Summary
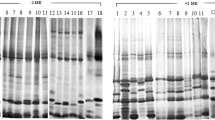
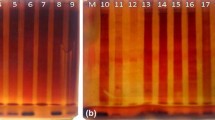
Starch-gel electrophoresis was used to study esterase, acid phosphatase, and peroxidase isozyme patterns in the primary leaves, stems, and roots of 13 species within the genus Phaseolus (P. acutifolius, P. adenanthus, P. angularis, P. atropurpureus, P. aureus, P. bracteatus, P. calcaratus, P. lathyroides, P. mungo, P. ricciardianus, domestic P. vulgaris, and wild P. coccineus and P. vulgaris). Most species showed unique banding patterns in each isozyme system. However, a close similarity in banding patterns was observed for the domestic P. vulgaris, wild P. vulgaris, and wild P. coccineus indicating close genetic relationships, possibly through species introgression or common descent.
Great differences in isozyme patterns were found for different tissues from the same species in all systems indicating the high tissue specificity of isozymes. Upon compilation of bands from all the species, a very large number of isozymes were obtained in each system or tissue, making the electrophoretic isozyme technique of high potential in studies of isozyme variants in this genus.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Yasiri, S. A. & D. P., Coyne, 1966. Interspecific hybridization in the genus Phaseolus. Crop Sci. 6: 59–60.
Allard, R. W. & A. L., Kahler, 1971. Allozyme polymorphisms in plant populations. Stadler Symp. 3: 9–24.
Bassiri, A., 1976. Barley cultivar identification by use of isozyme electrophoretic patterns. Can. J. Plant Sci. 56: 1–6.
Bassiri, A., 1977. Identification and polymorphism of cultivars and wild ecotypes of safflower based on isozyme patterns. Euphytica 26: 709–719.
Bergman, J. W. & S. S. Mann, 1973. Genetic control of isozymes in wheat-rye addition lines with rye or wheat cytoplasm. Proc. Fourth Int. Wheat Genet. Symp., Columbia, MO, pp. 329–336.
Boulter, D., D. A., Thurman & E., Derbyshire, 1967. A disc electrophoretic study of globulin proteins of legume seeds with reference to their systematics. New Phytol. 66: 27–36.
Brown, A. H. D. & R. W., Allard, 1969. Inheritance of isozyme differences among the inbred parents of a reciprocal recurrent selection population of maize. Crop Sci. 9: 72–75.
Buishand, T. J., 1956. The crossing of beans (Phaseolus sp.). Euphytica 5: 42–50.
Chavan, V. M., G. D., Patil & D. G., Bhapkar, 1965. Improvement of cultivated Phaseolus species need for interspecific hybridization. Indian J. Genet. 26A: 152–154.
Cherry, J. P., F. R. H., Katterman & J. E., Endrizzi, 1970. Comparative studies of seed proteins of species Gossypium by gel electrophoresis. Evolution 24: 431–477.
Coyne, D. P., 1964. Species hybridization in Phaseolus. J. Hered. 55: 5–6.
Dana, S., 1966. The cross between Phaseolus aureus Roxb. and P. mungo L. Genetica 37: 259–274.
De, D. N. & R., Krishnan, 1966. Cytological studies of the hybrid, Phaseolus aureus x P. mungo. Genetica 37: 588–600.
Derbyshire, E., J. N., Yarwood, E., Neat & D., Boulter, 1976. Seed proteins of Phaseolus and Vigna. New Phytol. 76: 283–288.
Fedak, G., 1974. Allozymes as aids to Canadian barley cultivar identification. Euphytica 23: 166–173.
Freytag, G. F., 1965. Classification del frijol comun (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) y especies affines. Ceiba (Honduras) 11: 51–64 (English summary).
Gentry, H. S., 1969. Origin of the common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris. Econ. Bot. 23: 55–69.
Hart, G. E. & C. R., Bhatia, 1967. Acrylamide gel electrophoresis of soluble leaf proteins and enzymes from Nicotiana species. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 9: 367–374.
Honma, S., 1956. A bean interspecific hybrid. J. Hered. 47: 217–220.
Jacob, F. & J., Monod, 1961. Genetic regulatory mechanisms in the synthesis of proteins. J. Mol. Biol. 3: 318–356.
Jacobsen, J. V., J. G. Scandalios & R. G. Sculley, 1966. Tissue specificity of isozymes in barley seeds and the hormonal control of specific isozymes secreted by aleurone cells. Ann. Rept. Michigan State Univ./Atomic Energy Comm. Plant Res. Lab, p. 72–75.
