adenosine in mammalian cell membranes. In: Jacobson KA, Daly JW, Manganiello V (eds) Purines in cellular signaling — Targets for new drugs. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong, pp 26–32
Correia de Sá P, Sebastiäo AM, Ribeiro JA (1991) Inhibitory and excitatory effects of adenosine receptor agonists on evoked transmitter release from phrenic nerve endings of the rat. Br J Pharmacol 103:1614–1620
Daly JW, Padgett W, Shamim MT (1986) Analogs of caffeine and theophylline: effects of structural alterations on affinity at adenosine receptors. J Med Chem 29:1305–1308
Fuder H, Brink A, Meincke M, Tauber U (1992) Purinoceptor-mediated modulation by endogenous and exogenous agonists of stimulation-evoked [3H]noradrenaline release on rat iris. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 345:417–423
Geiger JD, Padua RA, Nagy JI (1990) Adenosine deaminase and adenosine transport systems in the CNS. In: Jacobson KA, Daly JW, Manganiello V (eds) Purines in cellular signaling — Targets for new drugs. Springer, New York Berlin Heidelberg London Paris Tokyo Hong Kong, pp 20–25
Gonçalves J (1991) Co-transmissão noradrenalina-ATP: razões da variabilidade da participação noradrenérgica. Dr Thesis, Faculty of Pharmacy, University of Porto, O'Porto, Portugal
Gonçalves J, Guimarães S (1991) Influence of neuronal uptake on pre-and postjunctional effects of α-adrenoceptor agonists in tissues with noradrenaline-ATP cotransmission. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:532–537
Guimarães S, Oswald W (1969) Adrenergic receptors in the veins of the dog. Eur J Pharmacol 72:133–140
Guimarães G, Brandão F, Paiva MQ (1978) A study of the adrenoceptor mediated feedback mechanisms by using adrenaline as a false transmitter. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 305:185–188
Hedqvist P, Fredholm BB (1976) Effects of adenosine on adrenergic transmission; prejunctional inhibition and postjunctional enhancement. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 293:217–223
Hutchison AJ, Webb RL, Oei HH, Ghai GR, Zimmerman MB, Williams M (1989) CGS21680C, an A2 selective adenosine receptor agonist with preferential hypotensive activity. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251:47–55
Jarvis MF, Schulz R, Hutchison AJ, Do UH, Sills M, Williams M (1989) [3H]-CGS 21680, a selective A2 adenosine receptor agonist directly labels A2 receptors in rat brain. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 251: 888–893
Lohse MJ, Klotz K-N, Lindenborn-Fotinos J, Reddington M, Schwabe U, Olsson RA (1987) 8-Cyclopentyl-1,3-dipropylxanthine (DPCPX) — a selective high affinity antagonist radioligand for A1 adenosine receptors. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336:204–210
Lupica CR, Cass WA, Zahniser NR, Dunwiddie TV (1990) Effects of the selective adenosine A2 receptor agonist CGS 21680 on in vitro electrophysiology, CAMP formation and dopamine release in rat hippocampus and striatum. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 252:1134–1141
Muller MJ, Paton DM (1979) Presynaptic inhibitory actions of 2-substituted adenosine derivates on neurotransmission in rat vas deferens: Effects of inhibitors of adenosine uptake and deamination. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 306:23–28
Pfleiderer G, Dose K (1955) Eine enzymatische Bestimmung der L [±]-Milchsäure mit Milchäduredehydrogenase. Biochem Z 326:436–441
Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM (1986) Adenosine receptors and calcium: basis for proposing a third (A3) adenosine receptor. Prog Neurobiol 26:179–209
Ribeiro JA, Sebastião AM (1991) Purinergic modulation of neurotransmitter release in the peripheral and central nervous systems. In: Feigenbaum J, Hanani M (eds) Presynaptic regulation of neurotransmitter release. Freund, London, pp 451–495
Russ H, Schömig E, Trendelenburg U (1991) The energy requirements for the basal efflux of 3H-noradrenaline from sympathetically innervated organs. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 344:286–296
Sebastião AM, Stone TW, Ribeiro JA (1990) The inhibitory adenosine receptor at the neuromuscular junction and hippocampus of the rat: antagonism by 1,3,8-substituted xanthines. Br J Pharmacol 101:453–459
Shinozuka K, Bjur RA, Westfall DP (1990) Effects of α,β-methylene ATP on the prejunctional purinoceptors of the sympathetic nerves of the rat caudal artery. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 254:900–904
Soares-da-Silva P (1988) Evidence for dopaminergic cotransmission in dog mesenteric artery. Br J Pharmacol 95:218–224
Starke K (1987) Presynaptic α-autoreceptors. Rev Physiol Biochem Pharmacol 107:73–146
von Kügelgen I, Starke K (1991) Noradrenaline-ATP cotransmission in the sympathetic nervous system. Trends Pharmacol Sci 12:319–324
von Kügelgen I, Schöffel E, Starke K (1989) Inhibition by nucleotides acting at presynaptic P2-receptors of sympathetic neuro-effector transmission in the mouse isolated vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:522–532
Wakade AR, Wakade TD (1978) Inhibition of noradrenaline release by adenosine. J Physiol (Lond) 282:35–49
Wennmalm M, Fredholm BB, Hedqvist P (1988) Adenosine as a modulator of sympathetic nerve-stimulation-induced release of noradrenaline from the isolated rabbit heart. Acta Physiol Scand 132: 487–494
Williams M (1987) Purine receptors in mammalian tissues: pharmacology and functional significance. Ann Rev Pharmacol Toxicol 27:315–345
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to J. Gongalves at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gonçalves, J., Queiroz, G. Facilitatory and inhibitory modulation by endogenous adenosine of noradrenaline release in the epididymal portion of rat vas deferens. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 348, 367–371 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171335
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171335