Abstract
The suborder Anthropoidea of the primates has traditionally been divided in three superfamilies: the Hominoidea (apes and humans) and the Cercopithecoidea (Old World monkeys), together comprising the infraorder Catarrhini, and the Ceboidea (New World monkeys) belonging to the infraorder Platyrrhini.
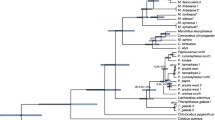
We have sequenced an approximately 390-base-pair part of the mitochondrial 12S rRNA gene for 26 species of the major groups of African monkeys and apes and constructed an extensive phylogeny based upon DNA evidence. Not only is this phylogeny of great importance in classification of African guenons, but it also suggests rearrangements in traditional monkey taxonomy and evolution. Baboons and mandrills were found to be not directly related, while we could confirm that the known four superspecies of mangabeys do not form a monophyletic group, but should be separated into two genera, one clustering with baboons and the other with mandrills. Patas monkeys are clearly related to members of the genus Cercopithecus despite their divergence in build and habitat, while the talapoin falls outside the Cercopithecus clade (including the patas monkey).
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aldrich-Blake FPG (1968) A fertile hybrid between two Cercopithecus spp. in the Budongo Forest, Uganda. Folia Primatol 9:15–21
Allan JS, Short M, Taylor ME, Su S, Hirsch VM, Johnson PR, Shaw GM, Hahn BH (1991) Species-specific diversity among simian immunodeficiency viruses from African Green monkeys. J Virol 65: 2816–2828
Ballard JWO, Olsen GJ, Faith DP, Odgers WA, Rowell DM, Atkinson PW (1992) Evidence from 12S ribosomal RNA sequences that onychophorans are modified arthropods. Science 258:1345–1348
Boom R, Sol CIA, Salimans MMM, Jansen CL, Wertheim-van Dillen PME, van der Noordaa J (1990) Rapid and simple method for purification of nucleic acids. J Clin Microbiol 28:495–503
Conroy GC (1990) Primate evolution. WW Norton and Company, New York, p 22
Cooper A, Mourer-Chauviré C, Chambers GK, Von Haeseler A, Wilson AC, Pääbo S (1992) Independent origins of New Zealand moas and kiwis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:8741–8744
Cronin JE, Sarich VM (1979) Molecular evidence for dual origin of mangabeys among Old World monkeys. Nature 260:700–702
Disotell TR, Honeycutt RL, Ruvolo M (1992) Mitochondrial DNA phylogeny of the Old-World monkey tribe Papionini. Mol Biol Evol 9:1–13
Dutrillaux B, Fosse A-M, Chauvier G (1979) Étude cytogénétique de six espèces ou sous-espèces de mangabeys (papiinae, cercopithecidae). Ann Genet 22:88–92
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J, Chauvier G (1980) Chromosomal evolution of 19 species or sub-species of cercopithecinae. Ann Genet 23:133–143
Dutrillaux B, Couturier J, Muleris M, Lombard M, Chauvier G (1982) Chromosomal phylogeny of forty-two species or subspecies of cercopithecoids (primates catarrhini). Ann Genet 25:96–109
Eck GG, Jablonski NG (1984) A reassessment of the taxonomic status and phyletic relationships of Papio baringensis and Papio quadratirostris (Primates: Cercopithecidae). Am J Phys Anthropol 65:109–134
Felsenstein J (1985) Confidence limit on phylogenies: an approach using the bootstrap. Evolution 39:783–791
Felsenstein J (1990) PHYLIP manual version 3.2. University Herbarium of the University of California, Berkeley
Fomsgaard A, Hirsch VM, Johnson PR (1992) Cloning and sequences of primate CD4 molecules: diversity of the cellular receptor for simian immunodeficiency virus/human immunodeficiency virus. Eur J Immunol 22:2973–2981
Gautier J-P (1988) Interspecific affinities among guenons as deduced from vocalizations. In: Gautier-Hion A, Bourlière F, Gautier J-P, Kingdon J (eds) A primate radiation, evolutionary biology of the African guenons. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 194–226
Hayasaka K, Gcjobori T, Horai S (1988) Molecular phylogeny and evolution of primate mitochondrial DNA. Mol Biol Evol 5:626–644
Higgins DG, Sharp PM (1988) CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignments on a microcomputer. Gene 73:237–244
Hill WCO (1972) Evolutionary biology of the primates. Academic Press, London, p 123
Hillis DM, Huelsenbeck JP (1992) Signal, noise, and reliability in molecular phylogenetic analysis. J Hered 83:189–195
