Abstract
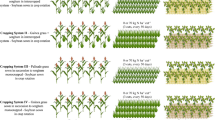
Three multipurpose tree species (MPTS)-leucaena (Leucaena leucocephala), sesbania (Sesbania sesban var. nubica) and pigeonpea (Cajanus cajan) were pruned at a height of 60 cm above the ground every two months, and resulting plant biomass was incorporated into the soil as green manure. For comparison, maize (Zea mays) stover was also incorporated into some plots, while some other plots were left fallow. Varying quantities of plant biomass which were incorporated into the soil over a period of 12 months caused large changes in major soil plant nutrients, and it substantially improved soil fertility. To test for improved soil fertility, test crops of maize and beans (Phaseolus vulgaris) were grown on the plots after six biomass incorporations of 4806, 13603, 16659 and 7793 kg. ha−1yr−1 for pigeonpea, sesbania leucaena and maize, respectively. Responses of the test crops indicated that sesbania and leucaena green manures improved maize stover, cobs and grain yields; and bean haulms and grain yields by 77.6% when compared to fallow plots. Residual effects of green manures still resulted in significant (P < 0.05) yield differences in the test cropin the third testing season. Economic significance of green manures in increasing food crop yields to small scale farmers is discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anonymous (1919) Propagation and culture of the date palm. USAID Farmer's Bulletin 1016, In: Sesbania in Agriculture by DO Evans and PP Rotar. Westview Tropical Agriculture Series No 8 p 27–46
Buckman HO and Brady NC (1969) The nature and properties of soils. 7th ed, Macmillan Co. p 132–486
Budelman A (1988) The decomposition of the leaf mulches of Leucaena leucocephala, Gliricidia sepium and Flemingia under humid tropical conditions. Agroforestry Systems 7(1): 33–46
Dargan KS Chillar RK and Bhardwaj KKR (1975) Green manuring for more paddy in alkali soils. Indian Farming 25(3): 13–14
Dunbar AR (1969) The annual crops of Uganda. East African Literature Bureau, p 68–70
Evans DO, Yost RS and Lundeen BW (1983) A selection and annotated bibliography of tr tropical green manures and legume covers. Hawaii Institute of Tropical Agricultural and human resources research and extension series 028, p 211
Mehlich A (1960) Charge characterisation of soils. Trans 7th Int Congr SoilSci, Madison, Wis
Muchena FN and Nyandat NN (1980) Rating of land qualities and the conversion into land suitability in Kenya with particular emphasis on soil moisture storage and climatic conditions. Paper presented at 14th meeting of Eastern Africa sub-committee for soil correlation and land evaluation, Arusha, 29th October 4th November 1980
Musalia LM, Semenye PP and Fitzhugh HA (1989) Mineral status of dual-purpose goats and forage in western Kenya. Small Ruminant Research 2: 1–9
Onim JFM, Mathuva M, Hart R, Fitzhugh HA and Otieno K (1986) Recommendation domains for dual-purpose goat research in Nyanza and Western provinces of Kenya. Proceedings of the 5th Small Ruminant CRSP Kenya Workshop, Kabete, Kenya. November 4, 5 and 6th, 1986. p 40–47
Onim JFM, Ochola P, Mathuva M, Otieno K and Fitzhugh HA (1987) Dry matter Nitrogen and green manure yields of Leuceana Sesbania and Pigeonpea in a cutting frequency study. Proceedings of the sixth Kenya Veterinary Association and Small Ruminant CRSP Workshop. ILRAD, Nairobi — Kenya, p 103–113
Rao JVDK, Dart PJ, Matsumoto T and Day JM (1980) Nitrogen fixation by pigeonpea. ICRISAT (International crops Research Institute for the Semi-Arid Tropics) 1981 Proceedings of the international workshop on pigeonpeas, Volume 1, 15–19 December 1980. Patancheru AP India. p 190–199
Robinson JBD and Semp G (1968) Advisory Soilor plant analysis and fertilizer use. I. Comparison of soil analysis methods. E AFr agric For J 34: 117–139
Singh MP and Sinha KS (1962) Studies in the green manuring of wheat in Bihar II: Green manuring without losing a kharif crop. Indian Journal of Agronomy 7: 38–45
Ssali H and Keya SO (1982) Effect of nitrogen fertilizer on yield of beans inoculated with Rhizobium phaseoli. Kenya J Sci Technol (B) p 387–389
Stephens D (1969) The effects of fertilizers, manure and trace elements in continuous cropping, rotations in Southern and Western Uganda. E Afr agric For J 34: 401–417
US National Academy of Science (1977). In: Browse in Africa—The Current State of Knowledge. HN Le Houerou (Ed), p 141–149
William WA and Doneen LD (1960) Field infiltration studies with green manures and crop residues on irrigated soils. Soil Science Society of America proceeding, 24: 58–61
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Onim, J.F.M., Mathuva, M., Otieno, K. et al. Soil fertility changes and response of maize and beans to green manures of leucaena, sesbania and pigeonpea. Agroforest Syst 12, 197–215 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123474
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123474