Abstract
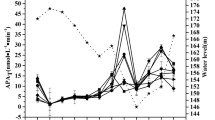
Alkaline phosphatase activity (APA) was investigated monthly for 4 years in the eutrophic Lake Nantua, a lake colonized by a large population of Cyanobacteria. Total enzymatic activity as well as specific activities (the ratios between APA and biomass expressed as dry weight, chlorophyll a, cell phosphorus) varied strongly but they followed a similar pattern during each year. The data were processed using correspondence analysis. Specific APA was never related to depth but highest activities were always associated with low particulate phosphorus and nitrogen, low dissolved inorganic phosphorus (DIP) concentrations, low chlorophyll a to filament number ratio and zero nitrate in the waters, indicating P and N limiting conditions. However a high N/P ratio, close to Redfield optimum also occurred at these conditions. Low activities were associated only with high chlorophyll a to filament number ratio.
The results suggest that, during summer P-depletion and as long as the N/P ratio is close or above an optimum value, the DIP enzymatically regenerated from DOP pool by phosphatases could temporarily contribute to the algal phosphorus supply.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berman, T., 1985. Uptake of 32P orthophosphate by algae and bacteria in Lake Kinneret. J. Plankton Res. 7: 71–84.
Berman, T., 1988. Differential uptake of orthophosphate and organic phosphorus substrates by bacteria and algae in Lake Kinneret. J. Plankton Res. 10: 1239–1249.
Bonin, D. J. & S. Y. Maestrini, 1981. Importance of organic nutrients for phytoplankton growth in natural environments: implications for algal species succession. In T. Platt, (ed.). Physiological bases of phytoplankton ecology. Can. Bull. Fish. aquat. Sci. 210: 279–911.
Chróst, R. J., 1986. Algal-bacterial metabolic coupling in the carbon and phosphorus cycle in lakes. In F. Megusar & M. Gantar (eds), Perspectives in microbial activity. Slovene Soc. Microbiol., Ljubljana: 360–366.
Chróst, R. J. & J. Overbeck, 1987. Kinetics of alkaline phosphatase activity and phosphorus availability for phytoplankton and bacterioplankton in Lake Plußsee (North German eutrophic lake). Microb. Ecol. 13: 229–248.
Currie, D. J. & J. Kalff, 1984a. The relative importance of bacterioplankton and phytoplankton in phosphorus uptake in freshwater. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 311–321.
Currie, D. J. & J. Kalff, 1984b. A comparison of the abilities of freshwater algae and bacteria to acquire and retain phosphorus. Limnol. Oceanogr. 29: 298–310.
Currie, D. J., E. Bentzen & J. Kalff, 1986. Does algal-bacteria phosphorus partitioning vary among lakes? A comparative study of orthophosphate uptake and alkaline phosphatase activity in freshwater. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 43: 311–318.
Feuillade, J., 1988. Nutrient status and response of an eutrophicated lake to reduced external nutrient loading. In G. Balvay (ed.), Eutrophication and lake restoration. Water quality and biological impacts. Thonon-les-Bains. 99–111.
Feuillade, J., G. Balvay, P. Blanc, M. Feuillade, A. Orand, J. Pelletier & F. Chahuneau, 1982. Caractérisation et essais de restauration d'un écosystème dégradé: le lac de Nantua. Feuillade, J. (ed.), I.N.R.A., Versailles. 165 pp.
Feuillade, M., J. Bohatier, G. Bourdier, P. Dufour, J. Feuillade & H. Krupka, 1988. Amino acid uptake by a natural population of Oscillatoria rubescens in relation to uptake by bacterioplankton. Arch. Hydrobiol. 113: 345–358.
Fitzgerald, G. P. & T. C. Nelson, 1966. Extractive and enzymatic analyses for limiting or surplus phosphorus in algae. J. Phycol. 2: 32–7.
Gage, M. A. & E. Gorham, 1985. Alkaline phosphatase activity and cellular phosphorus as an index of the phosphorus status of phytoplankton in Minnesota lakes. Freshwat. Biol. 15: 227–233.
Healey, F. P. & L. L. Hendzel, 1980. Physiological indicators of nutrient deficiency in lake phytoplankton. Can. J. Fish. aquat. Sci. 37: 442–453.
Hino, S., 1988. Fluctuation of algal alkaline phosphatase activity and the possible mechanisms of hydrolysis of dissolved organic phosphorus in Lake Barato. Hydrobiologia 157: 77–84.
Huber, A. L. & K. S. Hamel, 1985. Phosphatase activities in relation to phosphorus nutrition in Nodularia spumigena (Cyanobacteriaceae). I. Field studies. Hydrobiologia 123: 145–152.
Jansson, M., H. Olsson & K. Pettersson, 1988. Phosphatases; origin, characteristics and function in lakes. Hydrobiologia 170: 157–175.
Kuenzler, E. J. & J. P. Perras, 1965. Phosphatases of marine algae. Biol. Bull. 128: 271–284.
Lebart, L. & J. P. Fénelon, 1971. Statistique et informatique appliquées. Dunod, Paris. 426 pp.
Wynne, D., 1981. Phosphorus, phosphatases and the Peridinium bloom in Lake Kinneret. Verh. int. Ver. Limnol. 21: 523–527.
Wynne, D. & T. Berman, 1980. Hot water extractable phosphorus: an indicator of nutritional status of Peridinium cinctum (Dinophyceae) from Lake Kinneret? J. Phycol. 16: 40–46.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Feuillade, J., Feuillade, M. & Blanc, P. Alkaline phosphatase activity fluctuations and associated factors in a eutrophic lake dominated by Oscillatoria rubescens . Hydrobiologia 207, 233–240 (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041461
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00041461