Hirsch VM, Dapolito GA, Goldstein S, McClure H, Emau P, Fultz PN, Isahakia M, Lenroot R, Myers G, Johnson PR (1993) A distinct African lentivirus from Sykes' monkeys. J Virol 67:1517–1528
Janczewski DN, Yuhki N, Gilbert DA, Jefferson GT, O'Brien SJ (1992) Molecular phylogenetic inference from saber-toothed cat fossils of Rancho La Brea. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:9769–9773
Jolly CJ, Brett FL (1973) Genetic markers and baboon biology. J Med Primatol 31:85–99
Kocher TD, Thomas WK, Meyer A, Edwards SV, Pääbo S, Villablanca FX, Wilson AC (1989) Dynamics of mitochondrial DNA evolution in animals: amplification and sequencing with conserved primers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:6196–6200
Kumar S, Tamura K, Nei M (1993) MEGA: molecular evolutionary genetics analysis, version 1.0. The Pennsylvania State University, University Park, PA
Leaky M (1988) Fossil evidence for the evolution of the guenons. In: Gautier-Hion A, Bourliere F, Gautier J-P, Kingdon J (eds) A primate radiation, evolutionary biology of the African guenons. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 7–12
Lucotte G (1979) Distances électrophorétiques entre les différentes espéces de singes du groupe des mangabeys. Ann Genet 22:88–92
Lucotte G, Gautreau C, Galat G, Galat-Luong A (1982) Polymorphisme électrophorétique des differentes sous-especes de Cercopithecus aethiops. Folia Primatol 38:183–195
Martin RD, MacLarnon AM (1988) Quantitative comparisons of the skull and teeth in guenons. In: Gautier-Hion A, Bourliere F, Gautier J-P, Kingdon J (eds) A primate radiation, evolutionary biology of the African guenons. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 160–183
Martin RD (1993) Primate origins: plugging the gaps. Nature 363:223–234
Meyer A, Dolven SI (1992) Molecules, fossils and the origin of tetrapods. J Mol Evol 35:102–113
Milinkovitch MC, Ortf G, Meyer A (1993) Revised phylogeny of whales suggested by mitochondrial DNA sequences. Nature 361: 346–348
Mindell DP, Dick CW, Baker RJ (1991) Phylogenetic relationships among megabats, microbats and primates. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10322–10326
Miyamoto MM, Kraus F, Ryder OA (1990) Phylogeny and evolution of antlered deer determined from mitochondrial DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87:6127–6131
Müller MC, Saksena NK, Nerrienet E, Chappey C, Hervé VMA, Durand J-P, Legal-Campodonico P, Lange M-C, Digoutte J-P, Georges AJ, Georges-Courbot M-C, Sonigo P, Barré-Sinoussi F (1993) Simian immunodeficiency viruses from Central and Western Africa: evidence for a new species-specific lentivirus in tantalus monkeys. J Virol 67:1227–1235
Napier JR, Napier PH (1985) The natural history of the primates. British Museum (Natural History). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, p 146
Ponsà M, Estop AM, Miró R, Rubio A, Egozcue J (1980) Banding patterns of the chromosomes of Miopithecus talapoin compared with Macaca mulatta and Cercopithecus aethiops. Cytogenet Cell Genet 28:41–46
Ruvolo M (1988) Genetic evolution of the African guenons. In: Gautier-Hion A, Bourlière F, Gautier J-P, Kingdon J (eds) A primate radiation, evolutionary biology of the African guenons. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 127–149
Saitou N, Nei M (1987) The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol 4:406–425
Swofford DL (1991) Phylogenetic analysis using parsimony version 3.0. Illinois Natural History Survey, Champaign, IL
Tamura K (1992) Estimation of the number of nucleotide substitutions when there are strong transition-transversion and G + C-content biases. Mol Biol Evol 9:678–687
Tsujimoto H, Hasegawa A, Maki N, Fukasawa M, Miura T, Speidel S, Cooper RW, Moriyama EN, Gojobori T, Hayami M (1989) Sequence of a novel simian immunodeficiency virus from a wildcaught African mandrill. Nature 341:539–541
Williams-Blangero S, VandeBerg JL, Blangero J, Konigsberg L, Dyke B (1990) Genetic differentiation between baboon subspecies: relevance for biomedical research. Am J Primatol 20:67–81
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: A.C. van der Kuyl
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
van der Kuyl, A.C., Kuiken, C.L., Dekker, J.T. et al. Phylogeny of African monkeys based upon mitochondrial 12S rRNA sequences. J Mol Evol 40, 173–180 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167111
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00167111