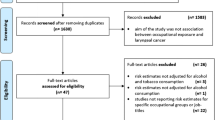
The significance of tobacco smoking, alcohol consumption and occupation as risk factors for the development of vocal chord dysplasia was evaluated in a case-control study. Twenty-seven male patients with dysplasia of the vocal chords were chosen from the 1. ENT-University Clinic in Vienna (1985–1988) and compared with 54 controls.
The main results are: The relative risk (RR) of a smoker compared to that of a non-smoker for vocal chord dysplasia is 7.27 (6.81–7.73); the RR adjusted for occupation is 3.58 (2.31–4.84). The most important risk factor, however, is occupational exposure. The relative risk of a blue collar worker compared to that of a white collar worker is 11.04 (10.61–11.46), which is reduced only to 10.02 (10.61–11.46) after stratification according to smoking habits.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Auerbach, O., Hammond, E.C. and Garfnkel, L. (1970): Histologic changes in the larynx in relation to smoking habits. - Cancer, 25: 92–104.
Brownson, R.C. (1987): Exposure to alcohol and tobacco and the risk of laryngeal cancer. - Arch. Environ Health, 42: 192–196.
Burch, J.D., Howe, G.R., Miller, A.B. and Semenciw, R. (1981): Tobacco, alcohol, asbestos, and nickel in the etiology of cancer of the larynx: a case-control study. J. nat. Cancer Inst., 67: 1219–1224.
Feuerlein, W. (1984): Alkoholismus - Mißbrauch und Abhängigkeit. Thieme Verlag Stuttgart - New York.
Flanders, W.D. and Rothman, K.J. (1982): Occupational risk for laryngeal cancer. - Amer. J. public Hlth., 72: 369–372.
Flanders, W.D. and Rothman, K.J. (1982): Interaction of alcohol and tobacco in laryngeal cancer. - Amer. J. Epidemiol., 115: 371–379.
Glasenapp, G.B. (1975): Beitrag zur berufsbedingten Entstehung des Kehlkopfkarzinoms. - Laryng. Rhinol. Otol., 54: 565–568.
Henry, C.R. (1979): The transformation of laryngeal leucoplacia to cancer. - The Journal of Laryngology and Otology, 93: 447–459.
Kleinsasser, O. (1963): Die Klassifikation und Differentialdiagnose der Epithelhyperplasien der Kehlkopfschleimhaut auf Grund histomorphologischer Merkmale. - Laryng. Rhinol. Otol., 42: 339–362.
Mantel, N. and Haenzel, W. (1959): Statistical aspects of the analysis of data from retrospective studies of diseases. - J. Natl. Cancer Inst., 22: 719–748.
Miettinen, O. (1976): Establishment and estimation in case-referent studies. - Amer. J. Epidemiol., 103:226–235.
Mueller, K.M. and Krohn, B.R. (1980): Smoking habits and their relationship to precancerous lesions of the larynx. - J. Cancer Res. clin. Oncol., 96: 211–217.
US Department of Health and Human Services (1982): The Health Consequences of Smoking. A report of the Surgeon General.
Vutuc, C. (1980): Epidemiologische Untersuchung zur Ätiologie des Bronchuskarzinoms in Österreich. In: “Sozialmedizin des Brochuskarzinoms”. - Eds. Kunze, M. and Vutuc, C. Wien, Facultas Verlag, p. 77–132.
Wilke, J. (1984): Laryngological sreening of industrial workers (galvanizers, spray painters, enamblers). In: Functional Partial Laryngectomy: Convervation Surgery for Carcinoma of the Larynx. Wigand, M.E., Steiner, W., Stell, P.M. - Eds. New York, Springer-Verlag, p. 42–43.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Corresponding author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasp, M.C., Neuwirth-Riedl, K., Vutuc, C. et al. Risk of vocal chord dysplasia in relation to smoking, alcohol intake and occupation. Eur J Epidemiol 6, 45–48 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00155548
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00155548