Abstract
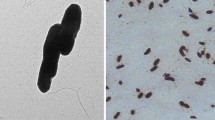
Strain TEA, a strictly anaerobic, motile rod with one to four lateral flagella and a crystalline surface layer was isolated from a mixed culture that completely reduces chlorinated ethenes to ethene. The organism coupled reductive dehalogenation of tetrachloroethene or trichloroethene to cis-1,2-dichloroethene to growth, using molecular hydrogen as the electron donor. It was unable to grow fermentatively or in the presence of tri- or tetrachloroethene with glucose, pyruvate, lactate, acetate or formate. The 16S rDNA sequence of strain TEA was 99.7% identical to that of Dehalobacter restrictus. The two organisms thus are representatives of the same species or the same genus within the Bacillus/Clostridium subphylum of the gram-positive bacteria.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
DeBruin, WP, Kotterman, MJJ, Posthumus, MA, Schraa, G & Zehnder, AJB (1992) Complete biochemical transformation of tetrachloroethene to ethane. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 58: 1996–2000
Devereux, R, Delaney, M, Widdel, F & Stahl, DSA (1989) Natural relationships among sulfate-reducing eubacteria. J. Bacteriol. 171: 6689–6695
DiStefano, TD, Gossett, JM & Zinder, SH (1991) Reductive dechlorination of high concentrations of tetrachloroethene to ethene by an anaerobic enrichment culture in the absence of methanogenesis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 57: 2287–2292
Freedman, DL & Gossett, JM (1989) Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 55: 2144–2151
Hohenberg, H, Mannweiler, K & Müller, M (1994) High-pressure freezing of cell suspensions in cellulose capillary tubes. J. Microsc. 175: 34–43
Hilliger, C (1992) Reductive dehalogenation by anaerobic bacteria. Ph.D. Thesis, Wageningen Agricultural University, The Netherlands
Holliger, C, Schraa, G, Stams, AJM & Zehnder, AJB (1993) A highly purified enrichment culture couples the reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene to growth. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 59: 2991–2997
Holliger, C & Schumacher, W (1994) Reductive dehalogenation as a respiratory process. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 66: 239–246
Jukes, TH & Cantor, CR (1969) Evolution of protein molecules. In: Munro, N (Ed) Mammalian Protein Metabolism (pp 21–132). Academic Press, New York
Mägli, A, Rainey, FA & Leisinger, T (1995) Acetogenesis from dichloromethane by a two-component mixed culture comprising a novel bacterium. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 2943–2949
Müller, M, Meister, N & Moor, H (1980) Freezing in a propane jet and its application in freeze-fracturing. Mikroskopie (Wien) 36: 129–140
Müller M & Moor H (1984) Cryofixation of suspensions and tissues by propane-jet freezing and high-pressure freezing. Proc. 42nd Ann. Meet. Electron Microsc. Soc. Am.: 6–9
Oremland, RS & Capone, DG (1988) Use of ‘specific’ inhibitors in biogeochemistry and microbial ecology. Adv. Microbiol. Ecol. 10: 285–383
Rainey, FA, Dorsch, M, Morgan, HW & Stackenbrandt, E (1992) 16S rDNA analysis of Spirochaeta thermophila: position and implications for the systematics of the order Spirochaetales. System. Appl. Microbiol. 16: 224–226
Rainey, FA & Stackebrandt, E (1993) 16S rDNA analysis reveals phylogenetic diversity among the polysaccharolytic Clostridia. FEMS Microbiol. Lett. 113: 125–128
Scholz-Muramatsu, H, Neumann, A, Messmer, M, Moore, E & Diekert, G (1995) Isolation and characterization of Dehalospirillum multivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., a tetrachloroethene-utilizing, strictly anaerobic bacterium. Arch. Microbiol. 163: 48–56
Sleytr, UB & Messner, P (1988) Crystalline surface layers in prokaryotes. J. Bacteriol. 170: 2891–2897
Sharma, PK & McCarty, PL (1966) Isolation and characterization of a facultatively aerobic bacterium that reductively dehalogenates tetrachloroethene to cis-1,2-dichloroethene. Appl. Env. Microbiol. 62: 761–765
Stromeyer, SA, Cook, AM, Kohler, H, Winkelbauer, W & Leisinger, T (1991) Dichloromethane utilized by an anaerobic mixed culture: acetogenesis and methanogenesis. Biodegradation 2: 129–137
Utkin, I, Woese, C & Wiegel, J (1994) Isolation and characterization of Desulfitobacterium dehalogenans gen. nov., sp. nov., an anaerobic bacterium which reductively dechlorinates chlorophenolic compounds. Int. J. Syst. Bact. 44: 612–619
Wild, AP, Winkelbauer, W & Leisinger, T (1995) Anaerobic dechlorination of trichloroethene, tetrachloroethene and 1,2-dichloroethane by an acetogenic mixed culture in a fixed bed reactor. Biodegradation 6: 309–318
Zehnder, AJB & Wuhrmann, K (1976) Titanium(III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science 194: 1165–1166
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wild, A., Hermann, R. & Leisinger, T. Isolation of an anaerobic bacterium which reductively dechlorinates tetrachloroethene and trichloroethene. Biodegradation 7, 507–511 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00115297
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00115297