Abstract
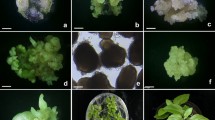
A procedure is described for the isolation and culture of protoplasts from embryogenic callus (gel-like callus — GLC) and embryogenic suspension cultures (ESC) of Cucumis sativus c.v. Borszczagowski. Maximal protoplast yields from GLC and ESC were 5×106 and 1×107 protoplasts/g tissue respectively. They were obtained following 14–16 h digestion with 1.2% Cellulase Onozuka R-10, 1.2% Macerozyme R-10 and 0.3% Driselase. At a plating density of 2×105 / ml, first divisions occurred in 4–5 days and 7–8 days in ESC-and GLC-derived protoplasts respectively. The highest percentage of direct embryogenesis (over 80%) was observed with ESC. It was possible to obtain approximately 5000 embryo structures / g tissue. Some embryos converted into plants after 6 weeks, but most of them after 2 months of culture. ESC-derived plants, when transferred into the glasshouse, bloomed normally, and set seeds.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CMS:
-
Murashige & Skoog (1962) medium for cucumber
- GLC:
-
gel-like callus
- ESC:
-
established embryogenic suspension culture
- 2,4-d :
-
2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
References
Abdullah R, Cocking E C & Thompson J A (1986) Efficient plant regeneration from rice protoplasts through somatic embryogenesis. Bio/Technology 1986: 1087–1090
Attree S M, Bekkaoui F, Dunstan D I & Fowke L C (1987) Regeneration of somatic embryos from protoplasts isolated from an embryogenic suspension culture of white spruce (Picea glauca). Plant Cell Rep. 6: 480–483
Burza W & Malepszy S (1994) Direct plant regeneration from leaf explants in cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) is free of genetic variation. Plant Breeding 113 (In press)
Cocking E G (1960) A method for the isolation of plant protoplasts. Nature (Lond.) 187: 962–963
Colijn-Hooymans C M, Bouwer R, Orczyk W & Dons J J M (1988) Plant regeneration from cucumber (Cucumis sativus) protoplasts. Plant Sci. 57: 63–71
Deyang L & Cocking E C (1984) Regeneration of shoots from seedling cotyledon protoplasts of Cucumis sativus L. (cucumber), Kexue Tongbao 29(11): 1539–1542
Eapen S, Abraham V, Gerdemann M & Schieder O (1989) Direct somatic embryogenesis, plant regeneration and evaluation of plants obtained from mesophyll protoplasts of Brassica juncea. Ann. Bot. 63: 369–372
Jia S R, Fu Y Y & Lin Y (1986) Embryogenesis and plant regeneration from cotyledon protoplasts culture of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). J. Plant Physiol. 124: 393–398
Kirti P B & Chopra V L (1990) Rapid plant regeneration through organogenesis and somatic embryogenesis from cultured protoplasts of Brassica juncea. Plant Cell Tiss. Org. Cult., 20: 65–67
Lazarte J E & Sasser C C (1982) Asexual embryogenesis and plantlet development in anther culture of Cucumis sativus L. Hort. Sci. 17(1): 88
Lührs R & Lörz H (1987) Plant regeneration in vitro from embryogenic cultures of spring- and winter-type barley (Hordeum vulgare L.) varieties. Theor. Appl. Genet. 75: 16–25
Malepszy S & Nadolska-Orczyk A (1983) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L. Regeneration of plantlets from callus formed by leaf explants. Z. Pflanzenphysiol. 111: 273–276
Malepszy S (1988) Cucumber (Cucumis sativus L. In: Bajaj Y P S (Ed.) Biotechnology in Agriculture and Forestry, Vol. 6. Crops II: 277–293. Springer-Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg
Malepszy S & Nadolska-Orczyk A (1989) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus VIII. Variation in the progeny of phenotypically not altered R1 plants. Plant Breeding 102: 66–72
Malepszy S, Solarek E (1986) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus III. Some aspects of cell culture. Intern. Symp. Plant Tissue and Cell Culture Applic. to Plant Improvement, Olomouc, Czechoslowakia: 189
Malepszy S, Marciniak S & Nadolska-Orezyk A (1990) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L. IX. Yielding of regenerated plants. Gartenbauwissenschaft 55(5): 206–208
Murashige T & Skoog F (1962) A revised medium for rapid growth and bioassays with tobacco tissue cultures. Physiol. Plant. 15: 473–495
Nagata T & Takebe J (1971) Cell wall regeneration and cell division in isolated tobacco mesophyll protoplasts. Planta 92: 301–308
Nadolska-Orczyk A & Malepszy S (1986) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L. VI. Histological analysis of leaf explants cultured on media with 2,4-d or 2,4,5-T. Acta Soc. Bot. Pol. 56(1): 55–60
Nomura K & Komamine A (1985) Identification and isolation of single cells that produce somatic embryos at a high frequency in a carrot suspension culture. Plant Physiol. 79: 988–991
Orczyk W & Malepszy S (1985) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L.V. Stabilising effect of glycine on leaf protoplasts. Plant Cell Rep. 4: 269–273
Punja Z K, Tang F A & Sarmento G G (1990) Isolation, culture and plantlet regeneration from cotyledon and mesophyl protoplasts of two pickling cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) genotypes. Plant Cell Rep. 9: 61–64
Rajasekaran K, Mullins M G & Nair Y (1983) Flower formation in vitro by hypocotyl explants of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.). Ann. Bot. (London) 52: 417–420
Song J, Sorensen L & Liang G H (1990) Direct embryogenesis from single mesophyll protoplasts in alfalfa (Medicago sativa L.). Plant Cell Rep. 9: 21–25
Trulson A J, Simpson R B & Shahin E A (1986) Transformation of cucumber (Cucumis sativus L.) plants with Agrobacterium rhizogenes. Theor. Appl. Genet. 71: 11–15
Vasil V & Vasil J K (1980) Isolation and culture of cereal protoplasts. Embryogenesis and plantlet formation from protoplasts of Pennisetum americanum. Theor. Appl. Genet. 56: 97–99
Vasil K I, Vasil V & Redway F (1990) Plant regeneration from embryogenic calli, cell suspension cultures and protoplasts of Triticum aestivum L. (Wheat). Bio/Technology 8: 1171–1174
Wildholm J M (1972) The use of fluorescein diacetate and phenosafranine for determining viability of cultured plant cells. Stain technology 47: 189–194
W'óblewski T & Malepszy S (1992) In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L. XVI. Established long-term culture. Proc. of V EUCARPIA Cucurbitaceae Symposium Skierniewice-Warsaw. July 27–31, Poland: 105–107
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Burza, W., Malepszy, S. In vitro culture of Cucumis sativus L. XVIII. Plants from protoplasts through direct somatic embryogenesis. Plant Cell Tiss Organ Cult 41, 259–266 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00045090
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00045090