Summary
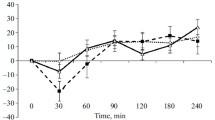
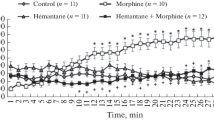
The antinociceptive effect of morphine, as determined by the tail-flick test, was dose-dependently increased by the intraperitoneal injection of zopiclone. The benzodiazepine antagonists Ro 15-1788 (flumazepil) and Ro 15-3505, when intraperitoneally injected, significantly antagonized the effect of intraperitoneal injection of zopiclone on morphine antinociception. Intrathecal injection of zopiclone potentiated morphine antinociception, while the intracerebroventricular injection of zopiclone failed to enhance morphine antinociception and the intracerebroventricular injection of flumazepil to antagonize the intraperitoneal-zopiclone-induced increase in morphine antinociception. These results suggest that benzodiazepine sites are specifically involved in the potentiating effect of zopiclone on morphine antinociception. The anatomical locations of the receptors involved seem to be at the spinal level.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Altaffer FB, De Balbian Werster F, Hall S, Long CJ, D'Encarnacao P (1970) A simple and inexpensive cannula technique for chemical stimulation of the brain. Physiol Behav 5:119–121
Armitage P (1974) Statistical methods in medical research. Blackwell Scientific Publications, London, p 394
Blanchard JC, Boireau A, Garret C, Julou L (1979) In vitro and in vivo inhibition by zopiclone of benzodiazepine binding to rodent brain receptors. Life Sci 24:2417–2420
Brady LS, Mansbach RS, Skurdal DN, Muldoon SM, Barret JE (1984) Reversal of the antinociceptive effects of centrally administered morphine by the benzodiazepine receptor antagonist Ro 15–1788. Life Sci 35:2593–2600
Campbell RC (1974) Statistics for biologists. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 61
D'Amour EF, Smith DL (1941) A method for determining loss of pain sensation. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 72:74–79
Del Zompo M, Post RM, Tallman JF (1983) Properties of two benzodiazepine binding sites in spinal cord. Neuropharmacology 22:115–118
Fan SG, Qu ZC, Han JS (1982) GABA: antagonistic effect of electroacupuncture analgesia and morphine analgesia in the rat. Life Sci 31:1225–1228
Fennessy MR, Sawynok J (1973) The effect of benzodiazepines on the analgesic effect of morphine and sodium salicylate. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 204:77–85
Gluckman MI (1965) Pharmacology of oxazepam (Serax) a new antianxiety agent. Curr Ther Res 7:721–740
Goldberg ME, Salama AI, Patel JB, Malick JB (1983) Novel nonbenzodiazepine anxiolytics. Neuropharmacology 22:1499–1504
Gupta SK, Gaitonde BB (1964) Analgesic activity of a new quinoline derivative Ro 4–1788. Indian J Physiol Pharmacol 8:27–32
Haefely W (1983) Antagonists of benzodiazepines: functional aspects. In: Biggio G, Costa E (eds) benzodiazepine recognition ligands: Biochemistry and pharmacology. Raven Press, New York, pp 73–93
Hunkeler W, Mohler H, Pieri I, Pole P, Bonetti EP, Cumin R, Schaffner R, Haefely W (1981) Selective antagonists of benzodiazepine. Nature 290:514–516
Julou L, Bardone ML, Blanchard JC, Garret C, Stutzmann JM (1983) Pharmacological studies on zopiclone. Pharmacology (Suppl 2) 27:46–58
Julou L, Blanchard JC, Dreyfus JF (1985) Pharmacological and clinical studies of cyclopyrrolones: zopiclone and suriclone. Pharmacology Biochemistry Behav 23:653–659
Jurna I (1984) Depression by diazepam, GABA and muscimol of activity in ascending axons of the rat spinal cord. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol (Suppl) 325:309
Mantegazza P, Parenti M, Tammiso R, Vita P, Zambotti F, Zonta N (1982) Modification of the antinociception effect of morphine by centrally administered diazepam and midazolam. Br J Pharmacol 75:569–572
Möhler H, Richards JG (1981) Agonist and antagonist benzodiazepine receptor interaction in vitro. Nature 294:763–765
Patel JB, Martin C, Malick JB (1983) Differential antagonism of the anticonflict effects of typical and atypical anxiolytics. Eur J Pharmacol 86:295–298
Randall LO, Scheckel CL, Pool W (1970) Pharmacology of medazepam and metabolites. Archs Int Pharmacodyn Ther 185:135–148
Shannon HE, Holtzman SG, Davis DC (1976) Interactions between narcotic analgesics and benzodiazepine derivatives on behavior in the mouse. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 199:389–399
Villiger JW (1984) CL 218, 872 binding of benzodiazepine receptors in rat spinal cord: modulation by γ-aminobutyric acid and evidence for receptor heterogeneity. J Neurochem 43:903–905
Weis H (1969) Morphine antagonistic effect of chlordiazepoxide (Librium). Experientia 25:381
Whitwam JG, Niv D, Loh L, Jack RD (1982) Depression of nociceptive reflexes by intrathecal benzodiazepine in dogs. Lancet 2:1465
Yaksh TL, Rudy TA (1976) Chronic catheterization of the spinal subarachnoid space. Physiol Behav 17:1031–1036
Zambotti F, Zonta N, Parenti M, Tammiso R, Vicentini L, Conci F, Mantegazza P (1982) Periaqueductal gray matter involvement in muscimol-induced decrease on morphine antinociception. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 318:368–369
Zambotti F, Zonta N, Tammiso R, Ferrario P, Hafner B, Mantegazza P (1986) Reversal of the effect of centrally-administered diazepam on morphine antinociception by specific (Ro 15–1788 and Ro 15–3505) and non specific (bicuculline and caffeine) benzodiazepine antagonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 333:43–46
Zonta N, Zambotti F, Vicentini L, Tammiso R, Mantegazza P (1981) Effects of some GABA-mimetic drugs on the antinociceptive activity of morphine and β-endorphin in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 316:231–234
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
This work was supported by MPI 60% grant Send offprint requests to F. Zambotti
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zambotti, F., Zonta, N., Tammiso, R. et al. Zopiclone potentiates the antinociceptive effect of morphine in rats. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 336, 526–529 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169309
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00169309