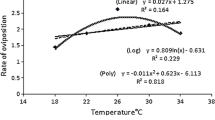
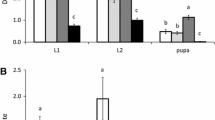
Abstract
Generalist predatory mites are the common phytoseiid fauna in many agroecosystems, but little attention has been paid to their potential as biological control agents. In this study, we determined the functional responses of adult females of the generalist predator Neoseiulus barkeri Hughes on eggs, larvae, and adults of the two-spotted spider mite, Tetranychus urticae Koch, in the laboratory. Predation experiments were conducted on pepper leaf discs over a 24 h period at 25±1°C, 70–80% RH and 16L:8D photoperiod. Prey densities ranged 5 to 80 eggs, or 5 to 40 larvae, or 1 to 8 female adults of T. urticae per disc. The predation rate of N. barkeri adult females on T. urticae eggs was the same as on its larvae, but the predation rate on adult females was much lower. The role of generalist predatory mites in integrated and biological control of greenhouse pests was discussed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abou-Setta, M.M. and Childers, C.C., 1989. Biology of Euseius mesembrinus (Acari: Phytoseiidae): Life tables and feeding behavior on tetranychid mites on citrus. Environ. Entomol., 18: 665–669.
Bakker, F.M., and Sabelis, M.W., 1987. Attack success of Amblyseius mckenziei and the stage related defensive capacity of thrips larvae. Bull. SROP/WPRS, 10(2): 26–29.
Bonde, J., 1989. Biological studies including population growth parameters of the predatory mite Amblyseius barkeri (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) at 25°C in the laboratory. Entomophaga, 34: 275–287.
Currie, F.J. 1982. Estimating Michaelis-Menten parameters: bias, variance, and experimental design. Biometrics, 38: 907–919.
Duso, C., 1989. Role of Amblyseius aberrans (Oud.), Typhlodromus pyri Scheuten and Amblyseius andersoni (Chant) (Acari, Phytoseiidae) in vineyards. I. The Effect of single or mixed phytoseiid population releases on spider mite densities (Acari, Tetranychidae). J. Appl. Ent., 104: 474–492.
Duso, C., 1992. Role of Amblyseius aberrans (Oud.), Typhlodromus pyri Scheuten and Amblyseius andersoni (Chant) (Acari, Phytoseiidae) in vincyards. III. Influence of variety characteristics on the success of A aberrans and T. pyri releases. J. Appl. Ent., 114: 455–462.
Everson, P., 1980. The relative activity and functional response of Phytoseiulus persimilis (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) and Tetranychus urticae (Acarina: Tetranychidae): the effect of temperature. Can. Ent., 112: 17–24.
Fan, Y.Q. and Petitt, F.L., 1994a. Parameter estimation of the functional response. Environ. Entomol., 23: 785–794.
Fan, Y.Q. and Petitt, F.L., 1994b. Biological control of broad mite, Polyphagotarsonemus latus (Banks), by Neoseiulus barkeri Hughes on pepper. Biological Control., 4: 390–395.
Fernando, M.N.J.P. and Hassell, M.P., 1980. Predator-prey responses in an acarine systems. Res. Popul. Ecol., 22: 301–322.
Foglar, H., Malausa, J.C. & Wajnberg, E., 1990. The functional response and preference of Macrolophus caliginosus (Heteroptera: Miridae) for two of its prey: Myzus persicae and Tetranychus urticae. Entomophaga 35: 465–474.
Hansen, L.S., 1988. Control of Thrips tabaci (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) on glasshouse cucumber using large introductions of predatory mites Amblyseius barkeri (Acarina: Phytoseiidae). Entomophaga, 33: 33–42.
Helle, W. and Sabelis, M.W. (Editors), 1985. Spider Mites: Their Biology, Natural Enemies, and Control, Vol. B. Elsevier, Amsterdam, 458 pp.
Holling, C.S., 1959. Some characteristics of simple types of predation and parasitism. Can. Entomol., 91: 385–398.
