Abstract
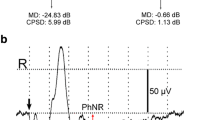
We have recorded both pattern and flash electroretinograms (ERG) in two patients with unilateral optic nerve damage due to optic canal fracture over one year. The pattern ERG from the affected eye was reduced in amplitude by approximately 40% in one patient, 60% in the other, compared with that from their other, normal eyes, while the flash ERG was normal in all eyes. Reduced pattern ERG responses may depend on retrograde degeneration following damage to the optic nerve. The pattern ERG, however, was not totally lost in the eyes with marked optic atrophy. There is a possibility that the pattern ERG contains both contrast and luminance components in various proportions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arden GB, Vaegan CR and Hogg CR (1982) Clinical and experimental evidence that the pattern electroretinogram (PERG) is generated in more proximal retinal layers than the focal electroretinogram (FERG). Ann NY Acad Sci 388:580–601
Brown KT (1968) The electroretinogram: its components and their origins. Vision Res, 8:633–677
Dawson WW, Maida TM and Rubin ML (1982) Human pattern-evoked retinal responses are altered by optic atrophy. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 22:796–803
Fiorentini A, Maffei L, Pirchio M, Spinelli D and Porcellati V (1981) The ERG in response to alternating gratings in patients with diseases of the peripheral visual pathway. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 21:490–493
Hogan MJ and Zimmerman LE (1962) Optic nerve. In: Ophthalmic pathology: an atlas and textbook. WB Saunders Company, Philadelphia, pp. 623–625
Maffei L and Fiorentini A (1981) Electroretinographic responses to alternating gratings before and after section of the optic nerve. Science 211:953–955
Mashima Y and Oguchi Y (1983) Pattern ERG: several moot points for clinical application. Act Soc Ophthalmol Jpn 87:473–481
May JG, Ralston JV, Reed JL and Van Dyk HJL Loss in pattern-elicited electro-retinograms in optic nerve dysfunction. Am J Ophthalmol 93:418–422
Sherman J (1982) Simultaneous pattern-reversal electroretinograms and visual evoked potentials in diseases of the macula and optic nerve. Ann NY Acad Sci 388:214–226
Spekreijse H, Estévez O and van der Tweel LH (1973) Luminance responses to pattern reversal. Doc Opthalmol Proc Ser 2:205–211
Vaegan, Arden GB and Hogg CR (1982) Properties of normal electroretinograms evoked by patterned stimuli in man, abnormalities in optic nerve disease and amblyopia. Doc Ophthalmol Proc Ser 31:111–129
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mashima, Y., Oguchi, Y. Clinical study of the pattern electroretinogram in patients with optic nerve damage. Doc Ophthalmol 61, 91–96 (1985). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143220
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00143220