Abstract
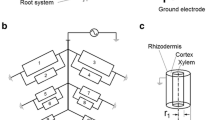
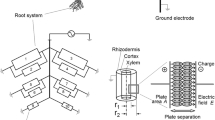
A conceptual model is presented that provides a rational basis for using plant root capacitance as an in-situ measurement for assessing plant root development. This method is based on measuring the electricla capacitance of an equivalent parallel resistance-capacitance circuit formed by the interface between soil-water and the plant root surface. Nutrient solution studies using tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum Mill.) showed a good correlation between plant root capacitance and root mass. Stage of development studies showed plant root capacitance measurements capable of detecting root development rate and suggested the method to be sensitive to root function. Soil water content was shown to have a significant effect on plant root capacitance measurement. The possibility of using this technique to assess relative root function is discussed. Positioning of the plant shoot electrode was shown to also have a significant effect on measurement of plant root capacitance, demonstrating the need for using consistent measurement techniques. The electrical capacitance method shows considerable promise. More research is needed before it can be used routinely.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber, S A 1962 A diffusion mass flow concept of soil nutrient availability. Soil Sci. 93, 39–49.
Baver, L D 1940 Soil Pysics. John Wiley and Sons, New York, 211 p.
Bonner, J 1959 Water transport. Science 129, 447–459.
Brower, R 1953 Water absorption by the roots of Vicia faba at various transpiration strengths. II. Crucial relation between suction tension, resistance and uptake. Proc. K. Ned. Akad. Wet. Ser. Co. 56, 129–136.
Chloupek, O 1972 The relation between electric capacitance and some other parameter of plant roots. Biol. Plant. 14(3), 227–230.
Chloupek, O 1977 Evaluation of the size of a plant's root system using its electrical capacitance. Plant and Soil 48, 535–532.
Cowan, I R and Milthorpe, F L 1968 Plant factors influencing the water status of plant tissues. In Water Deficits and Plant Growth. Ed. Kozlowski. pp 137–193. Academic Press, New York.
Dalton, F N, Raats, P A C and Gardner, W R 1975 Simultaneous uptake of water and solutes by plant roots. Agron. J. 67, 334–339.
Dalton, F N and Gardner, W R 1978 Temperature dependence of water uptake by plants. Agron. J. 20, 404–406.
Dalton, F N 1989 Plant root water extraction studies using stable isotopes. Plant and Soil 111, 217–221.
Dvorak, M J, Cernohorska, J and Janacek, K 1981 Characteristic of current passage through plant tissue. Biol. Plant. 23(4), 306–310.
Gardner, W R 1964 Relation of root distribution to water uptake and availability. Agron. J. 56, 41–45.
Ginsburg, H and Ginzburg, B Z 1970 Radial water and solute flow in roots of Zea mays. II. Ion fluxes across root cortex. J. Exp. Bot. 21, 593–604.
Herkelrath, W N, Miller, E E and Gardner, W R 1977 Water uptake by plants. II. The root contact model. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 41, 1039–1043.
Huck, M G, Klepper, B and Taylor, H M 1970 Diurnal variations in root diameter. Plant Physiol. 45, 529–530.
Kendal, W A, Pederson, G A and Hill, R R 1982 Root size estimates of red clover and alfalfa based on electrical capacitance and root diameter mesurements. Grass For. Sci. 37, 253–256.
Merrill, S D, Doering, E J and Reichman, G A 1987 Application of a minirhizotron with flexible, pressurized walls to a study of corn root growth. In Minirhizotron Observations Tubes: Methods and Applications for Measuring Rhizosphere Dynamics. Ed. H M Taylor. pp 131–143. Spec. Publ. No. 50, Am. Soc. Agron., Madison, WI.
Merrill, S D 1992 Pressurized-wall Minirhizotron for field observation of root growth dynamics. Agron. J. 84, 755–758.
Mualem, Y and Friedman, S P 1991 Theoretical prediciton of electrical conductivity in saturated and unsaturated soil. Water Resour. Res. (27) 10, 2771–2777.
Philip J R 1957 The physical principles of soil water movement during the irrigation cycle. Third Congr., Int. Comm. Irrig. Drain., San Francisco CAO, Quest. 8, p8. 125–8. 154.
Robinson, R A and Stokes, R H 1959 Electrolytic Solutions. London Butterworths. 559p.
Taylor, H M 1987 Minirhizotron observation tubes: methods and applications for measuring rhizosphere dynamics. ASA Special Publ. No. 50. Am. Soc. Agron., Madison, WI.
Upchurch, D R and Ritchie, J T 1984 Battery-operated color video camera for root observations in minirhizotrons. Agron. J. 76, 1015–1017.
Upchurch D R 1985 Relationship between observations in minirhizotrons and true root length density. Ph.D. diss. Texas Tech Univ. (Diss. Abstr. 85-28594).
Veen, B W, VanNoordwijk, M, DeWilligen, P, Boone, F R and Kooistra M J 1992 Root-soil contact of maize, as measured by a thinsection technique. III. Effects on shoot growth, nitrate and water uptake efficiency. Plant and Soil 139, 131–138.
VanNoordwijk, M, Kooistra, M J, Boone, F R, Veen, B W and Schoonderbeek, D 1992 Root-soil contact of maize, as measured by a thin-section technique. I. Validity of the method. Plant and Soil 139, 109–118.
Zhang, M I N and Willison, J H M 1992 Electrical impedance analysis in plant tissues: in vivo detection of freezing injury. Can. J. Bot. 70, 2254–2258.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dalton, F.N. In-situ root extent measurements by electrical capacitance methods. Plant Soil 173, 157–165 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00155527
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00155527