Houck, M.A. and Strauss, R.E., 1985. The comparative study of functional responses: Experimental design and statistical interpretation. Can. Entomol., 117: 617–629.
Huffaker, C.B., Simmonds, S.J. and Laing, J.E., 1976. The theoretical and empirical basis of biological control. In: Huffaker, C.B. and Messenger, P.S. (Editors), Theory and Practice of Biological Control. Academic Press, New York pp. 41–78.
James, D.G., 1990. Biological control of Tetranychus urticae (Koch) (Acari: Tetranychidae) in southern New South Wales peach orchards: the role of Amblyseius victoriensis (Acari: Phytoseiidac). Aust. J. Zool., 37: 645–655.
Karg, W., Mack, S., and Baier, A., 1987. Advantages of oligophagous predatory mites for biological control. Bull. SROP/WPRS, 10(2): 66–73.
Mackauer, M., Ehler, L.E., and Roland, J. (Editors), 1990, Critical Issues in Biological Control. Intercept. Andover, Hants.
McMurtry, J.A., 1982. The use of phytoseiids for biological control: Progress and future prospects. In: M.A., Hoy (Editor), Recent Advances in Knowledge of the Phytoseiidae, Publ. 3284. University of California Press, Berkeley, pp. 23–48.
McMurtry, J.A., 1992. Dynamics and potential impact of ‘generalist’ phytoseiids in agroecosystems and possibilities for establishment of exotic species. Exp. Appl. Acarol., 14: 371–382.
McMurtry, J.A. and Rodriguez, J.G., 1987. Nutritional ecology of phytoseiid mites. In: F., SlanskyJr. and J.G., Rodriguez (Editors), Nutritional Ecology of Insects, Mites and Spiders. John Wiley, New York, NY, pp. 609–644.
Petitt, F.L., 1988. Temperature-dependent development and influence of larval instars of Liriomyza sativae Blanchard on parasitization by Opius dissitus Muesebeck. Ph.D. dissertation. University of Florida, Gainesville.
Ramakers, P.M.J., and van, Lieburg, M.J., 1982. Start of commercial production and introduction of Amblyseius mckenziei Sch. and Pr. (Acarina: Phytoseiidae) for the control of Thrips tabaci Lind. (Thysanoptera: Thripidae) in glasshouses. Med. Fac. Landbouww. Rijksuniv. Gen., 47: 541–545.
SAS Institute., 1988. SAS/STAT User's Guide. SAS Institute, Cary, NC.
Sabelis, M.W., 1985. Predation on spider mites. In: W., Helle and M.W., Sabelis (Editors), World Crop Pests. Spider Mites, Their Biology, Natural Enemies and Control, Vol. 1B, Elsevier, Armsterdam, pp. 103–130.
Sandness, J.N. and McMurtry, J.A., 1972. Prey consumption behavior of Amblyseius largoensis in relation to hunger. Can. Ent., 104: 461–470.
van, Houten, Y.M., 1991. Diapause induction in the thrips predators Amblyseius barkeri and Amblyseius cucumeris (Acari: Phytoseiidae) in Dutch greenhouses. Proc. Exp. & Appl. Entomol., N. E. V. Armsterdam, 2: 202–207.
van, Lenteren, J.C., 1992. Biological control in protected crops: Where do we go? Pestic. Sci., 36: 321–327.
van, Lenteren, J.C. and Woets, J., 1988. Biological and integrated pest control in greenhouses. Ann. Rev. Entomol., 33: 239–269.
Walter, D.E., and O'Dowd, D.J., 1992. Leaf morphology and predators: Effect of leaf domatia on the abundance of predatory mites (Acari: Phytoseiidae). Environ. Entomol., 21: 478–484.
Zhang, Z.-Q., 1992. Functional response of Allothrombium pulvinum deutonymphs (Acari: Trombidiidae) on two-spotted spider mites (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp. Appl. Acarol., 15: 249–257.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fan, Y., Petitt, F.L. Functional response of Neoseiulus barkeri Hughes on two-spotted spider mite (Acari: Tetranychidae). Exp Appl Acarol 18, 613–621 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00051724
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00051724