Johnson, B. L., 1967. Tetraploid wheats: seed electrophoretic patterns of the Emmer and Timopheevi groups. Science 158: 131–132.
Johnson, B. L., 1968. The protein electrophoresis approach to species relationships in wheat. In: Bogard, R. (Ed.), Genetic lectures. Vol. I, p. 19–44. Oregon State Univ. Press.
Johnson, B. L., 1972. Protein electrophoretic profiles and the origin of the B genome of wheat. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 69: 1398–1402.
Johnson, B. L., D., Barnhart & O., Hall, 1967. Analysis of genome and species relationships in the polyploid wheats by protein electrophoresis. Amer. J. Bot. 54: 1089–1089.
Johnson, B. L. & O., Hall, 1965. Analysis of phylogenic affinities in the Triticinae by protein electrophoresis. Amer. J. Bot. 52: 506–513.
Johnson, B. L. & O., Hall, 1966. Electrophoretic studies of species relationships in Triticum. Acta Agric. Scand. 16: 222–224.
Johnson, B. L. & M. M., Thein, 1970. Assessment of evolutionary affinities in Gossypium by protein electrophoresis. Amer. J. Bot. 57: 1081–1092.
Kahler, A. L. & R. W., Allard, 1970. Genetics of isozyme variants in barley. I. Esterases. Crop Sci. 10: 444–448.
Macdonald, J. & J. L., Brewbaker, 1972. Isozyme polymorphism in flowering plants. VIII. Control and dimeric nature of two transaminase isozymes in maize. J. Hered. 63: 11–14.
Menke, J. F., R. S., Singh, C. O., Qualset & S. K., Jain, 1973. Protein electrophoresis aids cereal variety identification. Calif. Agric. 27: 3–5.
Peirce, L. C. & J. L., Brewbaker, 1973. Applications of isozyme analysis in horticultural science. HortScience 8: 17–22.
Purseglove, J. W., 1968. Tropical crops. Dicotyledons 1. p. 284–310. Wiley & Sons, New York.
Rendel, J. & C., Stormont, 1964. Variants of ovine alkaline serum phosphatases and their association with the R-O blood group. Proc. Soc. Expt. Biol. Med. 115: 853–856.
Rick, C. M., R. W., Zobel & J. F., Fobes, 1974. Four peroxidase loci in red-fruited tomato species: genetics and geographical distribution. Proc. Nat. Acad. Sci. 71: 835–839.
Scandalios, J. G., 1969. Genetic control of multiple molecular forms of enzymes in plants: a review. Biochem. Genet. 3: 37–79.
Scandalios, J. G., 1974. Isozymes in development and differentiation. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 25: 225–258.
Shannon, L. M., 1968. Plant isozymes. Ann. Rev. Plant Physiol. 19: 187–120.
Shaw, G. R. & A. L., Koen, 1968. Starch gel zone electrophoresis of enzymes. p. 325–364. In: Smith, I. (Ed)., Chromatographic and electrophoretic techniques. Interscience Publishers, New York.
Sheen, S. J., 1970. Peroxidases in the genus Nicotiana. Theor. Appl. Genet. 40: 18–25.
Smartt, J., 1970. Interspecific hybridization between cultivated American species of the genus Phaseolus. Euphytica 19: 480–489.
Smith, H. H., D. E., Hamill, E. A., Weaver & K. H., Thompson, 1970. Multiple molecular forms of peroxidases and esterases among Nicotiana species and amphidiploids. J. Hered. 61: 203–212.
Strand, A. B., 1943. Species crosses in the genus Phaseolus. Proc. Amer. Soc. Hort. Sci. 42: 569–573.
Thurman, D. A., D., Boulter, E., Derbyshire & B. L., Turner, 1967. Electrophoretic mobilities of formic and glutamic dehydrogenases in the Fabaceae: A systematic survey. New Phytol. 66: 37–45.
Wall, J. R., 1968. Leucine aminopeptidase polymorphism in Phaseolus and differential elimination of the donor parent genotype in interspecific backcrosses. Biochem. Genet. 2: 109–118.
West, N. B. & E. D., Garber, 1967. Genetic studies of variant enzymes. I. An electrophoretic survey of esterases and leucine aminopeptidases in the genus Phaseolus. Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 9: 640–645.
Yarnell, S. H., 1965. Cytogenetics of the vegetable crops. IV. Legumes. Bot. Rev. 31: 250–330.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bassiri, A., Adams, M.W. An electrophoretic survey of seedling isozymes in several Phaseolus species. Euphytica 27, 447–459 (1978). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043171
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00043171